AArest
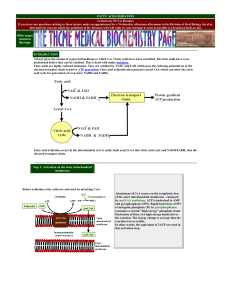
... Start with PRPP and ATP: form phosphoribosyl ATP 3 reactions involving glutamine as nitrogen donor for ring lead to imidazole glycerol phosphate That gets modified and transaminated t make histidine ...
... Start with PRPP and ATP: form phosphoribosyl ATP 3 reactions involving glutamine as nitrogen donor for ring lead to imidazole glycerol phosphate That gets modified and transaminated t make histidine ...
UNIT 11. CATABOLISM OF GLUCOSE • Aerobic glycolysis: scheme
... the point below about shuttle systems ...
... the point below about shuttle systems ...
bme-biochem-3-kh-enzymes-9
... Enzymes are mostly proteins They are highly specific to a reaction They catalyze many reactions including breaking down nutrients, storing and releasing energy, creating new molecules, and coordinating biological reactions. Enzymes use an active site, but can be affected by bonding at other areas ...
... Enzymes are mostly proteins They are highly specific to a reaction They catalyze many reactions including breaking down nutrients, storing and releasing energy, creating new molecules, and coordinating biological reactions. Enzymes use an active site, but can be affected by bonding at other areas ...
Document
... The NADH and FADH2 formed in glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and the citric acid cycle are energy-rich molecules because each contains a pair of electrons having a high transfer potential. When these electrons are used to reduce molecular oxygen to water, a large amount of free energy is liberated ...
... The NADH and FADH2 formed in glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and the citric acid cycle are energy-rich molecules because each contains a pair of electrons having a high transfer potential. When these electrons are used to reduce molecular oxygen to water, a large amount of free energy is liberated ...
What is an enzyme? Function of enzymes
... the mitochondria using pyruvate and NAD+. • Acetyl-CoA can then be used to transfer an acetyl group (CH3CO) to aid in fatty acid synthesis. ...
... the mitochondria using pyruvate and NAD+. • Acetyl-CoA can then be used to transfer an acetyl group (CH3CO) to aid in fatty acid synthesis. ...
BIOENERGETICS AND METABOLISM
... simultaneous synthesis and degradation of fatty acids would be wasteful, however, and this is prevented by reciprocally regulating the anabolic and catabolic reaction sequences: when one sequence is active, the other is suppressed. Such regulation could not occur if anabolic and catabolic pathways w ...
... simultaneous synthesis and degradation of fatty acids would be wasteful, however, and this is prevented by reciprocally regulating the anabolic and catabolic reaction sequences: when one sequence is active, the other is suppressed. Such regulation could not occur if anabolic and catabolic pathways w ...
Tn917 insertion site in the 2C4 mutant
... Summary of the Evidence that E. faecium kills Worms with Hydrogen Peroxide 1. The E. faecium toxin is diffusible and does not require direct contact with the bacteria. 2. The NADH peroxidase mutant produces more H2O2 and has enhanced C. elegans killing activity 3. The NADH oxidase and the potential ...
... Summary of the Evidence that E. faecium kills Worms with Hydrogen Peroxide 1. The E. faecium toxin is diffusible and does not require direct contact with the bacteria. 2. The NADH peroxidase mutant produces more H2O2 and has enhanced C. elegans killing activity 3. The NADH oxidase and the potential ...
- Wiley Online Library
... persistent dormant form of the bacilli. The generation of alanine is accompanied by the oxidation of NADH. This aspect of alanine synthesis might play a role under the oxygen limiting conditions encountered after de£ection from aerobic growth and later during anaerobic dormancy. Therefore, we propos ...
... persistent dormant form of the bacilli. The generation of alanine is accompanied by the oxidation of NADH. This aspect of alanine synthesis might play a role under the oxygen limiting conditions encountered after de£ection from aerobic growth and later during anaerobic dormancy. Therefore, we propos ...
ATP Synthesis
... generate ATP in a process referred to as “Oxidative Phosphorylation” - Oxidative phosphorylation (OP) is in stark contrast to “substrate-level phosphorylation”— whereby the transfer of a phosphoryl group from a “high-energy” compound (eg phosphoenol pyruvate) to ADP is used to synthesize ATP (see §3 ...
... generate ATP in a process referred to as “Oxidative Phosphorylation” - Oxidative phosphorylation (OP) is in stark contrast to “substrate-level phosphorylation”— whereby the transfer of a phosphoryl group from a “high-energy” compound (eg phosphoenol pyruvate) to ADP is used to synthesize ATP (see §3 ...
lec 7 Metabolism of purine nucleotides
... De novo biosynthesis occur in liver due to presence of enzymes. Other tissues can’t do de novo synthesis. In these organs, free purine bases (guanine, hypoxanthine and adenine) reacts with PRPP again to resynthesize purine nucleotides. These free purine bases are obtained from diet or result during ...
... De novo biosynthesis occur in liver due to presence of enzymes. Other tissues can’t do de novo synthesis. In these organs, free purine bases (guanine, hypoxanthine and adenine) reacts with PRPP again to resynthesize purine nucleotides. These free purine bases are obtained from diet or result during ...
Preview as PDF - Pearson Higher Education
... comes from the sun. In photosynthesis, the energy of sunlight is used to rearrange the atoms of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), producing organic molecules and releasing oxygen (O2). In cellular respiration, O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 and H2O, and the cell captu ...
... comes from the sun. In photosynthesis, the energy of sunlight is used to rearrange the atoms of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), producing organic molecules and releasing oxygen (O2). In cellular respiration, O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 and H2O, and the cell captu ...
