FibulA FlAP
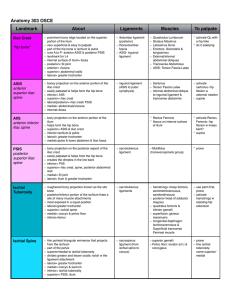
... short (and vein grafts may be necessary). The skin island may be supplied by perforators from the posterior tibial system traversing the soleus and thus separate from the peroneal artery system. It is a misconception from the pre-perforator flap era that including a cuff of soleus/ flexor hallucis l ...
... short (and vein grafts may be necessary). The skin island may be supplied by perforators from the posterior tibial system traversing the soleus and thus separate from the peroneal artery system. It is a misconception from the pre-perforator flap era that including a cuff of soleus/ flexor hallucis l ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Nerve to vastus medialis c) Sural nerve d) Saphenous nerve PTO ...
... Nerve to vastus medialis c) Sural nerve d) Saphenous nerve PTO ...
Structure and Function of the Hip
... • Identify the supporting structures of the hip joint • Discuss the actions of the hip musculature through understanding of the origin and insertion • Identify the force couples involved with an anterior and posterior pelvic tilt • Explain the function of the hip abductor muscles while walking • Ide ...
... • Identify the supporting structures of the hip joint • Discuss the actions of the hip musculature through understanding of the origin and insertion • Identify the force couples involved with an anterior and posterior pelvic tilt • Explain the function of the hip abductor muscles while walking • Ide ...
Ear Anatomy
... At day 56, further increase in auricular definition with the first branchial cleft being obscured by the developing tragus. (Below, left) At day 63, the definitive auricle at the end of the embryologic development. (Below, right) A fully developed auricle. Note that the majority of the auricular com ...
... At day 56, further increase in auricular definition with the first branchial cleft being obscured by the developing tragus. (Below, left) At day 63, the definitive auricle at the end of the embryologic development. (Below, right) A fully developed auricle. Note that the majority of the auricular com ...
PDF 12 MB - med
... the behavior of the parathyroid artery after it enters the glandular hilus, but it may be said here that, in general, this vessel a central course, off obliquely directedvessels since giving here both branchescame in Fig. pursues 4 is interesting parathyroid which ramify peripherally, givingthyroid, ...
... the behavior of the parathyroid artery after it enters the glandular hilus, but it may be said here that, in general, this vessel a central course, off obliquely directedvessels since giving here both branchescame in Fig. pursues 4 is interesting parathyroid which ramify peripherally, givingthyroid, ...
Transcripts/3_19 8
... b. This is the genioglossus, which is an extrinsic tongue muscle. The tongue is basically a grouping of several skeletal muscles. They have several different attachments one coming from the mandible, the genioglossus. c. We have cut the tongue out and we see the mylohyoid that extends from molars to ...
... b. This is the genioglossus, which is an extrinsic tongue muscle. The tongue is basically a grouping of several skeletal muscles. They have several different attachments one coming from the mandible, the genioglossus. c. We have cut the tongue out and we see the mylohyoid that extends from molars to ...
Cranial Nerves Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain
... They continue to the thalamus where they synapse From there, the optic radiation fibers run to the visual cortex Functions solely by carrying afferent impulses for vision ...
... They continue to the thalamus where they synapse From there, the optic radiation fibers run to the visual cortex Functions solely by carrying afferent impulses for vision ...
The vertebral column and joints-2015_4
... • is the term used to describe a lateral deviation of the vertebral column. • abnormal curvature that is laterally • The most common type of abnormal curvature • Many case of scoliosis are of unknown origin, “idiopathic scoliosis” • may result from an assymetric weakness of the vertebral muscle, is ...
... • is the term used to describe a lateral deviation of the vertebral column. • abnormal curvature that is laterally • The most common type of abnormal curvature • Many case of scoliosis are of unknown origin, “idiopathic scoliosis” • may result from an assymetric weakness of the vertebral muscle, is ...
3. EMBRYONIC CEPHALOCAUDAL AND LATERAL FLEXION
... flexion commence at approximately the same time (days 22-28) but we shall discuss them separately (see Fig. 3-5, 3-6). Cephalocaudal flexion: The cranial rim of the embryo contains the buccopharyngeal membrane (BPM See Lecture 2 and Fig. 3-5) and cranial to the BPM is the cardiogenic area (gives ris ...
... flexion commence at approximately the same time (days 22-28) but we shall discuss them separately (see Fig. 3-5, 3-6). Cephalocaudal flexion: The cranial rim of the embryo contains the buccopharyngeal membrane (BPM See Lecture 2 and Fig. 3-5) and cranial to the BPM is the cardiogenic area (gives ris ...
Abdomen - Kalam Books
... ♦ The head contains the elongated flattened nucleus with condensed, deeply staining chromatin and the acrosomal cap anteriorly, which contains acid phosphatase, hyaluronidase, neuraminidase and proteases necessary for fertilisation ♦ In the centre of the neck, is a well - formed centriole, correspon ...
... ♦ The head contains the elongated flattened nucleus with condensed, deeply staining chromatin and the acrosomal cap anteriorly, which contains acid phosphatase, hyaluronidase, neuraminidase and proteases necessary for fertilisation ♦ In the centre of the neck, is a well - formed centriole, correspon ...
Accessory head of flexor pollicis longus and its significance in
... Flexor pollicis longus is one of the deep flexors of the forearm. It takes its origin from the grooved anterior surface of the radius and from the adjacent interosseus membrane and gets inserted onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb [1]. It has been noted that it frequently arises from a ...
