Per 5 - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... 30. 0.490 g of tin (Sn) combines with 0.132 g of oxygen to form tin oxide. Calculate the simplest formula of the compound. ...
... 30. 0.490 g of tin (Sn) combines with 0.132 g of oxygen to form tin oxide. Calculate the simplest formula of the compound. ...
Per 3 - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... 30. 0.490 g of tin (Sn) combines with 0.132 g of oxygen to form tin oxide. Calculate the simplest formula of the compound. ...
... 30. 0.490 g of tin (Sn) combines with 0.132 g of oxygen to form tin oxide. Calculate the simplest formula of the compound. ...
Questions - SMK Raja Perempuan Ipoh
... 2. The molar volume of any gas is 24 dm3 at room conditions and 22.4 dm3 at standard temperature and pressure (STP) 3. generalization : One mole of any gas always occupies the same volume under the same temperature and pressure; Example i) 1 mol of oxygen gas, 1 mol of ammonia gas, 1 mol helium gas ...
... 2. The molar volume of any gas is 24 dm3 at room conditions and 22.4 dm3 at standard temperature and pressure (STP) 3. generalization : One mole of any gas always occupies the same volume under the same temperature and pressure; Example i) 1 mol of oxygen gas, 1 mol of ammonia gas, 1 mol helium gas ...
Lecture 8 - Pauli exclusion principle, particle in a box, Heisenberg
... Bosons and fermions II We classify particles into two types: bosons and fermions. Bosons: particles such as photons and mesons, these have integer spin and use the plus sign. Fermions: particles such as electrons and protons, these have half-integer spin and take the minus sign. Suppose we have two ...
... Bosons and fermions II We classify particles into two types: bosons and fermions. Bosons: particles such as photons and mesons, these have integer spin and use the plus sign. Fermions: particles such as electrons and protons, these have half-integer spin and take the minus sign. Suppose we have two ...
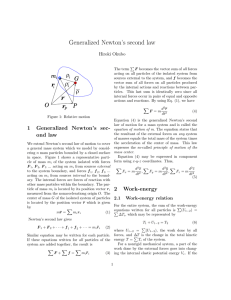
27. Generalized Newton`s second law
... law of motion for a mass system and is called the 1 Generalized Newton’s sec- equation of motion of m. The equation states that the resultant of the external forces on any system ond law of masses equals the total mass of the system times We extend Newton’s second law of motion to cover the accelera ...
... law of motion for a mass system and is called the 1 Generalized Newton’s sec- equation of motion of m. The equation states that the resultant of the external forces on any system ond law of masses equals the total mass of the system times We extend Newton’s second law of motion to cover the accelera ...
Chapter 6:Electronic Structure of Atoms
... crystal, they were diffracted by the crystal, just as x-rays are diffracted. Thus, a stream of electrons exhibits the same kinds of wave behavior as electromagnetic radiation and has both particle and wavelike characteristics. • The technique of electron diffraction has been highly developed to prod ...
... crystal, they were diffracted by the crystal, just as x-rays are diffracted. Thus, a stream of electrons exhibits the same kinds of wave behavior as electromagnetic radiation and has both particle and wavelike characteristics. • The technique of electron diffraction has been highly developed to prod ...
Chem 1151
... Many emission lines were observed when the hydrogen atom was excited. Which equation corresponds to the process in which n = 1 = quantum number of the initial state and m = ∞ = quantum number of the final state? equation **A H H+ + eB H+ + e- H C H (1s1) H(3s1) D H+ H2+ + eWhen you go from l ...
... Many emission lines were observed when the hydrogen atom was excited. Which equation corresponds to the process in which n = 1 = quantum number of the initial state and m = ∞ = quantum number of the final state? equation **A H H+ + eB H+ + e- H C H (1s1) H(3s1) D H+ H2+ + eWhen you go from l ...
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Outline I. Molar Mass and
... 26. How many moles of CuO can be produced from 0.450 mol of Cu2O in the following reaction? 2 Cu2O (s) + O2 (g) Æ 4 CuO (s) a. 1.80 mol b. 0.225 mol c. 0.900 mol d. 0.450 mol 27. 10 g of nitrogen is reacted with 5.0 g of hydrogen to produce ammonia according to the chemical equation shown below. Whi ...
