Muscles of the Elbow
... laterally off the olecranon feeling the prominences. Note that the medial is larger. Supracondylar ridges: Sitting; Locate the epicondyles, slide your fingers proximally toward the shoulder feeling the medial and lateral supracondylar ridges. Roll your fingers back and forth to feel the edges. Shaft ...
... laterally off the olecranon feeling the prominences. Note that the medial is larger. Supracondylar ridges: Sitting; Locate the epicondyles, slide your fingers proximally toward the shoulder feeling the medial and lateral supracondylar ridges. Roll your fingers back and forth to feel the edges. Shaft ...
Anatomy of the Thorax
... Anything in this highlighted green is a definition or explains basically something's function. Text highlighted in yellow or with a star is what I would deem important and key information. Italics and bold just help to make certain terms stand out. The notes are a bit quirky but I hope you like them ...
... Anything in this highlighted green is a definition or explains basically something's function. Text highlighted in yellow or with a star is what I would deem important and key information. Italics and bold just help to make certain terms stand out. The notes are a bit quirky but I hope you like them ...
Foot and Ankle Injuries
... component in the kinetic chain and has great influence on how we propel ourselves through space as well as what happens further up the chain from the knee to the hip and onto the back. As showed in the illustration and description below the foot and ankle have 33 joints (20 of which articulate) 26 b ...
... component in the kinetic chain and has great influence on how we propel ourselves through space as well as what happens further up the chain from the knee to the hip and onto the back. As showed in the illustration and description below the foot and ankle have 33 joints (20 of which articulate) 26 b ...
20 SCIATIC NERVE.IIppt[1].
... foramen, below the piriformis & passes in the gluteal region (between ischial tuberosity & greater trochanter) then to posterior compartment of thigh. Termination: ...
... foramen, below the piriformis & passes in the gluteal region (between ischial tuberosity & greater trochanter) then to posterior compartment of thigh. Termination: ...
4. ijbtr - finite element analysis of injuries in shoulder1
... the clavicle to the roof of shoulder. Consequently, the clavicle is pushed out of place forming a bump at the top of shoulder. The shoulder separation occurs when arm is stretched to stop topple on a rigid surface. The shoulder separation causes severe pain. The most rotator cuff injuries (figure 7a ...
... the clavicle to the roof of shoulder. Consequently, the clavicle is pushed out of place forming a bump at the top of shoulder. The shoulder separation occurs when arm is stretched to stop topple on a rigid surface. The shoulder separation causes severe pain. The most rotator cuff injuries (figure 7a ...
8. Appendicular Skeleton
... that articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula. Adjacent to the head are two tubercles. The prominent greater tubercle is positioned more laterally and helps form the rounded contour of the shoulder. The lesser tubercle is smaller and located more anteromedially. Between the two tubercles i ...
... that articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula. Adjacent to the head are two tubercles. The prominent greater tubercle is positioned more laterally and helps form the rounded contour of the shoulder. The lesser tubercle is smaller and located more anteromedially. Between the two tubercles i ...
POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT
... - Terminates by dividing into number of lateral calcanean branches. Branches of Peroneal artery: - Muscular branches: posterior & lateral compartments. - Nutrient artery: fibula. - Anastomotic branches - Perforating branch - Communicating branch - Calcaneal branch ...
... - Terminates by dividing into number of lateral calcanean branches. Branches of Peroneal artery: - Muscular branches: posterior & lateral compartments. - Nutrient artery: fibula. - Anastomotic branches - Perforating branch - Communicating branch - Calcaneal branch ...
Neuro Anatomy
... Spinal nerves emerge from dura mater as ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) nerve roots The ventral nerve root carries motor information away from the spine The dorsal nerve root carries sensory information from the body to the spine The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sen ...
... Spinal nerves emerge from dura mater as ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) nerve roots The ventral nerve root carries motor information away from the spine The dorsal nerve root carries sensory information from the body to the spine The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sen ...
Neuro-Anatomy-and-Neurodynamics-Teaching-Pack
... roots The ventral nerve root carries motor information away from the spine The dorsal nerve root carries sensory information from the body to the spine The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons The dorsal root ganglion is particularly sensitive and is often the cause o ...
... roots The ventral nerve root carries motor information away from the spine The dorsal nerve root carries sensory information from the body to the spine The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons The dorsal root ganglion is particularly sensitive and is often the cause o ...
Leg, Hands and Feet
... Fibular notch of tibia Articular surface for talus Medial malleolus ...
... Fibular notch of tibia Articular surface for talus Medial malleolus ...
The Respiratory System
... • Type I cells—single layer of simple squamous epithelial cells • Surrounded by basal lamina • Alveolar and capillary walls plus their basal lamina form the ... ...
... • Type I cells—single layer of simple squamous epithelial cells • Surrounded by basal lamina • Alveolar and capillary walls plus their basal lamina form the ... ...
Clinical Anatomy of Neck and Clinical Correlations
... patient? - Cervical spine radiographs should be obtained in children with acquired torticollis to ensure there is no cervical spine fracture or dislocation ...
... patient? - Cervical spine radiographs should be obtained in children with acquired torticollis to ensure there is no cervical spine fracture or dislocation ...
Nerve injuries
... • If the eighth cervical nerve is also damaged, the extent of anesthesia will be greater and will involve the medial side of the forearm, hand, and medial two fingers. • Lower lesions of the brachial plexus can also be produced by the presence of a cervical rib or malignant metastases from the lungs ...
