
Document
... *the extension of the lower denture anteriorly is affected by mylohyoid muscle indirectly because we have sublingual gland in between the denture and the muscle so as mylohyoid muscle contracts the sublingual gland moves upward and downward limiting the extension of the lower denture anteriorly. *po ...
... *the extension of the lower denture anteriorly is affected by mylohyoid muscle indirectly because we have sublingual gland in between the denture and the muscle so as mylohyoid muscle contracts the sublingual gland moves upward and downward limiting the extension of the lower denture anteriorly. *po ...
MS WORD VERSION ()
... cervical (comes from holding up head) and the lumbar (comes from bowing your back to balance when you learn to walk). -look up the definitions for scoliosis, lordosis, and kyphosis. ...
... cervical (comes from holding up head) and the lumbar (comes from bowing your back to balance when you learn to walk). -look up the definitions for scoliosis, lordosis, and kyphosis. ...
The Nasal Cavity
... paranasal sinuses. These sinuses are named according to the bones in which they are found; thus, there are the maxillary, frontal, sphenoidal, and ethmoidal sinuses. Each sinus communicates via drainage ducts within the nasal cavity on its own side. ### Paranasal sinuses may help to • warm and moist ...
... paranasal sinuses. These sinuses are named according to the bones in which they are found; thus, there are the maxillary, frontal, sphenoidal, and ethmoidal sinuses. Each sinus communicates via drainage ducts within the nasal cavity on its own side. ### Paranasal sinuses may help to • warm and moist ...
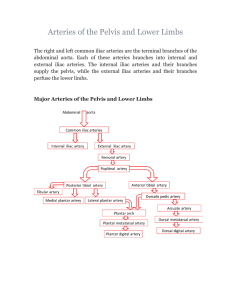
Lower Limb – Jessica Magid
... Union of this serious type of fracture may take up to a year Fractures of the distal femur may be complicated by separation of the condyles ...
... Union of this serious type of fracture may take up to a year Fractures of the distal femur may be complicated by separation of the condyles ...
Layers of the Lungs Appendix
... known as the intercostal. This makes the chest cavity bigger allowing air to rush into the lungs. As you breathe out (exhalation), the ribs and diaphragm go back to the normal position. When the chest is back to normal position, air is forced out of the lungs through the nose and mouth. The diaphrag ...
... known as the intercostal. This makes the chest cavity bigger allowing air to rush into the lungs. As you breathe out (exhalation), the ribs and diaphragm go back to the normal position. When the chest is back to normal position, air is forced out of the lungs through the nose and mouth. The diaphrag ...
An Anatomical Variation. - International Journal of Health Sciences
... proceeds distally just deep to the skin and reaches the dorsum of the hand where it branches out into dorsal digital nerves to supply the dorsum of the thumb, index, and ...
... proceeds distally just deep to the skin and reaches the dorsum of the hand where it branches out into dorsal digital nerves to supply the dorsum of the thumb, index, and ...
notes: axial skeleton joints * lesson 2 kinesiology
... joint is, the less it moves. Although each spinal joint usually only allows a small amount of movement, when the movements of all 25 spinal segmental levels are added up, the spine allows a great deal of movement in all three planes. Slide 12: ● The joints of the axial body that will be covered are ...
... joint is, the less it moves. Although each spinal joint usually only allows a small amount of movement, when the movements of all 25 spinal segmental levels are added up, the spine allows a great deal of movement in all three planes. Slide 12: ● The joints of the axial body that will be covered are ...
The superficial veins of the lower limb begin as the dorsal venous
... Arising from the dorsal venous network (arch) on the dorsum of the hand are the two most important superficial veins: the cephalic and basilic veins. The cephalic vein ascends along the lateral aspect of the forearm. (This side of your arm is considered "cephalic" because the limbs develop projecti ...
... Arising from the dorsal venous network (arch) on the dorsum of the hand are the two most important superficial veins: the cephalic and basilic veins. The cephalic vein ascends along the lateral aspect of the forearm. (This side of your arm is considered "cephalic" because the limbs develop projecti ...
