Anatomy Lab – Exam 2
... Superficial dorsal vein of penis – note that this is covered by a thin layer of dartos fascia ○ Is the major structure outside the Buck’s fascia ○ drains into superficial external pudendal vein ...
... Superficial dorsal vein of penis – note that this is covered by a thin layer of dartos fascia ○ Is the major structure outside the Buck’s fascia ○ drains into superficial external pudendal vein ...
Fascia and compartments of the middle forearm
... Anterior Interosseous Nerve Half of the Flexor Digitorum Profundus which is innervated by the ulnar nerve, unlike the rest of the flexors (which are all supplied by the Median nerve ...
... Anterior Interosseous Nerve Half of the Flexor Digitorum Profundus which is innervated by the ulnar nerve, unlike the rest of the flexors (which are all supplied by the Median nerve ...
The Evolution of the Skull and the Cephalic muscles
... the superior edge and outer and inner surfaces of the mandible from the tip of the coronoid process almost back to the joint. The insertion on to the outer and inner surfaces extends about half-way down the depth of the mandible; the insertion on to the coronoid tip is in part effected by the tendon ...
... the superior edge and outer and inner surfaces of the mandible from the tip of the coronoid process almost back to the joint. The insertion on to the outer and inner surfaces extends about half-way down the depth of the mandible; the insertion on to the coronoid tip is in part effected by the tendon ...
The Vagus Nerve - Lightweight OCW University of Palestine
... 1. Arises by 4-5 rootlets from the posterolateral sulcus of medulla. 2. It leaves the skull through the jugular foramen. 3. While it lies in jugular foramen it has 2 small sensory ganglia (superior and inferior). 4. It descends downwards inside the upper carotid sheath superficial to vagus nerve and ...
... 1. Arises by 4-5 rootlets from the posterolateral sulcus of medulla. 2. It leaves the skull through the jugular foramen. 3. While it lies in jugular foramen it has 2 small sensory ganglia (superior and inferior). 4. It descends downwards inside the upper carotid sheath superficial to vagus nerve and ...
Pelvis and Contents
... • Sacrum and Coccyx help create pelvis and form pelvic cavity • Function – attaches lower limb to axial skeleton – supports viscera – transmits weight g of upper pp bodyy Pg 187 ...
... • Sacrum and Coccyx help create pelvis and form pelvic cavity • Function – attaches lower limb to axial skeleton – supports viscera – transmits weight g of upper pp bodyy Pg 187 ...
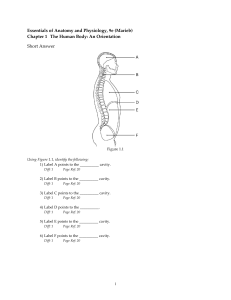
Chapter 1 Notes 2014-2015
... Which body system includes the lymph nodes? Which body system includes the skin? Which body system releases hormones? What is the smallest unit of all living things? ...
... Which body system includes the lymph nodes? Which body system includes the skin? Which body system releases hormones? What is the smallest unit of all living things? ...
The Larynx
... • Sudden involuntary muscle movements or spasms cause the vocal folds to open. • The vocal folds can not vibrate when they are open. • The open position of the vocal folds also allows air to escape from the lungs during speech. • The voices sounds weak, quiet and breathy or whispery. ...
... • Sudden involuntary muscle movements or spasms cause the vocal folds to open. • The vocal folds can not vibrate when they are open. • The open position of the vocal folds also allows air to escape from the lungs during speech. • The voices sounds weak, quiet and breathy or whispery. ...
1b-Schimp-Surgical Complications
... • Through greater sciatic foramen around ischial spine and back into pelvis through lesser sciatic foramen then through Alcock's canal with nerve and vein • Three branches • Inferior rectal nerve—anus and perirectal skin • Perineal nerve—small muscles of superficial and deep perineal spaces and labi ...
... • Through greater sciatic foramen around ischial spine and back into pelvis through lesser sciatic foramen then through Alcock's canal with nerve and vein • Three branches • Inferior rectal nerve—anus and perirectal skin • Perineal nerve—small muscles of superficial and deep perineal spaces and labi ...
The thigh: blood supply
... from the lateral side of the deep artery of thigh, but may arise directly from the femoral artery. The medial circumflex femoral artery normally originates proximally from the posteromedial aspect of the deep artery of thigh. The first perforating arteries originates above the adductor brevis muscle ...
