Tertiary Structure
... • There are always two adjacent bstrands on opposite sides of a bsheet. One of the loops from one of these two b-strands goes above the b-sheet, whereas the other loop goes below, which creates a crevice outside the edge of the b-sheet between two loops. ...
... • There are always two adjacent bstrands on opposite sides of a bsheet. One of the loops from one of these two b-strands goes above the b-sheet, whereas the other loop goes below, which creates a crevice outside the edge of the b-sheet between two loops. ...
RuBISCO WS - St Paul`s School Intranet
... atoms of atmospheric carbon dioxide are made available to organisms in the form of energy-rich molecules such as sucrose. While RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme in the world, it is also one of the least efficient. RuBisCO is so slow that it can "capture" only a few carbon dioxide molecules each s ...
... atoms of atmospheric carbon dioxide are made available to organisms in the form of energy-rich molecules such as sucrose. While RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme in the world, it is also one of the least efficient. RuBisCO is so slow that it can "capture" only a few carbon dioxide molecules each s ...
Richards_CH09x
... individuals are referred to as “fast acetylators.” – Individuals who possess a mutation that codes for this enzyme possess one that is less effective, requiring about 3 hours to eliminate half of the dose. These individuals are referred to as “slow acetylators” and are at greater risk for developing ...
... individuals are referred to as “fast acetylators.” – Individuals who possess a mutation that codes for this enzyme possess one that is less effective, requiring about 3 hours to eliminate half of the dose. These individuals are referred to as “slow acetylators” and are at greater risk for developing ...
ppt
... The DNA fragment produced by a pair of adjacent cuts in a DNA molecule is called a restriction fragment. A large DNA molecule will typically be cut into many restriction fragments of different sizes. For example, an E. coli DNA molecule, which contains 4.6 x 106 base pairs, is cut into several hundr ...
... The DNA fragment produced by a pair of adjacent cuts in a DNA molecule is called a restriction fragment. A large DNA molecule will typically be cut into many restriction fragments of different sizes. For example, an E. coli DNA molecule, which contains 4.6 x 106 base pairs, is cut into several hundr ...
Direct Conversion of Ethane to Ethanol by Engineered Cytochrome P450 BM3 Peter Meinhold,
... sites in P450s assist in the release of singly hydroxylated products, and we have witnessed very little (less than 5 %) overoxidation of longer and more hydrophobic alcohols in any BM-3 mutants. In addition, we have observed that alkane-hydroxylating mutants generally overoxidize longer-chain alkane ...
... sites in P450s assist in the release of singly hydroxylated products, and we have witnessed very little (less than 5 %) overoxidation of longer and more hydrophobic alcohols in any BM-3 mutants. In addition, we have observed that alkane-hydroxylating mutants generally overoxidize longer-chain alkane ...
楔汴ꅥꝇꕑ닎떢껦䆺慲楢潮伭楬潧慳捣慨楲敤 佁 抦햸ºÞ澵쎻䆡 ¾Ü
... When total basidiomata production was analyzed on the basis of the total dry weight per bag (300 g), we found that P. ostreatus production was significantly higher than the obtained with monocultures of P. citrinopileatus and higher than any other treatment. In all co-cultivation combinations yields ...
... When total basidiomata production was analyzed on the basis of the total dry weight per bag (300 g), we found that P. ostreatus production was significantly higher than the obtained with monocultures of P. citrinopileatus and higher than any other treatment. In all co-cultivation combinations yields ...
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 16: Chemistry in Everyday Life Top
... produce lasting lather. These contain glycerol to prevent rapid drying. A gum called rosin is added in these soaps which forms sodium rosinate which lathers well Transparent soaps: These soaps are prepared by dissolving the soap in ethanol and then evaporating the excess solvent Floating soaps: Thes ...
... produce lasting lather. These contain glycerol to prevent rapid drying. A gum called rosin is added in these soaps which forms sodium rosinate which lathers well Transparent soaps: These soaps are prepared by dissolving the soap in ethanol and then evaporating the excess solvent Floating soaps: Thes ...
BiochemTargetPracticeKEY2014 - Self
... TARGET VII. What types of molecules are formed by dehydration synthesis (also called condensation) reactions? What types of molecules are formed by hydrolysis? Dehydration synthesis involves monomers combining to form larger molecules (like monosaccharides forming disachharides or polysachharides) H ...