Name: Period:______ EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE CRAYFISH
... 1. Place the crayfish in the dissecting pan on its belly (dorsal side up – back is up). 2. Insert the point of the scissors under the top of the carapace at the back of the cephalothorax and cut up towards the eyes, stopping when you are between the eyes. 3. Cut across the carapace behind the eyes, ...
... 1. Place the crayfish in the dissecting pan on its belly (dorsal side up – back is up). 2. Insert the point of the scissors under the top of the carapace at the back of the cephalothorax and cut up towards the eyes, stopping when you are between the eyes. 3. Cut across the carapace behind the eyes, ...
Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System
... nasopharynx. The function of the pharyngeal tonsil is not well understood, but it contains a rich supply of lymphocytes and is covered with ciliated epithelium that traps and destroys invading pathogens that enter during inhalation. The pharyngeal tonsils are large in children, but interestingly, te ...
... nasopharynx. The function of the pharyngeal tonsil is not well understood, but it contains a rich supply of lymphocytes and is covered with ciliated epithelium that traps and destroys invading pathogens that enter during inhalation. The pharyngeal tonsils are large in children, but interestingly, te ...
LAPAROSCOP*C *NGU*NAL HERN*A SURGERY TECHN*CAL
... Medial to anterior superior iliac spine or the side of hernia (5 mm ) ...
... Medial to anterior superior iliac spine or the side of hernia (5 mm ) ...
Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016
... Clinical Significance of the Oral part of Pharynx •The palatine tonsils are two masses of lymphoid tissue located in lateral walls of the oral part of pharynx in the tonsillar sinuses. •The palatine tonsils are the common sites of infection, producing the characteristic tonsilitis. •The deep cervic ...
... Clinical Significance of the Oral part of Pharynx •The palatine tonsils are two masses of lymphoid tissue located in lateral walls of the oral part of pharynx in the tonsillar sinuses. •The palatine tonsils are the common sites of infection, producing the characteristic tonsilitis. •The deep cervic ...
Neuroanatomy-and-Neurodynamics-Teaching-Pack
... The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons The dorsal root ganglion is particularly sensitive and is often the cause of radicular pain The two nerve roots then come together as they go through intervertebral foramen They will then split into ventral and dorsal rami to b ...
... The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons The dorsal root ganglion is particularly sensitive and is often the cause of radicular pain The two nerve roots then come together as they go through intervertebral foramen They will then split into ventral and dorsal rami to b ...
Laryngeal Anatomy Medscape 2015
... The arytenoid cartilages form the part of the larynx to which the vocal ligaments and vocal folds attach. They are pyramidal in shape and have 3 surfaces, a base, and an apex. They are located superior to the cricoid cartilage in the posterior part of the larynx, with the base of the arytenoid carti ...
... The arytenoid cartilages form the part of the larynx to which the vocal ligaments and vocal folds attach. They are pyramidal in shape and have 3 surfaces, a base, and an apex. They are located superior to the cricoid cartilage in the posterior part of the larynx, with the base of the arytenoid carti ...
m5zn_53718fd0061b5d6
... 1- muscles of facial expression 2- facial nerve 3- cutane. branches of trigeminal nerve and great auricular n. 4- parotid gland and duct 5- buccal pad of fat 6- facial L.N. ...
... 1- muscles of facial expression 2- facial nerve 3- cutane. branches of trigeminal nerve and great auricular n. 4- parotid gland and duct 5- buccal pad of fat 6- facial L.N. ...
Anatomy of the rectum and anus
... • Blood return from the rectum and anal canal is via two systems: portal and systemic. Hence a site of porto-systemic anastomosis. • The superior rectal vein drains the rectum and upper part of the anal canal, where the internal hemorrhoidal plexus is situated, into the portal system via the inferio ...
... • Blood return from the rectum and anal canal is via two systems: portal and systemic. Hence a site of porto-systemic anastomosis. • The superior rectal vein drains the rectum and upper part of the anal canal, where the internal hemorrhoidal plexus is situated, into the portal system via the inferio ...
20.脊神经
... biceps femoris and its tendon; passes over posterior aspect of head of fibula and then winds around neck of fibula, deep to peroneus longus, where it divides into deep and superficial peroneal nerves腓浅和腓深神 经,to supply the anterior and lateral groups m. of the leg. ...
