No Slide Title
... – Each type of protein has its own 3-D shape – If shape is altered the protein can not function right. ...
... – Each type of protein has its own 3-D shape – If shape is altered the protein can not function right. ...
for ESL students
... INTRODUCTION: what would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes ar ...
... INTRODUCTION: what would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes ar ...
Biochemical studies in FRUIT DEVELOPMENT
... This type of compound is known to chelate with copper. If it can be shown that these copper chelates have some of the properties of copper enzymes, this will help advance knowledge of the mechanism of action of the copper enzymes. -Lloyd L. Ingraham, Dept. of Agricultural Biochemistry, Davis. ...
... This type of compound is known to chelate with copper. If it can be shown that these copper chelates have some of the properties of copper enzymes, this will help advance knowledge of the mechanism of action of the copper enzymes. -Lloyd L. Ingraham, Dept. of Agricultural Biochemistry, Davis. ...
Here - Sycamore
... 1. You are querying for the Km value of the substrate of the glucose-6phosphate isomerase from Homo sapiens. 2. Insert the SwissProt identifier for that enzyme (P06744). 3. In Structural Information, 30 homologuous protein structures are found in the PDB with the same EC number 5.3.1.9 1. Select the ...
... 1. You are querying for the Km value of the substrate of the glucose-6phosphate isomerase from Homo sapiens. 2. Insert the SwissProt identifier for that enzyme (P06744). 3. In Structural Information, 30 homologuous protein structures are found in the PDB with the same EC number 5.3.1.9 1. Select the ...
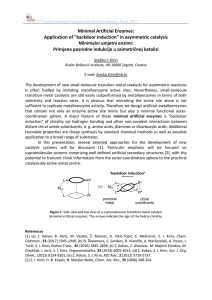
Application of "backdoor induction" in asymmetric catalysis
... is often fuelled by imitating metalloenzyme active sites. Nevertheless, small-molecule transition metal catalysts are still easily outperformed by metalloenzymes in terms of both selectivity and reaction rates. It is obvious that mimicking the active site alone is not sufficient to replicate metallo ...
... is often fuelled by imitating metalloenzyme active sites. Nevertheless, small-molecule transition metal catalysts are still easily outperformed by metalloenzymes in terms of both selectivity and reaction rates. It is obvious that mimicking the active site alone is not sufficient to replicate metallo ...
Pancreatic enzyme replacement in congenital hyperinsulinism
... The beads then move along to the small intestine where the coating dissolves releasing the enzymes. Food is then broken down and the nutrients are absorbed by the body. Pancrex V® is a powder form of enzymes and can be mixed with water or milk and taken orally or through a nasogastric tube or ...
... The beads then move along to the small intestine where the coating dissolves releasing the enzymes. Food is then broken down and the nutrients are absorbed by the body. Pancrex V® is a powder form of enzymes and can be mixed with water or milk and taken orally or through a nasogastric tube or ...
Product:
... The combination of the active components of A. bisporus has a mutagenic effect on the aromatase enzyme. Upon binding with the enzyme, these components cause the cleavage of certain amino acids that make up the aromatase protein, disabling it from converting androgens into estradiol. Eurycoma longif ...
... The combination of the active components of A. bisporus has a mutagenic effect on the aromatase enzyme. Upon binding with the enzyme, these components cause the cleavage of certain amino acids that make up the aromatase protein, disabling it from converting androgens into estradiol. Eurycoma longif ...
Control of Enzymes
... (So if you think about it, allosteric site are kind of nice because they more or less have an on/off switch. In many cases, one of the products of the reaction actually will serve as an allosteric inhibitor. Why do you think that is often the case?) (This is because if the product actually accumula ...
... (So if you think about it, allosteric site are kind of nice because they more or less have an on/off switch. In many cases, one of the products of the reaction actually will serve as an allosteric inhibitor. Why do you think that is often the case?) (This is because if the product actually accumula ...
What is the effect of substrate concentration on - jehs
... Alkaline phosphatase catalyzes the cleavage of a phosphate group from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, protein, and alkaloids In humans alkaline phosphatase is particularly concentrated in the liver, bile duct, kidney, bone, and the placenta. Human phosphatase enzymes ALPI-int ...
