There can be only one
... light field. This simple picture, however, breaks down when the excited atoms interact with each other. The excitation of one atom then shifts other atoms out of resonance — this is because the interaction energy has to be added to, or subtracted from, the excitation energy for attractive and repuls ...
... light field. This simple picture, however, breaks down when the excited atoms interact with each other. The excitation of one atom then shifts other atoms out of resonance — this is because the interaction energy has to be added to, or subtracted from, the excitation energy for attractive and repuls ...
Document
... CONDUCTORS: materials that have freely moving electrons that respond to an electric field. INSULATORS: materials that have fixed, immobile electrons that are not easy to move. ...
... CONDUCTORS: materials that have freely moving electrons that respond to an electric field. INSULATORS: materials that have fixed, immobile electrons that are not easy to move. ...
C4C5C6
... Middle element has the atomic mass which is the mean of the total atomic mass of the triad Newlands every 8th element had similar properties so he organised them into groups of 7 called “octaves”. His work was not accepted because: 1) Not all elements had similar properties. 2) mixed up metals / non ...
... Middle element has the atomic mass which is the mean of the total atomic mass of the triad Newlands every 8th element had similar properties so he organised them into groups of 7 called “octaves”. His work was not accepted because: 1) Not all elements had similar properties. 2) mixed up metals / non ...
electric force - University of Toronto Physics
... atom or molecule is said to be electrically polarized. • An electron buzzing around the atomic nucleus produces an electron cloud. a. The center of the negative cloud normally coincides with the center of the positive nucleus in an atom. b. When an external negative charge is brought nearby to the r ...
... atom or molecule is said to be electrically polarized. • An electron buzzing around the atomic nucleus produces an electron cloud. a. The center of the negative cloud normally coincides with the center of the positive nucleus in an atom. b. When an external negative charge is brought nearby to the r ...
+l.
... 3-The Bohr Model of the Atom Bohr proposed that the possible energy states for atomic electrons were quantized – only certain values were possible. Then the spectrum could be explained as transitions from one level to another. ...
... 3-The Bohr Model of the Atom Bohr proposed that the possible energy states for atomic electrons were quantized – only certain values were possible. Then the spectrum could be explained as transitions from one level to another. ...
Lab: Millikan`s Oil Drop Experiment and Elements of the Periodic Table
... A set of capped film containers, each containing various numbers of metal nuts. A mass balance (accurate to the tenths place). ...
... A set of capped film containers, each containing various numbers of metal nuts. A mass balance (accurate to the tenths place). ...
SOL_Study_Book_4.3_Electricty
... Materials with a greater resistance will not allow energy to flow quickly. In materials with low resistance, energy flows easily. Insulators are materials that do NOT allow electric current to pass easily. Some examples of insulators are rubber, plastic, and wood. ...
... Materials with a greater resistance will not allow energy to flow quickly. In materials with low resistance, energy flows easily. Insulators are materials that do NOT allow electric current to pass easily. Some examples of insulators are rubber, plastic, and wood. ...
Chapter 25: Electric Potential Energy
... Energy concepts allow us to consider the behavior of charges in an electric field. ...
... Energy concepts allow us to consider the behavior of charges in an electric field. ...
Topics on Chapter 10 Test: The Mole
... Converting one metric unit to another metric unit (keeping in mind significant figures - example: 350.0 mL to L) ...
... Converting one metric unit to another metric unit (keeping in mind significant figures - example: 350.0 mL to L) ...
Electric Fields And Forces
... ⇒ We do not know what charge is, we only know that there are two types of charge. ⇒ The two types of charge were called positive (+) and negative (-) by Benjamin Franklin in 1747. ...
... ⇒ We do not know what charge is, we only know that there are two types of charge. ⇒ The two types of charge were called positive (+) and negative (-) by Benjamin Franklin in 1747. ...
5. The Hydrogenoid Atom
... atom, but this time it was derived rigorously from Quantum Mechanics. The quantization once again results from imposing boundary conditions on the wavefunction. ...
... atom, but this time it was derived rigorously from Quantum Mechanics. The quantization once again results from imposing boundary conditions on the wavefunction. ...