Amino Acid Oxidation, the Production of Urea, and Amino Acid
... Reactions in the Liver Using Amino Acids Preparation for Gluconeogenesis or Fatty Acid Biosynthesis When amino acids are used as precursors for gluconeogenesis (glucose poor state) or when they are present in excess and are going to be converted into fatty acids (energy rich state) the liver is the ...
... Reactions in the Liver Using Amino Acids Preparation for Gluconeogenesis or Fatty Acid Biosynthesis When amino acids are used as precursors for gluconeogenesis (glucose poor state) or when they are present in excess and are going to be converted into fatty acids (energy rich state) the liver is the ...
Assessing in silico the recruitment and functional spectrum of
... activities [6]. This remarkable diversity reflects the random manner in which their biosynthesis has evolved. The pathways have been acquired opportunistically and horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of complete pathways concentrated in genomic islands is common [7]. However, horizontal gene transfer can ...
... activities [6]. This remarkable diversity reflects the random manner in which their biosynthesis has evolved. The pathways have been acquired opportunistically and horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of complete pathways concentrated in genomic islands is common [7]. However, horizontal gene transfer can ...
Regulation of intermediary metabolism by protein acetylation
... Histone acetyltransferases (HATs): a group of enzymes that transfer an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form e-N-acetyl lysine. Although first discovered as enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine residues on histones and thus so-named, recent recommendations suggest renaming them as lysine-acetyltra ...
... Histone acetyltransferases (HATs): a group of enzymes that transfer an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form e-N-acetyl lysine. Although first discovered as enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine residues on histones and thus so-named, recent recommendations suggest renaming them as lysine-acetyltra ...
What is an enzyme? Func
... Enzyme ac9on theories • Induced Fit: An enzyme that is perfectly complementary to its substrate would actually not make a good enzyme because the reac9on has no room to proceed to the transi9on state ...
... Enzyme ac9on theories • Induced Fit: An enzyme that is perfectly complementary to its substrate would actually not make a good enzyme because the reac9on has no room to proceed to the transi9on state ...
6_Enzymes - WordPress.com
... 2. Effect of pH: It is greatly affected by pH of the medium. Each enzyme has a pH optima at which, it gives maximum reaction. Reduction in enzyme activity at extreme pH is due to denaturation of enzyme. pH optima of each enzyme may vary depending on the nature of enzymes. The enzyme may be acting in ...
... 2. Effect of pH: It is greatly affected by pH of the medium. Each enzyme has a pH optima at which, it gives maximum reaction. Reduction in enzyme activity at extreme pH is due to denaturation of enzyme. pH optima of each enzyme may vary depending on the nature of enzymes. The enzyme may be acting in ...
Amino acid Catabolism
... the pyridoxal part of the coenzyme to generate pyridoxamine phosphate. The pyridoxamine form of the coenzyme then reacts with an α-keto acid to form an amino acid, at the same time regenerating the original aldehyde form of the coenzyme. ...
... the pyridoxal part of the coenzyme to generate pyridoxamine phosphate. The pyridoxamine form of the coenzyme then reacts with an α-keto acid to form an amino acid, at the same time regenerating the original aldehyde form of the coenzyme. ...
PDF - MD Body and Med spa
... Alternatively you can email any problems to Dr. Brookes who will reply to your message as soon as possible ([email protected]). Other pages related to this topic ...
... Alternatively you can email any problems to Dr. Brookes who will reply to your message as soon as possible ([email protected]). Other pages related to this topic ...
Enzymology Lectures Year 1 - Emily Flashman`s
... • One of the most important targets for pharmaceuticals • Intrinsic in human biology - manipulation • Fermentation of pharmaceuticals and fine chemical • Useful in synthesis, especially for resolutions / asymmetric reactions, e.g. ...
... • One of the most important targets for pharmaceuticals • Intrinsic in human biology - manipulation • Fermentation of pharmaceuticals and fine chemical • Useful in synthesis, especially for resolutions / asymmetric reactions, e.g. ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... Glycolysis, occurs, at least in part, in almost every living cell. This series of reactions is believed to be among the oldest of all the biochemical pathways. Both the enzymes and the number and mechanisms of the steps in the pathway are highly conserved in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Also, glycoly ...
... Glycolysis, occurs, at least in part, in almost every living cell. This series of reactions is believed to be among the oldest of all the biochemical pathways. Both the enzymes and the number and mechanisms of the steps in the pathway are highly conserved in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Also, glycoly ...
Respiration - Biology Junction
... • The Krebs cycle is named after Hans Krebs who was largely responsible for elucidating its pathways in the 1930s. • This cycle begins when acetate from acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate. • Ultimately, the oxaloacetate is recycled and the acetate is broken down to CO2. • Each cy ...
... • The Krebs cycle is named after Hans Krebs who was largely responsible for elucidating its pathways in the 1930s. • This cycle begins when acetate from acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate. • Ultimately, the oxaloacetate is recycled and the acetate is broken down to CO2. • Each cy ...
Lactic Acid : Brief History
... dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine trip hosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it wa ...
... dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine trip hosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it wa ...
Enzyme Catalysis - faculty at Chemeketa
... affinity for the substrate. 1. It does not compete with the substrate for the active site. 2. It does not need to resemble the structure of the substrate. 3. Its’ effect cannot be reversed by increasing the substrate concentration. ...
... affinity for the substrate. 1. It does not compete with the substrate for the active site. 2. It does not need to resemble the structure of the substrate. 3. Its’ effect cannot be reversed by increasing the substrate concentration. ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.