1.3 Enzymes supplemental work
... The students conducted experiments to study digestive enzyme activity. In the first experiment, the students observed the rate at which salivary amylase breaks down starch (the substrate) in solutions with different pH values. The students then performed the same type of experiment with pepsin. The ...
... The students conducted experiments to study digestive enzyme activity. In the first experiment, the students observed the rate at which salivary amylase breaks down starch (the substrate) in solutions with different pH values. The students then performed the same type of experiment with pepsin. The ...
Page 1 Enzymes OK….so now we`ve done all of that Chemistry stuff
... o What is a catalyst? (We will look at how some work later) A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction (by lowering the activation energy) but it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction. Without catalysts, 37˚C would be too slow to sustain life. We will look at how differen ...
... o What is a catalyst? (We will look at how some work later) A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction (by lowering the activation energy) but it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction. Without catalysts, 37˚C would be too slow to sustain life. We will look at how differen ...
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Practice
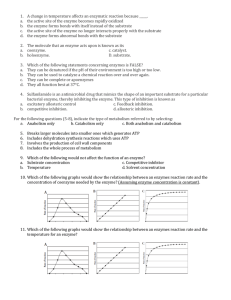
... ____ 2. SB 1 b What happens to an enzyme when placed in boiling water? a. It becomes sugar b. It is denatured c. It becomes stronger d. It speeds up the rate of reaction ____ 3. SB 1 c Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Nucleotides are to __________ as ____________ are ...
... ____ 2. SB 1 b What happens to an enzyme when placed in boiling water? a. It becomes sugar b. It is denatured c. It becomes stronger d. It speeds up the rate of reaction ____ 3. SB 1 c Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Nucleotides are to __________ as ____________ are ...
Enzymes: the little molecules that could
... is broken into maltose, a double-ring sugar composed of two glucose molecules; but fermentation reactions require ...
... is broken into maltose, a double-ring sugar composed of two glucose molecules; but fermentation reactions require ...
E = enzyme, S= substrate • The key does not fit the lock quite
... with a hinge. Some of the amino acids required for catalysis are in one domain and some in the other. When the hinge closes these amino acids come in contact with each other and the substrates, phosphoglycerate and ADP . ...
... with a hinge. Some of the amino acids required for catalysis are in one domain and some in the other. When the hinge closes these amino acids come in contact with each other and the substrates, phosphoglycerate and ADP . ...
Enzymes and How They Work
... 2) Catalysts- chemicals which speed up a reaction without being consumed B. Properties of enzymes: 1) Speed up reactions 2) Can be used over and over, only needed in small amount 3) Decrease amount of energy needed to start a reaction (activation energy) 4) Specific to a substrate based on its shape ...
... 2) Catalysts- chemicals which speed up a reaction without being consumed B. Properties of enzymes: 1) Speed up reactions 2) Can be used over and over, only needed in small amount 3) Decrease amount of energy needed to start a reaction (activation energy) 4) Specific to a substrate based on its shape ...
Enzymes
... The amount of energy needed to convert reactants into products This is the “cost of the reaction” The enzyme is a “coupon” ...
... The amount of energy needed to convert reactants into products This is the “cost of the reaction” The enzyme is a “coupon” ...
doc 3.1.2 starch glycogen cellulose Summary sheets on
... Can be seen as grains in the chloroplasts with light microscope Does not interfere with metabolic reactions or affect water potential Mixture of amylose and amylopectin Amylose is a straight chain of glucose molecules. In fact the chain is floppy, and it tends to coil up into a helix. Amylopec ...
... Can be seen as grains in the chloroplasts with light microscope Does not interfere with metabolic reactions or affect water potential Mixture of amylose and amylopectin Amylose is a straight chain of glucose molecules. In fact the chain is floppy, and it tends to coil up into a helix. Amylopec ...
Free Response Questions
... -Enzymes function in lowering energy to activation, and the shape of the active binding site must fit the substrate -Factors that modify enzyme structure, each one must be described: -changes in pH and temperature -competitive inhibitors prevent substrate binding, and thus affect its function. They ...
... -Enzymes function in lowering energy to activation, and the shape of the active binding site must fit the substrate -Factors that modify enzyme structure, each one must be described: -changes in pH and temperature -competitive inhibitors prevent substrate binding, and thus affect its function. They ...
Enzymes - hbwbiology.net
... A substrate is the substance upon which the enzyme acts. Enzymes are substrate-specific. The induced-fit model describes how enzymes work. The protein (enzyme) has an active site that is configured by the shape, polarity or other characteristics of the active site. The interaction of the reactants ( ...
... A substrate is the substance upon which the enzyme acts. Enzymes are substrate-specific. The induced-fit model describes how enzymes work. The protein (enzyme) has an active site that is configured by the shape, polarity or other characteristics of the active site. The interaction of the reactants ( ...
Enzyme Puzzle Activity
... Enzyme Puzzle Activity Purpose: In this activity, you will make up your own enzyme-substrate complex. Substrates and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (l ...
... Enzyme Puzzle Activity Purpose: In this activity, you will make up your own enzyme-substrate complex. Substrates and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (l ...
A change in temperature affects an enzymatic reaction because
... the enzyme forms bonds with itself instead of the substrate the active site of the enzyme no longer interacts properly with the substrate the enzyme forms abnormal bonds with the substrate ...
... the enzyme forms bonds with itself instead of the substrate the active site of the enzyme no longer interacts properly with the substrate the enzyme forms abnormal bonds with the substrate ...