... from the lateral side of the deep artery of thigh, but may arise directly from the femoral artery. The medial circumflex femoral artery normally originates proximally from the posteromedial aspect of the deep artery of thigh. The first perforating arteries originates above the adductor brevis muscle ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... posteriorlly by the palatoglussus arch, which is formed in part by the palatoglossus muscle and in part by the lingual extention of the superior constructor muscle and anteriorly by the posterior 3 mm of the mylohoid muscle. Forward on the lingual extension, the area is influence by the mylohoid mus ...
... posteriorlly by the palatoglussus arch, which is formed in part by the palatoglossus muscle and in part by the lingual extention of the superior constructor muscle and anteriorly by the posterior 3 mm of the mylohoid muscle. Forward on the lingual extension, the area is influence by the mylohoid mus ...
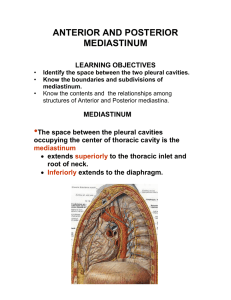
posterior mediastinum
... There are two in each of the articulations where an interarticular ligament exists One above and one below this structure However, only one in those joints where there is single cavity. ...
... There are two in each of the articulations where an interarticular ligament exists One above and one below this structure However, only one in those joints where there is single cavity. ...
Spine - Amazon Web Services
... shorter and heavier in construct. The posterior articular facets change their orientation to be more like those of lumbar vertebrae. In the early embryo starting in week 3, paired and segmented condensations of the paraxial mesoderm, known as somites, develop lying parallel to the developing neural ...
... shorter and heavier in construct. The posterior articular facets change their orientation to be more like those of lumbar vertebrae. In the early embryo starting in week 3, paired and segmented condensations of the paraxial mesoderm, known as somites, develop lying parallel to the developing neural ...
Potential Cranial Test questions: Lecture 1: Cranial I Know the 4
... extension o Flexion: Posterior aspect of the body elevates. The sella turcica moves anterosuperiorly. Greater wings move forward and slightly laterally and inferiorly. The pterygoids move posteriorly and inferolaterally. The body expands a little as it carries the resistance of the facial bo ...
... extension o Flexion: Posterior aspect of the body elevates. The sella turcica moves anterosuperiorly. Greater wings move forward and slightly laterally and inferiorly. The pterygoids move posteriorly and inferolaterally. The body expands a little as it carries the resistance of the facial bo ...
124
... 3. Name the arteries supplying the thyroid gland and discuss their origin, relationship of their terminal branches to the fascial coverings of the thyroid gland and their distribution to other structures. 4. Discuss the clinical significance of the proximity of the thyroid gland to the trachea and r ...
... 3. Name the arteries supplying the thyroid gland and discuss their origin, relationship of their terminal branches to the fascial coverings of the thyroid gland and their distribution to other structures. 4. Discuss the clinical significance of the proximity of the thyroid gland to the trachea and r ...
questions
... 90._____ At the digits, the flexor digitorum superficialis tendons split and insert onto the middle phalanx of digits 2-5. 91._____ The blood supply to the posterior compartment of the forearm is derived from the posterior interosseus artery which is typically a branch of the radial artery. 92.____ ...
... 90._____ At the digits, the flexor digitorum superficialis tendons split and insert onto the middle phalanx of digits 2-5. 91._____ The blood supply to the posterior compartment of the forearm is derived from the posterior interosseus artery which is typically a branch of the radial artery. 92.____ ...
live anatomy - University of New England
... the partner's hand again. If your partner reported 2 points, push the tips a bit closer together, and test again. Measure the minimal distance at which your partner reports two points. Skin receptors NOT uniformly distributed around the body. Some places, such as the fingers and lips, have more touc ...
... the partner's hand again. If your partner reported 2 points, push the tips a bit closer together, and test again. Measure the minimal distance at which your partner reports two points. Skin receptors NOT uniformly distributed around the body. Some places, such as the fingers and lips, have more touc ...
The Digestive System
... The stomach and small intestine also contain hormone-producing cells that, when stimulated by chemicals, nerve fibers, or local stretch, release their products to the extracellular space These hormones circulate in the blood and are distributed to their target cells within the same or different trac ...
