Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges
... A circuit is pulled with a 16-N force toward the right to maintain a constant speed v. At the instant shown, the loop is partially in and partially out of a uniform magnetic field that is directed into the paper. As the circuit moves, a 6.0-A current flows through a 4.0-? resistor. ...
... A circuit is pulled with a 16-N force toward the right to maintain a constant speed v. At the instant shown, the loop is partially in and partially out of a uniform magnetic field that is directed into the paper. As the circuit moves, a 6.0-A current flows through a 4.0-? resistor. ...
Microsoft Word document - Solar Radiation Monitoring Laboratory
... Pure single crystal silicon is a very poor conductor because all the valence electrons are bonded with their neighbors. To collect the photocurrent, solar cells are constructed like a battery. This is done by taking two semiconductors of opposite charge and putting them together. To make solar cell ...
... Pure single crystal silicon is a very poor conductor because all the valence electrons are bonded with their neighbors. To collect the photocurrent, solar cells are constructed like a battery. This is done by taking two semiconductors of opposite charge and putting them together. To make solar cell ...
Physical Science Final Exam
... Gasses” are special because They are the only elements on the periodic table that are always gasses They have more protons than electrons making them stable They have numbers of electrons that fill their orbitals They have properties of both metals and non-metals ...
... Gasses” are special because They are the only elements on the periodic table that are always gasses They have more protons than electrons making them stable They have numbers of electrons that fill their orbitals They have properties of both metals and non-metals ...
energy levels
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time. • This limitation is critical when dealing with small particles such as electrons. • But it does not matter for ordinary-s ...
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time. • This limitation is critical when dealing with small particles such as electrons. • But it does not matter for ordinary-s ...
File
... Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, usually bend without breaking (malleable) and are ductile. Most have extremely high melting points. Reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals. With metals the greater the tendency to lose electrons, the more reac ...
... Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, usually bend without breaking (malleable) and are ductile. Most have extremely high melting points. Reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals. With metals the greater the tendency to lose electrons, the more reac ...
A Historical Perspective on Quantum Physics and its Impact on Society
... Wien’s had justified his law using arguments of an unsatisfactory nature; hence a more rigorous derivation was needed. The German physicist Ludwig Planck, who was Kirchhoff successor at the time as professor of physics at the University of Berlin, was the first to provide a derivation of Wien’s law ...
... Wien’s had justified his law using arguments of an unsatisfactory nature; hence a more rigorous derivation was needed. The German physicist Ludwig Planck, who was Kirchhoff successor at the time as professor of physics at the University of Berlin, was the first to provide a derivation of Wien’s law ...
General Chemistry
... •O has a mass of 16 amu – but we can’t weigh out anything in amu •If we want to keep the number “16” for the mass of oxygen in some real units (like grams) then we are dealing with a whole bunch of atoms (in 16 g of oxygen). •That bunch of atoms is called a mole. ...
... •O has a mass of 16 amu – but we can’t weigh out anything in amu •If we want to keep the number “16” for the mass of oxygen in some real units (like grams) then we are dealing with a whole bunch of atoms (in 16 g of oxygen). •That bunch of atoms is called a mole. ...
General Chemistry
... •O has a mass of 16 amu – but we can’t weigh out anything in amu •If we want to keep the number “16” for the mass of oxygen in some real units (like grams) then we are dealing with a whole bunch of atoms (in 16 g of oxygen). •That bunch of atoms is called a mole. ...
... •O has a mass of 16 amu – but we can’t weigh out anything in amu •If we want to keep the number “16” for the mass of oxygen in some real units (like grams) then we are dealing with a whole bunch of atoms (in 16 g of oxygen). •That bunch of atoms is called a mole. ...
Example Midterm Solutions
... The proper frame for the lifetime of the Mamahuhu particle is in the Mamahuhu’s frame. This is because we would measure the “birth” and decay (into something else) of the particle as events that happen at the same spot in that frame. In the Mamahuhu’s frame, the lifetime is 1.8×10−4 s . In a lab fra ...
... The proper frame for the lifetime of the Mamahuhu particle is in the Mamahuhu’s frame. This is because we would measure the “birth” and decay (into something else) of the particle as events that happen at the same spot in that frame. In the Mamahuhu’s frame, the lifetime is 1.8×10−4 s . In a lab fra ...
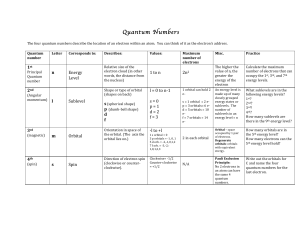
quantum number
... Classically, light was considered a wave phenomena. This was based on experimental observations such as the interference pattern for light observed in the two slit experiment. Interference – The increase or decrease in amplitude that occurs when two waves of the same wavelength are combined together ...
... Classically, light was considered a wave phenomena. This was based on experimental observations such as the interference pattern for light observed in the two slit experiment. Interference – The increase or decrease in amplitude that occurs when two waves of the same wavelength are combined together ...
The Basics - I`m a faculty member, and I need web space. What
... • The mole ratios can be obtained from the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. • What are the mole ratios in this problem? • Mole ratios can be used as conversion factors to predict the amount of any reactant or product involved in a reaction if the amount of another reactant and/or prod ...
... • The mole ratios can be obtained from the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. • What are the mole ratios in this problem? • Mole ratios can be used as conversion factors to predict the amount of any reactant or product involved in a reaction if the amount of another reactant and/or prod ...
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
... elements in a group, you can make a good guess at the properties of the other elements in the same group. Periods are the horizontal rows in the periodic table. Many patterns can be seen or predicted following periods and groups. Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams: ...
... elements in a group, you can make a good guess at the properties of the other elements in the same group. Periods are the horizontal rows in the periodic table. Many patterns can be seen or predicted following periods and groups. Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams: ...
Chapter 4
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
Relativity, Inertia, and Equivalence Principle
... attracting a cluster of admirers with each step… ...
... attracting a cluster of admirers with each step… ...
Unit 9 – Behavior of Gases
... a. oxygen atom b. silicon atom 5. a. Calculate the wavelength, in meters, of green light that has a frequency of 5.0x1014 s-1? What is the energy of this light? (h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js) 6. What happens when an electron drops from a higher to a lower energy level? 7. Where do you find the following on ...
... a. oxygen atom b. silicon atom 5. a. Calculate the wavelength, in meters, of green light that has a frequency of 5.0x1014 s-1? What is the energy of this light? (h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js) 6. What happens when an electron drops from a higher to a lower energy level? 7. Where do you find the following on ...
LECTURE 6
... Electronic Con gurations of the Elements and the Periodic Table (Reference: Charles E. Mortimer, Chemistry: A Conceptual Approach, 3rd ed. (1975)) A pretty good way to determine the electronic con gurations of the elements is to imagine adding one electron at a time to the energy levels of an atom. ...
... Electronic Con gurations of the Elements and the Periodic Table (Reference: Charles E. Mortimer, