"Particles or waves"()
... if the photon fills a large volume; yet when it is detected, it is found at particular point. This is one consequence of Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle – a law that affects absolutely everything in the sub-microscopic world. Quantum effects are not just confined to photons – electrons, protons a ...
... if the photon fills a large volume; yet when it is detected, it is found at particular point. This is one consequence of Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle – a law that affects absolutely everything in the sub-microscopic world. Quantum effects are not just confined to photons – electrons, protons a ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures.
... • Pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. – Pure substance- a substance in which there is only one type of particle (atom or molecule) ...
... • Pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. – Pure substance- a substance in which there is only one type of particle (atom or molecule) ...
1 - PLK Vicwood KT Chong Sixth Form College
... the excited atom returns to the ground state directly (or through an intermediate energy level). Thus a number of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation may be produced, which give rise to the emission line spectrum of hydrogen. (c) For photoelectric effect, electrons are emitted from metal surfac ...
... the excited atom returns to the ground state directly (or through an intermediate energy level). Thus a number of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation may be produced, which give rise to the emission line spectrum of hydrogen. (c) For photoelectric effect, electrons are emitted from metal surfac ...
Erwin Schroedinger, Max Born and Wave Mechanics
... Studied physics under Max Born and soon became his assistant Most famous for his discovery of The uncertainty principle which says that you cannot measure the position (x) and the momentum (p) of a particle with precision, the more accurate one of your values is, the less accurate the other will be ...
... Studied physics under Max Born and soon became his assistant Most famous for his discovery of The uncertainty principle which says that you cannot measure the position (x) and the momentum (p) of a particle with precision, the more accurate one of your values is, the less accurate the other will be ...
Section 1 - Tutor
... Section 30.5 The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Hydrogen Atom 26. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom? (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The groun ...
... Section 30.5 The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Hydrogen Atom 26. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom? (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The groun ...
Wave
... – The energy of a wave takes discrete values (quanta), because a wave consists of discrete particles. – For example, a laser beam consists of many photons, each carrying the same photon energy. ...
... – The energy of a wave takes discrete values (quanta), because a wave consists of discrete particles. – For example, a laser beam consists of many photons, each carrying the same photon energy. ...
compound - Coal City Unit #1
... • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
... • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
Solutions to the exam itself are now available.
... (f) The Cr4+ ion in the compound CrO2 is exploited in magnetic audio and video recording tape. The electron configuration of Cr4+ is [Ar] 3d2. The question here is simple: which four electrons does Cr with the [Ar] 4s1 3d5 configuration lose? There are two obvious possibilities for Cr4+ that make se ...
... (f) The Cr4+ ion in the compound CrO2 is exploited in magnetic audio and video recording tape. The electron configuration of Cr4+ is [Ar] 3d2. The question here is simple: which four electrons does Cr with the [Ar] 4s1 3d5 configuration lose? There are two obvious possibilities for Cr4+ that make se ...
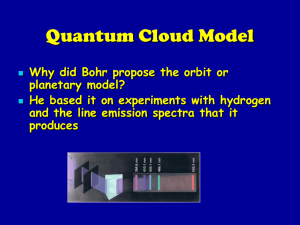
Quantum Cloud Model
... state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its specific wavelength and frequency ...
... state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its specific wavelength and frequency ...
Chapter 5 reveiw
... c. electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies _______________________ d. type of electromagnetic radiation which has the wavelength of 10 m_________ e. Speed of all types of electromagnetic radiation in a vacuum: i. In meters_________________________ ii. In nanometers ___________________ 23. ...
... c. electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies _______________________ d. type of electromagnetic radiation which has the wavelength of 10 m_________ e. Speed of all types of electromagnetic radiation in a vacuum: i. In meters_________________________ ii. In nanometers ___________________ 23. ...
1. Atomic Structure
... The orbital with the lowest (n + l) value is filled first. When two or more orbitals have the same (n + l) value, the one with the lowest ‘n’ value is preferred in filling. Consider two orbitals 3d and 4s. The n + l value of 3d = 3 + 2 = 5 and of 4s = 4 + 0 = 4. Since 4s has lowest (n + l) value, it ...
... The orbital with the lowest (n + l) value is filled first. When two or more orbitals have the same (n + l) value, the one with the lowest ‘n’ value is preferred in filling. Consider two orbitals 3d and 4s. The n + l value of 3d = 3 + 2 = 5 and of 4s = 4 + 0 = 4. Since 4s has lowest (n + l) value, it ...
Electrons in Atoms
... Much of what is known about the atom is due to the study of light Light has properties of waves Waves have amplitude, wavelength, and ...
... Much of what is known about the atom is due to the study of light Light has properties of waves Waves have amplitude, wavelength, and ...
Document
... Quantum field theory describes the quantum mechanics of fields, such as the electromagnetic field and the electron field. In this setup, particles and waves, both are different faces of the same type of object: the quantum field. Feynman’s pictorial representation of possibilities in the bubble of i ...
... Quantum field theory describes the quantum mechanics of fields, such as the electromagnetic field and the electron field. In this setup, particles and waves, both are different faces of the same type of object: the quantum field. Feynman’s pictorial representation of possibilities in the bubble of i ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry - Home 15-16
... 28. Electronegativity increases as you go up and to the right on the Periodic Table. Which element among the diagrams below has the greatest electronegativity? 29. The elements in Group 1 are the alkali metals; those in Group 2 are the alkaline earth metals. Get more reactive and softer as you go do ...
... 28. Electronegativity increases as you go up and to the right on the Periodic Table. Which element among the diagrams below has the greatest electronegativity? 29. The elements in Group 1 are the alkali metals; those in Group 2 are the alkaline earth metals. Get more reactive and softer as you go do ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.