... • If the eighth cervical nerve is also damaged, the extent of anesthesia will be greater and will involve the medial side of the forearm, hand, and medial two fingers. • Lower lesions of the brachial plexus can also be produced by the presence of a cervical rib or malignant metastases from the lungs ...
Pilates for Feet
... In Pilates, the feet are very important to the way we engage the body, and they deserve more attention. Feet bring to mind metaphors for moving us forward in life and finding our sense of place and existence in the world. Yet in our bodies, we pay little attention to them. We squish them into shoes, ...
... In Pilates, the feet are very important to the way we engage the body, and they deserve more attention. Feet bring to mind metaphors for moving us forward in life and finding our sense of place and existence in the world. Yet in our bodies, we pay little attention to them. We squish them into shoes, ...
الشريحة 1
... On auscultation • -The fetal back is not well flexed so the chest is thrust forward • - the fetal heart can be heard in the midline. • - the heart may be heard more easily at the flank on the same side as the back. ...
... On auscultation • -The fetal back is not well flexed so the chest is thrust forward • - the fetal heart can be heard in the midline. • - the heart may be heard more easily at the flank on the same side as the back. ...
RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF SUPERIOR TIBIO
... to the knee joint ln the light of previous experience, however, it was found easy head forwards with the knee partially flexed and the biceps ...
... to the knee joint ln the light of previous experience, however, it was found easy head forwards with the knee partially flexed and the biceps ...
Anatomy of neck + innervation of structures. Anatomy (gross
... skin and muscles of the anterior neck. Drains to the thoracic duct. • Paraesophageal group: Tracheal esophageal groove nodes and delphian node. Abnormal delphian node is often an indicator subglottic laryngeal cancer extension. • This group receives drainages from hypopharynx, larynx, thyroid, and e ...
... skin and muscles of the anterior neck. Drains to the thoracic duct. • Paraesophageal group: Tracheal esophageal groove nodes and delphian node. Abnormal delphian node is often an indicator subglottic laryngeal cancer extension. • This group receives drainages from hypopharynx, larynx, thyroid, and e ...
by collateral ligaments. A synovial membrane lines the fibrous
... other than pure extension and flexion. Since raising the foot produces a tightening of the ligaments of the articular socket the natural position of rest is that assumed by the foot depending in a position of partial flexion with the maximum relaxation of the joint ligaments. The second noteworthy f ...
... other than pure extension and flexion. Since raising the foot produces a tightening of the ligaments of the articular socket the natural position of rest is that assumed by the foot depending in a position of partial flexion with the maximum relaxation of the joint ligaments. The second noteworthy f ...
Document
... 1. Gross anatomy and function of the GHJ To understand the anatomical arrangement and clinical importance of the capsuloligamentous complex in the GHJ, it is appropriate to describe the comprehensive gross anatomy and basic function of the GHJ. The synovial GHJ is composed of the large spherical hea ...
... 1. Gross anatomy and function of the GHJ To understand the anatomical arrangement and clinical importance of the capsuloligamentous complex in the GHJ, it is appropriate to describe the comprehensive gross anatomy and basic function of the GHJ. The synovial GHJ is composed of the large spherical hea ...
fco notes - USA Blue Class
... 1st person to use the term “joint play” to describe the joints ability to withstand aberrant forces/motions; called it the wiggle or slack that is present in all mechanical and biomechanical structures; also wrote “Foot Pain” and “Back Pain” ...
... 1st person to use the term “joint play” to describe the joints ability to withstand aberrant forces/motions; called it the wiggle or slack that is present in all mechanical and biomechanical structures; also wrote “Foot Pain” and “Back Pain” ...
obstetric anatomy midw 201
... therefore contracted in all diameters. Delivery is by C/S 3. Naegele Pelvis – The sacrum has only one ala giving it its obliquity. It may be due to congenital abnormality or injury. Delivery is C/S. ...
... therefore contracted in all diameters. Delivery is by C/S 3. Naegele Pelvis – The sacrum has only one ala giving it its obliquity. It may be due to congenital abnormality or injury. Delivery is C/S. ...
neural crests
... The flat bones of neurocranium continue to grow after birth mainly because the brain grows. Microcephaly is usually an abnormality in which the brain fails to grow and the skull fails to expand. Many children with microcephaly are severely retarded. ...
... The flat bones of neurocranium continue to grow after birth mainly because the brain grows. Microcephaly is usually an abnormality in which the brain fails to grow and the skull fails to expand. Many children with microcephaly are severely retarded. ...
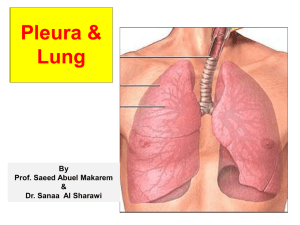
L4-lung & pleura
... Apex: lies one inch above the medial 1/3 of the clavicle. Right pleura: The anterior margin extends vertically from sternoclavicular joint to 6th costal cartilage. Left pleura: The anterior margin extends from sternoclavicular joint to the 4th costal cartilage, then deviates for about 1 inch to left ...
... Apex: lies one inch above the medial 1/3 of the clavicle. Right pleura: The anterior margin extends vertically from sternoclavicular joint to 6th costal cartilage. Left pleura: The anterior margin extends from sternoclavicular joint to the 4th costal cartilage, then deviates for about 1 inch to left ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.


![20 SCIATIC NERVE.IIppt[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000476916_1-da0a7875960c02fecd474919cb5375ce-300x300.png)