... TARGET VII. What types of molecules are formed by dehydration synthesis (also called condensation) reactions? What types of molecules are formed by hydrolysis? Dehydration synthesis involves monomers combining to form larger molecules (like monosaccharides forming disachharides or polysachharides) H ...
Role of Cys-295 on subunit interactions and allosteric regulation of
... protein concentration has been held constant. The scattered intensity correlated well with the loss of enzymatic activity, dropping to less than half of the initial value at the same GdnHCl concentration range where loss of activity was observed. Since unfolding proceeds from the native dimeric stat ...
... protein concentration has been held constant. The scattered intensity correlated well with the loss of enzymatic activity, dropping to less than half of the initial value at the same GdnHCl concentration range where loss of activity was observed. Since unfolding proceeds from the native dimeric stat ...
Week_4_Practice questions
... 3. You discover a bacterium, C. jejuni, which can only use fucose (C6H12O5) as an energy source. You isolate an enzyme from C. jejuni which phosphorylate fucose resulting in a molecule called fucose-1-phosphate also called fucose 1-P. Fucose must be converted into fucose 1-P in order to be used as a ...
... 3. You discover a bacterium, C. jejuni, which can only use fucose (C6H12O5) as an energy source. You isolate an enzyme from C. jejuni which phosphorylate fucose resulting in a molecule called fucose-1-phosphate also called fucose 1-P. Fucose must be converted into fucose 1-P in order to be used as a ...
Purification and Reengineering of Plastic
... genus are capable of producing polyethylenedegrading enzymes. ...
... genus are capable of producing polyethylenedegrading enzymes. ...
Interesting Info on Experiment 5
... What causes gas when you eat beans, cabbage and brussel sprouts? When you eat sugar it has to be broken down into monsaccharides to get into the bloodstream. Raffinose, which is more complex (trisaccharide), sometimes doesn’t get broken down in time and gets passed to the lower intestine where bacte ...
... What causes gas when you eat beans, cabbage and brussel sprouts? When you eat sugar it has to be broken down into monsaccharides to get into the bloodstream. Raffinose, which is more complex (trisaccharide), sometimes doesn’t get broken down in time and gets passed to the lower intestine where bacte ...
Lactose-Lactase Experiment Purpose
... Purpose: This lab will examine the specificity of an enzyme (lactase) to a specific substrate (lactose). Students will observe the actions of the enzyme and how shape is important to enzyme reactions. Introduction Lactose, the sugar found in milk, is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose ...
... Purpose: This lab will examine the specificity of an enzyme (lactase) to a specific substrate (lactose). Students will observe the actions of the enzyme and how shape is important to enzyme reactions. Introduction Lactose, the sugar found in milk, is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose ...
Catalysts and Inhibitors in Real Life 1. How do catalysts lower the
... Aspirin blocks an enzyme called cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2, which is involved with the ring closure and addition of oxygen to arachidonic acid converting to prostaglandins.(compounds involved in swelling) The acetyl group on aspirin is broken off by a reaction with water and then bonded to the ...
... Aspirin blocks an enzyme called cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2, which is involved with the ring closure and addition of oxygen to arachidonic acid converting to prostaglandins.(compounds involved in swelling) The acetyl group on aspirin is broken off by a reaction with water and then bonded to the ...
Chapter 8-3 Homework Questions
... use energy from this sunlight to produce energy-rich compounds, like ATP. The lightindependent reactions use these energy-rich compounds to produce sugars from carbon dioxide. Complete the T-chart. Write the phrases in the box that belong in each side of the chart. Use energy from the sun ...
... use energy from this sunlight to produce energy-rich compounds, like ATP. The lightindependent reactions use these energy-rich compounds to produce sugars from carbon dioxide. Complete the T-chart. Write the phrases in the box that belong in each side of the chart. Use energy from the sun ...
Response Coefficients
... where X is the pathway boundary species. Let us increase the activity of v1 by increasing the concentration of E1 . This will cause the steady state flux and concentration of S and in fact all downstream species to increase. Let us now decrease the concentration of X such that we restore the flux an ...
... where X is the pathway boundary species. Let us increase the activity of v1 by increasing the concentration of E1 . This will cause the steady state flux and concentration of S and in fact all downstream species to increase. Let us now decrease the concentration of X such that we restore the flux an ...
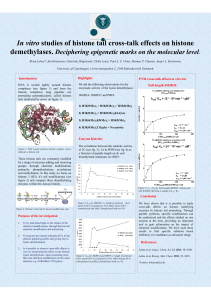
In vitro studies of histone tail cross
... We have shown that it is possible to study cross-talk effects on histone modifying enzymes by histone tail mimicking. Through peptide synthesis, specific combinations can be synthesized and the effects studied on one enzyme at the time, providing an important tool to gain information on the impact o ...