... Alkaline phosphatase catalyzes the cleavage of a phosphate group from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, protein, and alkaloids In humans alkaline phosphatase is particularly concentrated in the liver, bile duct, kidney, bone, and the placenta. Human phosphatase enzymes ALPI-int ...
Chapter 8 - HCC Learning Web
... The synthesis of protein from amino acids is an example of anabolism Bioenergetics is the study of how organisms manage their energy resources – the study of energy flow through the living organisms. ...
... The synthesis of protein from amino acids is an example of anabolism Bioenergetics is the study of how organisms manage their energy resources – the study of energy flow through the living organisms. ...
Protease Aqualysin 1 from Thermus aquaticus produced by B
... therefore not added to the final food product. The food enzyme is denatured during the baking process. Therefore it cannot have any technological function anymore in final baked foods. Food enzyme preparations are used by food manufacturers according to the Quantum Satis principle, which means that ...
... therefore not added to the final food product. The food enzyme is denatured during the baking process. Therefore it cannot have any technological function anymore in final baked foods. Food enzyme preparations are used by food manufacturers according to the Quantum Satis principle, which means that ...
No Slide Title
... Example: The drug marijuana contains the chemical THC. THC temporarily bonds to enzymes in our brain cells causing them to not function correctly thus causing the temporary feeling of being “high”. ...
... Example: The drug marijuana contains the chemical THC. THC temporarily bonds to enzymes in our brain cells causing them to not function correctly thus causing the temporary feeling of being “high”. ...
Nitric Oxide Production from Synthesized Ruthenium (III) Porphyrins
... Porphyrins play a vital role in the mechanism of life. A class of porphyrins (or hemes) that is utilized by multicellular organisms is found in hemoglobin and myoglobin. Both of these are used for oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) transportation throughout the body. Cytochromes are a class of mon ...
... Porphyrins play a vital role in the mechanism of life. A class of porphyrins (or hemes) that is utilized by multicellular organisms is found in hemoglobin and myoglobin. Both of these are used for oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) transportation throughout the body. Cytochromes are a class of mon ...
A metal enzyme that can cleave benzene rings
... Aromatic rings are extremely stable and very difficult to break apart. The Birch reduction of aromatic compounds is a common reaction in organic chemistry and requires conditions that even chemists regard as drastic. Prof. Dr. Matthias Boll from the University of Freiburg’s Faculty of Biology and hi ...
... Aromatic rings are extremely stable and very difficult to break apart. The Birch reduction of aromatic compounds is a common reaction in organic chemistry and requires conditions that even chemists regard as drastic. Prof. Dr. Matthias Boll from the University of Freiburg’s Faculty of Biology and hi ...
Avidin Based Enzyme Immobilization on Gold Nanoelectrodes
... Over the last decade, a considerable amount of research have been conducted in the field of biological electrochemistry, one example in particular is biosensors. Biosensors are used to analyze the composition of a solution and to detect the presence and concentration of a particular compound of inte ...
... Over the last decade, a considerable amount of research have been conducted in the field of biological electrochemistry, one example in particular is biosensors. Biosensors are used to analyze the composition of a solution and to detect the presence and concentration of a particular compound of inte ...
ENZYME ACTION - Southern Biological
... Tray (G11.38). Using a clean pipette, transfer two drops of the starch/amylase solution into the first well and record any change in colour. Repeat this process at set times. The strong blue colour that indicates the presence of starch will become less intense as the enzymic reaction progressively b ...
... Tray (G11.38). Using a clean pipette, transfer two drops of the starch/amylase solution into the first well and record any change in colour. Repeat this process at set times. The strong blue colour that indicates the presence of starch will become less intense as the enzymic reaction progressively b ...
Enzymes are Catalysts - nxc technologies, inc.
... range. They are also very selective in the reactions they take place in and often will react only with a single molecule or certain molecule types. An example of an enzyme as a catalyst in a reaction – digestion. Enzymes act in the break down of large protein, starch and fat molecules into smaller m ...
... range. They are also very selective in the reactions they take place in and often will react only with a single molecule or certain molecule types. An example of an enzyme as a catalyst in a reaction – digestion. Enzymes act in the break down of large protein, starch and fat molecules into smaller m ...
Enzymopathy as a result of Polymorphism
... mind that the human body is a complex web of biochemical processes. As a result, a deficiency in a cofactor or enzyme may lead to a deficiency in another cofactor that is required to make the original cofactor. As an example, Vitamin D is needed to make enzymes that are necessary to make P-5-P which ...
... mind that the human body is a complex web of biochemical processes. As a result, a deficiency in a cofactor or enzyme may lead to a deficiency in another cofactor that is required to make the original cofactor. As an example, Vitamin D is needed to make enzymes that are necessary to make P-5-P which ...
survey of biochemistry - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • General acid catalysis H+ transfer from an acid lowers the free energy of the transition state ...
... • General acid catalysis H+ transfer from an acid lowers the free energy of the transition state ...
Document
... De novo synthesis of purines begins with the metabolic precursors like amino acids, ribose-5-phosphate, CO2 and NH3. ...
... De novo synthesis of purines begins with the metabolic precursors like amino acids, ribose-5-phosphate, CO2 and NH3. ...
Properties of an Enzyme: Acid Phosphatase
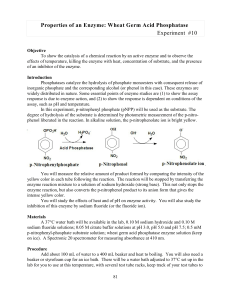
... Properties of an Enzyme: Wheat Germ Acid Phosphatase Experiment #10 Objective To show the catalysis of a chemical reaction by an active enzyme and to observe the effects of temperature, killing the enzyme with heat, concentration of substrate, and the presence of an inhibitor of the enzyme. Introduc ...
... Properties of an Enzyme: Wheat Germ Acid Phosphatase Experiment #10 Objective To show the catalysis of a chemical reaction by an active enzyme and to observe the effects of temperature, killing the enzyme with heat, concentration of substrate, and the presence of an inhibitor of the enzyme. Introduc ...
INFLUENCE OF PRETRATMENT TYPE OF Agave atrovirens
... hours at 30°C. Growth measurement and endoglucanase and β-glucosidase activity were determined. Results. The fastest growth was registered by the strain T2-31, as well as the highest enzyme activity. In the Fig 1, is shown that T2-31 present a wider and faster growth and also in sporulation time, be ...
... hours at 30°C. Growth measurement and endoglucanase and β-glucosidase activity were determined. Results. The fastest growth was registered by the strain T2-31, as well as the highest enzyme activity. In the Fig 1, is shown that T2-31 present a wider and faster growth and also in sporulation time, be ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... • Some allosteric enzymes have multiple active sites. • When one binding site is occupied, it changes the other(s) so that they bind additional substrate molecules more readily. • How the rate of a reaction changes with increasing substrate concentration depends on whether the enzyme is allosterical ...
... • Some allosteric enzymes have multiple active sites. • When one binding site is occupied, it changes the other(s) so that they bind additional substrate molecules more readily. • How the rate of a reaction changes with increasing substrate concentration depends on whether the enzyme is allosterical ...
fulltext
... and co-workers as being of paramount importance.10 In this view the substrate binding, transition state stabilisation, product release, and all transitions in-between, require different conformations of the enzyme for effective catalysis. Some enzymatic reactions require a non-protein moiety, a spec ...
... and co-workers as being of paramount importance.10 In this view the substrate binding, transition state stabilisation, product release, and all transitions in-between, require different conformations of the enzyme for effective catalysis. Some enzymatic reactions require a non-protein moiety, a spec ...
Expanding the Range of Substrate Acceptance of Enzymes
... information is not necessary, the process is fundamentally different from so-called rational design based on site-specific mutagenesis.[3] We have previously applied directed evolution to the creation of enantioselective lipases,[4] epoxide hydrolases,[5] and monooxygenases,[6] and other groups have ...
... information is not necessary, the process is fundamentally different from so-called rational design based on site-specific mutagenesis.[3] We have previously applied directed evolution to the creation of enantioselective lipases,[4] epoxide hydrolases,[5] and monooxygenases,[6] and other groups have ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.