... Flexor pollicis longus is one of the deep flexors of the forearm. It takes its origin from the grooved anterior surface of the radius and from the adjacent interosseus membrane and gets inserted onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb [1]. It has been noted that it frequently arises from a ...
answers
... typically a branch of the radial artery. 92. __A__ The lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm (antebrachial cutaneous nerve) is typically the terminal branch of the Musculocutaneous nerve. 93. __B__ The interosseus membrane uniting the radius and ulna is an example of a synchondrosis type of joint. ...
... typically a branch of the radial artery. 92. __A__ The lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm (antebrachial cutaneous nerve) is typically the terminal branch of the Musculocutaneous nerve. 93. __B__ The interosseus membrane uniting the radius and ulna is an example of a synchondrosis type of joint. ...
absence of musculocutaneous nerve
... musculocutaneous after piercing the coracobrachialis muscle re-joined the median nerve and its muscular and cutaneous branches then arose independently from median nerve. In three cases musculocutaneous pierced the biceps muscle instead of coracobrachialis (Joshi et al., 2008). Rajendra et al., (200 ...
... musculocutaneous after piercing the coracobrachialis muscle re-joined the median nerve and its muscular and cutaneous branches then arose independently from median nerve. In three cases musculocutaneous pierced the biceps muscle instead of coracobrachialis (Joshi et al., 2008). Rajendra et al., (200 ...
الجهاز الحركي الهيكلي THE MUSCOLUSKELETAL SYSTEM
... Anatomy of the lower limbs By Dr. Amjad Shatarat امجد الشطرات.د ...
... Anatomy of the lower limbs By Dr. Amjad Shatarat امجد الشطرات.د ...
Full Text PDF
... Variations involving the brachial plexus are not uncommon and have been linked with factors influencing the mechanism of limb muscles and peripheral nerves development during embryonic life [2]. These variations are clinically and surgically important. In normal anatomy, the middle brachial plexus t ...
... Variations involving the brachial plexus are not uncommon and have been linked with factors influencing the mechanism of limb muscles and peripheral nerves development during embryonic life [2]. These variations are clinically and surgically important. In normal anatomy, the middle brachial plexus t ...
Muscular Analysis of the Power Snatch Lift
... Newton goes into detail as to how the lifter should position their bodies to prepare for this lift. He first describes this set up as having the feet around hip-width apart with the feet flat on the ground. Notice in the image above where the bar is positioned in relation to the foot. According to N ...
... Newton goes into detail as to how the lifter should position their bodies to prepare for this lift. He first describes this set up as having the feet around hip-width apart with the feet flat on the ground. Notice in the image above where the bar is positioned in relation to the foot. According to N ...
Welcome to Chiropractic
... Scoliosis The vertebral column is straight when viewed from front to back, however lateral deviations from the midline are not normal and are called scoliosis. Lordotic curves: are normal spinal curves that are concave on the posterior aspect and convex on the anterior • Lordosis: exaggeration of a ...
... Scoliosis The vertebral column is straight when viewed from front to back, however lateral deviations from the midline are not normal and are called scoliosis. Lordotic curves: are normal spinal curves that are concave on the posterior aspect and convex on the anterior • Lordosis: exaggeration of a ...
Gross - Unit 1 arteries and nerves
... Passes into cubital fossa by piercing lateral intermuscular septum to lie between the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles. At lateral epicondyle, it divides into a SUPERFICIAL and DEEP BRANCHES. The SUPERFICIAL BRANCH accompanies the radial artery and both run under the brachioradialis to s ...
... Passes into cubital fossa by piercing lateral intermuscular septum to lie between the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles. At lateral epicondyle, it divides into a SUPERFICIAL and DEEP BRANCHES. The SUPERFICIAL BRANCH accompanies the radial artery and both run under the brachioradialis to s ...
parasacral nerve block
... obturator internus muscle (too lateral puncture) and should not be accepted. Obturator nerve stimulation (adduction of the thigh) is due to an excessively deep and medial puncture. This nerve runs in front of the parasacral plexus, in the same fascia plane. Contraction of the gluteal muscles indicat ...
... obturator internus muscle (too lateral puncture) and should not be accepted. Obturator nerve stimulation (adduction of the thigh) is due to an excessively deep and medial puncture. This nerve runs in front of the parasacral plexus, in the same fascia plane. Contraction of the gluteal muscles indicat ...
Hockey Snap Shot Checklist
... • -As the stick is rotated from the stick side to the non stick side of the body; the free leg is rotated in the opposite direction so that it can aid in taking up the reaction from the stick and arms: a clockwise rotation of the upper body will produce a counterclockwise reaction from the lower bod ...
... • -As the stick is rotated from the stick side to the non stick side of the body; the free leg is rotated in the opposite direction so that it can aid in taking up the reaction from the stick and arms: a clockwise rotation of the upper body will produce a counterclockwise reaction from the lower bod ...
13 Copy of EAR final2012-09-15 05:175.8 MB
... The semicircular ducts has the same configuration but smaller than the semicircular canals. They are arranged at right angle to each other so the three plans are represented ...
... The semicircular ducts has the same configuration but smaller than the semicircular canals. They are arranged at right angle to each other so the three plans are represented ...
I. The human skeleton contains 206 named bones which perform a
... two things to occur. It causes an increase in the conversion of the cartilage to bone (resulting in increased bone length), but it also decreases the rate of production of new cartilage in the plate (ultimately ending the ability of the long bone to grow). IX. Growth in width is a product of the act ...
... two things to occur. It causes an increase in the conversion of the cartilage to bone (resulting in increased bone length), but it also decreases the rate of production of new cartilage in the plate (ultimately ending the ability of the long bone to grow). IX. Growth in width is a product of the act ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.