... We have shown that it is possible to study cross-talk effects on histone modifying enzymes by histone tail mimicking. Through peptide synthesis, specific combinations can be synthesized and the effects studied on one enzyme at the time, providing an important tool to gain information on the impact o ...
Enzyme Regulation Strategies
... b. Imagine flipping the tower helices together to show how this structure would interact c. Yellow – glycogen binding site d. Allosteric site and PLP binding site are also shown e. When looking at the picture, remember the other subunit will be on top of this with the helices connected f. Point book ...
... b. Imagine flipping the tower helices together to show how this structure would interact c. Yellow – glycogen binding site d. Allosteric site and PLP binding site are also shown e. When looking at the picture, remember the other subunit will be on top of this with the helices connected f. Point book ...
Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
... D. number of protons plus the number of neutrons Chapter 3 – Water and Life This chapter is a review and extension of information you should have learned in Biology – we will be going through this chapter very quickly. If you have any problems – please see me before school for additional help. Conce ...
... D. number of protons plus the number of neutrons Chapter 3 – Water and Life This chapter is a review and extension of information you should have learned in Biology – we will be going through this chapter very quickly. If you have any problems – please see me before school for additional help. Conce ...
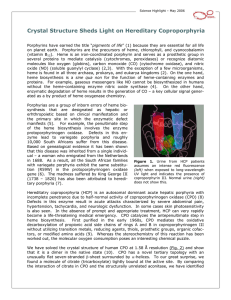
Crystal Structure Sheds Light on Hereditary Coproporphyria
... We have solved the crystal structure of human CPO at 1.58 Å resolution (Fig. 2) and show that it is a dimer in the native state (10). CPO has a novel tertiary topology with an unusually flat seven-stranded β-sheet surrounded by α-helices. To our great surprise, we found a molecule of citrate (tricar ...
... We have solved the crystal structure of human CPO at 1.58 Å resolution (Fig. 2) and show that it is a dimer in the native state (10). CPO has a novel tertiary topology with an unusually flat seven-stranded β-sheet surrounded by α-helices. To our great surprise, we found a molecule of citrate (tricar ...
enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins into tailored peptides and
... disadvantages of batch reaction such as inefficient use of enzymes, inconsistent products due to batch-to-batch variation, substrate–product inhibition, low productivity and excessive hydrolysis leading to bitter peptides and amino acids instead of peptides. In addition, immobilization of these pept ...
... disadvantages of batch reaction such as inefficient use of enzymes, inconsistent products due to batch-to-batch variation, substrate–product inhibition, low productivity and excessive hydrolysis leading to bitter peptides and amino acids instead of peptides. In addition, immobilization of these pept ...
Catalytic Wheel, Brownian Motor, and Biological Energy Transduction
... Folding of newly synthesized peptide(s) into an active, native form of a protein encompasses broad ranges of structural dynamics. The model is proposed to explain the folding of staphylococcal nuclease (SNase) by T. Y. Tsong and colleagues (to be published). The protein in its active form assumes th ...
... Folding of newly synthesized peptide(s) into an active, native form of a protein encompasses broad ranges of structural dynamics. The model is proposed to explain the folding of staphylococcal nuclease (SNase) by T. Y. Tsong and colleagues (to be published). The protein in its active form assumes th ...
Results and Discussion
... liquid system, in order for substrate and enzyme to react, both have to get rid of their solvation shells, and new interactions have to form around the transition state. However in the present work, the use of thermodynamic activities (instead of concentrations) is a method that has been proposed fo ...
... liquid system, in order for substrate and enzyme to react, both have to get rid of their solvation shells, and new interactions have to form around the transition state. However in the present work, the use of thermodynamic activities (instead of concentrations) is a method that has been proposed fo ...
From the Department of Biology, University of
... (No. 251) assays on tela subcutanea reveal the preponderance of the nonspecific enzyme. The activity of residue (tissue remaining after the removal of tela subcutanea) is low and variable at both concentrations; in some cases a negative value is found. This is interpreted as representing esterificat ...
... (No. 251) assays on tela subcutanea reveal the preponderance of the nonspecific enzyme. The activity of residue (tissue remaining after the removal of tela subcutanea) is low and variable at both concentrations; in some cases a negative value is found. This is interpreted as representing esterificat ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.