Disaccharides
... Sucrose: Table sugar, commonly just called sugar. Forms when the anomeric carbon of D-‐glucose reacts with the –OH of the anomeric carbon in D-‐fructose forming an α-‐1-‐β-‐2-‐glycosidic bond. Sucr ...
... Sucrose: Table sugar, commonly just called sugar. Forms when the anomeric carbon of D-‐glucose reacts with the –OH of the anomeric carbon in D-‐fructose forming an α-‐1-‐β-‐2-‐glycosidic bond. Sucr ...
Enzymes and ATP
... inside the cytoplasm. • They control the rate of metabolic reactions in the body. • They lower activation energy (energy needed to get a reaction started). • They weaken chemical bonds so molecules can be made or broken down by the body. ...
... inside the cytoplasm. • They control the rate of metabolic reactions in the body. • They lower activation energy (energy needed to get a reaction started). • They weaken chemical bonds so molecules can be made or broken down by the body. ...
3.2.1 enzymes - Haiku Learning : Login
... • Induced fit enhances catalysis, as the enzyme converts substrate to product. • Release of the products restores the enzyme to its original form. • The enzyme can repeat this reaction over and over, as long as substrate molecules are present. ...
... • Induced fit enhances catalysis, as the enzyme converts substrate to product. • Release of the products restores the enzyme to its original form. • The enzyme can repeat this reaction over and over, as long as substrate molecules are present. ...
Ch.21Pt.4_000
... 1. Aligning substrate molecules at correct angle 2. Holding substrate while rxn occurs (less E) Substrate and active site on enzyme must fit. Some substrate molecules will fit / others will not, Some substrates will react and others will not = “specificity.” ...
... 1. Aligning substrate molecules at correct angle 2. Holding substrate while rxn occurs (less E) Substrate and active site on enzyme must fit. Some substrate molecules will fit / others will not, Some substrates will react and others will not = “specificity.” ...
Text 5- Pre and Post Reading Activities Enzymes
... products. They can be some 10,000 times more efficient than ordinary inorganic catalysts used in industry. One enzyme molecule can catalyse 10 million reactions in a single second! They also work at relatively low temperatures (typically, about 40 °C), saving energy and therefore saving money. Some ...
... products. They can be some 10,000 times more efficient than ordinary inorganic catalysts used in industry. One enzyme molecule can catalyse 10 million reactions in a single second! They also work at relatively low temperatures (typically, about 40 °C), saving energy and therefore saving money. Some ...
Enzymes
... (4) The enzyme lets go. Big idea - When the enzyme lets go, it returns to normal, ready to do another reaction. The substrate is no longer the same. The substrate is now called the PRODUCT. ...
... (4) The enzyme lets go. Big idea - When the enzyme lets go, it returns to normal, ready to do another reaction. The substrate is no longer the same. The substrate is now called the PRODUCT. ...
Enzyme Activity - Model High School
... 1) Using the paper provided, you will make an enzyme puzzle. You need to create a substrate, an enzyme with a matching active site, and reactants that are formed after the enzyme speeds up the reaction. If you have problems, refer to page 76 in your biology book. 2) You will have to name your enzyme ...
... 1) Using the paper provided, you will make an enzyme puzzle. You need to create a substrate, an enzyme with a matching active site, and reactants that are formed after the enzyme speeds up the reaction. If you have problems, refer to page 76 in your biology book. 2) You will have to name your enzyme ...
Enzymes - CynthiaJankowski
... reactants of the reaction that it is catalyzing. • The reactant an enzyme works on is called a substrate. • The substrate binds to the active site to make the enzyme active. • Factors such as temperature, and pH affect enzyme activity. ...
... reactants of the reaction that it is catalyzing. • The reactant an enzyme works on is called a substrate. • The substrate binds to the active site to make the enzyme active. • Factors such as temperature, and pH affect enzyme activity. ...
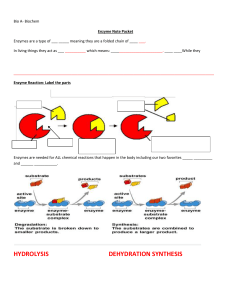
Bio A- Biochem Enzyme Note Packet Enzymes are a type of ___
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
Practice Q Ch 8 metabolism with key
... c. This is an exergonic reaction which is spontaneous and makes energy available d. The reaction requires free energy and is exergonic 15. Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by a. providing the substrate required for the reaction to occur b. affecting the rate at which reactions ...
... c. This is an exergonic reaction which is spontaneous and makes energy available d. The reaction requires free energy and is exergonic 15. Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by a. providing the substrate required for the reaction to occur b. affecting the rate at which reactions ...
Three Dimensional Protein Structures
... the deoxy state. When oxygen binds it pulls the iron back into the heme plane. Since the proximal His F8 is attached to the Fe this pulls the complete F helix like a lever on a ...
... the deoxy state. When oxygen binds it pulls the iron back into the heme plane. Since the proximal His F8 is attached to the Fe this pulls the complete F helix like a lever on a ...
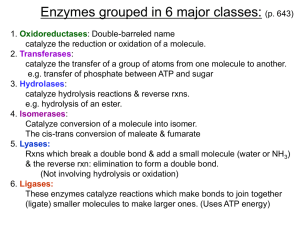
Isomerase

Isomerases are a general class of enzymes which convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases can either facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed or they can catalyze conformational changes. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:A–B → B–AThere is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangements. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism.