c - Greer Middle College
... Observed - photoelectric effect Concluded - light has properties of both waves and particles “wave-particle duality” Photon - particle of light that carries a quantum of energy The energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency. E: energy (J, joules) h: Planck’s constant (6.6262 1 ...
... Observed - photoelectric effect Concluded - light has properties of both waves and particles “wave-particle duality” Photon - particle of light that carries a quantum of energy The energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency. E: energy (J, joules) h: Planck’s constant (6.6262 1 ...
Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
... Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? ...
... Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? ...
Dec. 5 - The atom
... match with our intuition about the real world, but it explained all the behaviors of atoms! ...
... match with our intuition about the real world, but it explained all the behaviors of atoms! ...
Problem Set 11: Chemistry Graduate Quantum I Physics 6572
... ‘condensation energy’ aV A, where A = N + Z is the number of nucleons, and a surface tension energy aS A2/3 . (If the nucleus is a liquid of nucleons of roughly constant density, then its radius R ∼ A1/3 and hence the surface area ∼ R2 ∼ V 2/3 .) Packing Z protons into the nucleus costs a Coulomb en ...
... ‘condensation energy’ aV A, where A = N + Z is the number of nucleons, and a surface tension energy aS A2/3 . (If the nucleus is a liquid of nucleons of roughly constant density, then its radius R ∼ A1/3 and hence the surface area ∼ R2 ∼ V 2/3 .) Packing Z protons into the nucleus costs a Coulomb en ...
The Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciencies
... recording changes in electron density of the molecule, and thus for monitoring changes of its shape. The images obtained with this technique allowed to determine current positions of both protons. Therefore the researchers were able to observe the movement of atoms inside the molecule in the course ...
... recording changes in electron density of the molecule, and thus for monitoring changes of its shape. The images obtained with this technique allowed to determine current positions of both protons. Therefore the researchers were able to observe the movement of atoms inside the molecule in the course ...
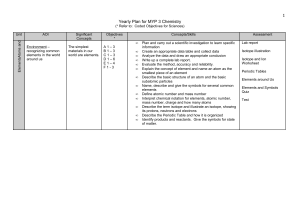
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... Create an appropriate data table and collect data Analyze the data and draw an appropriate conclusion Write up a complete lab report. Evaluate the method, accuracy and reliability. Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an ...
... Create an appropriate data table and collect data Analyze the data and draw an appropriate conclusion Write up a complete lab report. Evaluate the method, accuracy and reliability. Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2013 - Chapter 7 Homework 7 (Chapter 7: Periodic
... E) Ne-, Kr+ 10) __________ have the lowest first ionization energies of the groups listed. A) Alkali metals B) Noble gases C) Transition elements D) Halogens E) Alkaline earth metals ...
... E) Ne-, Kr+ 10) __________ have the lowest first ionization energies of the groups listed. A) Alkali metals B) Noble gases C) Transition elements D) Halogens E) Alkaline earth metals ...
3 molecules
... Molar Mass - the mass in grams of one mole of any element • Molar mass of sodium (Na) = mass of 1 mol of Na atoms = 22.99 g/mol = mass of 6.022 X 1023 Na atoms • Molar mass of lead (Pb) = mass of 1 mol of Pb atoms = 207.2 g/mol = mass of 6.022 X 1023 Pb atoms ...
... Molar Mass - the mass in grams of one mole of any element • Molar mass of sodium (Na) = mass of 1 mol of Na atoms = 22.99 g/mol = mass of 6.022 X 1023 Na atoms • Molar mass of lead (Pb) = mass of 1 mol of Pb atoms = 207.2 g/mol = mass of 6.022 X 1023 Pb atoms ...
primes - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... that the British chemist Henry Cavendish discovered that water is made of hydrogen and oxygen. Cavendish was very shy. He did not even complete his college degree. Luckily he came from a rich family and he could build a chemistry lab at home. At that time neither hydrogen nor oxygen were recognized ...
... that the British chemist Henry Cavendish discovered that water is made of hydrogen and oxygen. Cavendish was very shy. He did not even complete his college degree. Luckily he came from a rich family and he could build a chemistry lab at home. At that time neither hydrogen nor oxygen were recognized ...
Where are the electrons
... Dual wave-particle nature of light • Einstein expanded on Planck’s theory and said that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave-particle nature. • While light exhibits wave like properties, it can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle carries a quantum of energy – these par ...
... Dual wave-particle nature of light • Einstein expanded on Planck’s theory and said that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave-particle nature. • While light exhibits wave like properties, it can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle carries a quantum of energy – these par ...
Quantum Mechanics
... 4. A particle moves in one dimension and in a potential of the form V (x) = 0, for |x| < a and V (x) = V0 > 0 for |x| > a. The particle has energy 0 < E < V0 . a. Solve the Schrödinger equation in each of the three regions: I: −∞ < x < −a, II: −a < x < +a and III: +a < x < +∞. b. Specify the contin ...
... 4. A particle moves in one dimension and in a potential of the form V (x) = 0, for |x| < a and V (x) = V0 > 0 for |x| > a. The particle has energy 0 < E < V0 . a. Solve the Schrödinger equation in each of the three regions: I: −∞ < x < −a, II: −a < x < +a and III: +a < x < +∞. b. Specify the contin ...
Phys 197 Homework Solution 41A Q3.
... 2s, 2p, 3s, and 3p are filled. If all electrons were are stripped away and one given back, it would find the 3d to be lower in energy that the 4s. The presence of the lower electrons modifies this relationship. Q16. ...
... 2s, 2p, 3s, and 3p are filled. If all electrons were are stripped away and one given back, it would find the 3d to be lower in energy that the 4s. The presence of the lower electrons modifies this relationship. Q16. ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... The Quantum Model of the Atom Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
... The Quantum Model of the Atom Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A
... energetically preferred orientation has the magnetic moment aligned parallel with the applied field (spin +1/2) and is often given the notation , whereas the higher energy anti-parallel orientation (spin -1/2) is referred to as . The rotational axis of the spinning nucleus cannot be orientated exact ...
... energetically preferred orientation has the magnetic moment aligned parallel with the applied field (spin +1/2) and is often given the notation , whereas the higher energy anti-parallel orientation (spin -1/2) is referred to as . The rotational axis of the spinning nucleus cannot be orientated exact ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.