... The stomach and small intestine also contain hormone-producing cells that, when stimulated by chemicals, nerve fibers, or local stretch, release their products to the extracellular space These hormones circulate in the blood and are distributed to their target cells within the same or different trac ...
Brachial Plexus block 2 of 2
... The boundaries of the infraclavicular fossa are the pectoralis minor and major muscles anteriorly, ribs medially, clavicle and the coracoid process superiorly, and humerus laterally. At this location, the brachial plexus is composed of cords. The sheath surrounding the plexus is delicate. It contain ...
... The boundaries of the infraclavicular fossa are the pectoralis minor and major muscles anteriorly, ribs medially, clavicle and the coracoid process superiorly, and humerus laterally. At this location, the brachial plexus is composed of cords. The sheath surrounding the plexus is delicate. It contain ...
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
... -congenital – femoral head dislocated upward into iliac fossa –lessens full mobility of jt, may be detected on PE as shortening of limb on that side (also, makes glut med, min ms unable to contract effectively (b’se they are shortened) – impairs posture, gait -acquired – hip flexed and medially rota ...
... -congenital – femoral head dislocated upward into iliac fossa –lessens full mobility of jt, may be detected on PE as shortening of limb on that side (also, makes glut med, min ms unable to contract effectively (b’se they are shortened) – impairs posture, gait -acquired – hip flexed and medially rota ...
Anatomy – Exam 2 (Part 2)
... ○ Blood Supply – inferior gluteal artery Gluteus Medius and Minimus – medius is superficial to minimus ○ Origin – ala of ilium ○ Insertion – greater trocanter ○ Action – essential for normal gait Non-weight bearing – abductor of lower limb Weight-bearing – tips lateral portion of pelvic bone ↓ ...
... ○ Blood Supply – inferior gluteal artery Gluteus Medius and Minimus – medius is superficial to minimus ○ Origin – ala of ilium ○ Insertion – greater trocanter ○ Action – essential for normal gait Non-weight bearing – abductor of lower limb Weight-bearing – tips lateral portion of pelvic bone ↓ ...
Anatomy – Exam 2 (Part 2)
... ○ Blood Supply – inferior gluteal artery Gluteus Medius and Minimus – medius is superficial to minimus ○ Origin – ala of ilium ○ Insertion – greater trocanter ○ Action – essential for normal gait Non-weight bearing – abductor of lower limb Weight-bearing – tips lateral portion of pelvic bone ↓ ...
... ○ Blood Supply – inferior gluteal artery Gluteus Medius and Minimus – medius is superficial to minimus ○ Origin – ala of ilium ○ Insertion – greater trocanter ○ Action – essential for normal gait Non-weight bearing – abductor of lower limb Weight-bearing – tips lateral portion of pelvic bone ↓ ...
Pudendal Neuralgia
... 1.Trans-Ischio-rectal 2.Trans-gluteal 3.Trans-perineal 4.Laprascopic Complications from surgery: pain at incision site, scar tissue, SI jt dysfunction, gluteal tearing, sciatic nerve tension Back to PT? ...
... 1.Trans-Ischio-rectal 2.Trans-gluteal 3.Trans-perineal 4.Laprascopic Complications from surgery: pain at incision site, scar tissue, SI jt dysfunction, gluteal tearing, sciatic nerve tension Back to PT? ...
No Slide Title
... cutaneous receptors, proprioceptors (muscle and joint senses), and visceral receptors. Most of the sensory information that originates in the right side of the body crosses over (decusses) and eventually reach the region on the left side of the brain, which analyses this information. Similarly, the ...
... cutaneous receptors, proprioceptors (muscle and joint senses), and visceral receptors. Most of the sensory information that originates in the right side of the body crosses over (decusses) and eventually reach the region on the left side of the brain, which analyses this information. Similarly, the ...
Title Morphologic characteristics of the superior pharyngeal
... differences exist in the presence and absence of membrane, but no bone is present and both muscles attach to mucosa. Based on these findings, the superior pharyngeal constrictor and buccinator muscles appear to work cooperatively during swallowing in terms of morphology. It seemed that a series of s ...
... differences exist in the presence and absence of membrane, but no bone is present and both muscles attach to mucosa. Based on these findings, the superior pharyngeal constrictor and buccinator muscles appear to work cooperatively during swallowing in terms of morphology. It seemed that a series of s ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.