Chapter 7
... 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 ...
... 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 ...
Atomic Physics
... States with same n, have same energy and can have " = 0,1,2,...,n-1 orbital quantum number " =0 orbits are most elliptical " =n-1 most circular The z component of the angular momentum must also be quantized ...
... States with same n, have same energy and can have " = 0,1,2,...,n-1 orbital quantum number " =0 orbits are most elliptical " =n-1 most circular The z component of the angular momentum must also be quantized ...
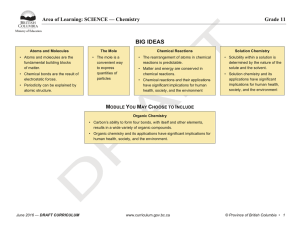
BIG IDEAS - BC Curriculum - Province of British Columbia
... • Demonstrate an awareness of assumptions, question information given, and identify bias in their own work and in primary and secondary sources • Consider the changes in knowledge over time as tools and technologies have developed • Connect scientific explorations to careers in science • Exercise a ...
... • Demonstrate an awareness of assumptions, question information given, and identify bias in their own work and in primary and secondary sources • Consider the changes in knowledge over time as tools and technologies have developed • Connect scientific explorations to careers in science • Exercise a ...
semester two final review key units 5 and 6 only
... Mole: The amount of elementary particles that are in exactly 12 g of Carbon. A mole is Avogadro’s number of particles; 1Mole = 6.02 × 1023 particles = gram formula mass of an element/compound Avogadro’s Number: 6.02 × 1023 particles of any substance Molar Mass: The total mass (in g/M) of all substan ...
... Mole: The amount of elementary particles that are in exactly 12 g of Carbon. A mole is Avogadro’s number of particles; 1Mole = 6.02 × 1023 particles = gram formula mass of an element/compound Avogadro’s Number: 6.02 × 1023 particles of any substance Molar Mass: The total mass (in g/M) of all substan ...
UNIT NUM="1" ID="UN
... The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in the atom’s electron shells. Beginning with hydrogen, the simplest atom, we can imagine building the atoms of the other elements by adding 1 proton and 1 electron at a time (along with an appropriate number of neutrons ...
... The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in the atom’s electron shells. Beginning with hydrogen, the simplest atom, we can imagine building the atoms of the other elements by adding 1 proton and 1 electron at a time (along with an appropriate number of neutrons ...
Introduction to Nanoscience
... The Wave-Particle duality of light and matter A central concept in quantum physics is the particle-wave duality, the fact that fundamental objects in the physical world, electrons, protons, neutrons, photons and others, all have the same dual nature: they are at the same time both particles and wav ...
... The Wave-Particle duality of light and matter A central concept in quantum physics is the particle-wave duality, the fact that fundamental objects in the physical world, electrons, protons, neutrons, photons and others, all have the same dual nature: they are at the same time both particles and wav ...
relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and
... In quantum electrodynamics, so-called "radiative corrections" to the Dirac theory are obtained by taking into account interactions of electrons with the quantized electromagnetic field. In QED, a quantized radiation field in the lowest-energy state of NOT the one with ZERO electromagnetic fields, bu ...
... In quantum electrodynamics, so-called "radiative corrections" to the Dirac theory are obtained by taking into account interactions of electrons with the quantized electromagnetic field. In QED, a quantized radiation field in the lowest-energy state of NOT the one with ZERO electromagnetic fields, bu ...
39 Questionable Assumptions in Modern Physics
... • Matter cannot act “where it is not” • Definition of ‘contact’. – A. Billiard ball interaction OR – B. Field (energy) interaction ...
... • Matter cannot act “where it is not” • Definition of ‘contact’. – A. Billiard ball interaction OR – B. Field (energy) interaction ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Lattice: a repeating pattern, like a lattice-work fence. In solids, it is a repeating pattern of atoms. All solids are made up of a lattice. The points of the lattice are different in different types of solids. ...
... Lattice: a repeating pattern, like a lattice-work fence. In solids, it is a repeating pattern of atoms. All solids are made up of a lattice. The points of the lattice are different in different types of solids. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.