... biceps femoris and its tendon; passes over posterior aspect of head of fibula and then winds around neck of fibula, deep to peroneus longus, where it divides into deep and superficial peroneal nerves腓浅和腓深神 经,to supply the anterior and lateral groups m. of the leg. ...
Development and growth of the mandible
... The mandible is ossified in the fibrous membrane covering the outer surfaces of Meckel's cartilages. These cartilages form the cartilaginous bar of the mandibular arch and are two in number, a right and a left. Their proximal or cranial ends are connected with the ear capsules, and their distal extr ...
... The mandible is ossified in the fibrous membrane covering the outer surfaces of Meckel's cartilages. These cartilages form the cartilaginous bar of the mandibular arch and are two in number, a right and a left. Their proximal or cranial ends are connected with the ear capsules, and their distal extr ...
Anatomy, Joint Orientation and Arthrokinematics
... Lateral flexion- occurs with same side rotation, contralateral inferior articular surface of superior vertebrae glides superiorly and rolls anteriorly, ipsilateral inferior articular surface of superior vertebrae glides inferiorly and rolls posteriorly Rotation- inferior articular surface of sup ...
... Lateral flexion- occurs with same side rotation, contralateral inferior articular surface of superior vertebrae glides superiorly and rolls anteriorly, ipsilateral inferior articular surface of superior vertebrae glides inferiorly and rolls posteriorly Rotation- inferior articular surface of sup ...
Slide 1
... It ascends to the right, behind the first part of the duodenum, and enters the lesser omentum . It then runs upward in front of the opening into the lesser sac to the porta hepatis, where it divides into right and left terminal branches The portal circulation begins as a capillary plexus in the orga ...
... It ascends to the right, behind the first part of the duodenum, and enters the lesser omentum . It then runs upward in front of the opening into the lesser sac to the porta hepatis, where it divides into right and left terminal branches The portal circulation begins as a capillary plexus in the orga ...
[G. 32.26A] The parotid duct passes lateral (superficial) and anterior
... The vagus nerve is positioned posterior – medial to the internal jugular vein. The vagus nerve is positioned posterior – lateral to the common carotid artery. The subclavian artery passes directly posterior to the anterior scalene muscle. The phrenic nerve passes directly anterior to the anterior sc ...
... The vagus nerve is positioned posterior – medial to the internal jugular vein. The vagus nerve is positioned posterior – lateral to the common carotid artery. The subclavian artery passes directly posterior to the anterior scalene muscle. The phrenic nerve passes directly anterior to the anterior sc ...
VisualSonics_Guide To Abdominal Imaging using the Vevo 770 Rev
... I. Imaging the IVC and Abdominal Aorta A. Imaging in Transverse (cross-sectionally) First, position the scanhead in transverse (ie. the notch of the probe is placed to the left of the mouse). The scanhead is placed in the midline of the mouse just below the rib cage. Two dark circles will be visual ...
... I. Imaging the IVC and Abdominal Aorta A. Imaging in Transverse (cross-sectionally) First, position the scanhead in transverse (ie. the notch of the probe is placed to the left of the mouse). The scanhead is placed in the midline of the mouse just below the rib cage. Two dark circles will be visual ...
PTA Hip presentation
... I: Iliotibial tract of fascia latae & lateral part of linea aspera under greater trochanter (gluteal tuberosity) of femur A: Extends thigh at hip & laterally rotates thigh; upper fibers abduct N: Inferior gluteal nerve R: L5, S1, S2 S: Flex: rectus femoris, TFL, iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius; Med ...
... I: Iliotibial tract of fascia latae & lateral part of linea aspera under greater trochanter (gluteal tuberosity) of femur A: Extends thigh at hip & laterally rotates thigh; upper fibers abduct N: Inferior gluteal nerve R: L5, S1, S2 S: Flex: rectus femoris, TFL, iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius; Med ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.



















![[G. 32.26A] The parotid duct passes lateral (superficial) and anterior](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006076211_1-58575f197d50e9622baacdf4c36cbab7-300x300.png)