... 26. How many moles of CuO can be produced from 0.450 mol of Cu2O in the following reaction? 2 Cu2O (s) + O2 (g) Æ 4 CuO (s) a. 1.80 mol b. 0.225 mol c. 0.900 mol d. 0.450 mol 27. 10 g of nitrogen is reacted with 5.0 g of hydrogen to produce ammonia according to the chemical equation shown below. Whi ...
Chemistry Ch 4
... between light and matter that were not explained with the wave theory Their research led them to discover the dual wave particle nature. How electromagnetic radiation behaves as waves and as particles. ...
... between light and matter that were not explained with the wave theory Their research led them to discover the dual wave particle nature. How electromagnetic radiation behaves as waves and as particles. ...
Study Island Copyright © 2012 Study Island
... 5. How many elements are found in the following chemical equation? K + Cl → KCl A. 1 B. 2 C. 0 D. 3 ...
... 5. How many elements are found in the following chemical equation? K + Cl → KCl A. 1 B. 2 C. 0 D. 3 ...
From Last Time… - High Energy Physics
... Molecular Symmetries • These symmetries can determine many physical properties. • Can be related to microscopic quantum mechanical properties such as the wavefunction and the probability. • These are easiest to see if we start with a very simple molecule – Two protons and one electron. ...
... Molecular Symmetries • These symmetries can determine many physical properties. • Can be related to microscopic quantum mechanical properties such as the wavefunction and the probability. • These are easiest to see if we start with a very simple molecule – Two protons and one electron. ...
Document
... A photon of energy E0 strikes a free electron, with the scattered photon of energy E moving in the direction opposite that of the incident photon. In this Compton effect interaction, the resulting kinetic energy of the electron is (a) E0 , (b) E , (c) E0 E , (d) E0 + E , (e) none of the ...
... A photon of energy E0 strikes a free electron, with the scattered photon of energy E moving in the direction opposite that of the incident photon. In this Compton effect interaction, the resulting kinetic energy of the electron is (a) E0 , (b) E , (c) E0 E , (d) E0 + E , (e) none of the ...
May 2006
... To compensate for the fact that the period of a simple pendulum depends on the amplitude of oscillation, the 17th century Dutch physicist Christian Huygens devised the following setup, depicted in the figure below. It shows a simple pendulum consisting of a mass m and a string of length `0 whose mot ...
... To compensate for the fact that the period of a simple pendulum depends on the amplitude of oscillation, the 17th century Dutch physicist Christian Huygens devised the following setup, depicted in the figure below. It shows a simple pendulum consisting of a mass m and a string of length `0 whose mot ...
MSE 221 Quantum Physics of Materials
... Elementary quantum concepts, wave mechanics, energy states, bonding, transitions, electronic properties Prerequisite: PHYS 151 14 weeks, lectures (3 times a week), recitation (once a week) Introduction Old Quantum Theory, Bohr model, De Broglie, duality Interference and Diffraction—Young’s experimen ...
... Elementary quantum concepts, wave mechanics, energy states, bonding, transitions, electronic properties Prerequisite: PHYS 151 14 weeks, lectures (3 times a week), recitation (once a week) Introduction Old Quantum Theory, Bohr model, De Broglie, duality Interference and Diffraction—Young’s experimen ...
ICP Final Study Guide for 2013 Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... 4. State of matter where the particles are in a rigid, fixed structure. a. b. ...
... 4. State of matter where the particles are in a rigid, fixed structure. a. b. ...
Solid State Electronic Devices
... Electron eventually “crashes” into nucleus. In 1913, Bohr proposed quantized model of the H atom to predict the observed spectrum. ...
... Electron eventually “crashes” into nucleus. In 1913, Bohr proposed quantized model of the H atom to predict the observed spectrum. ...
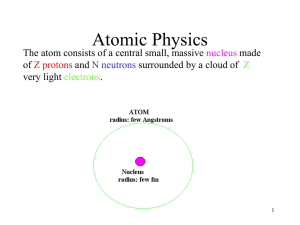
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.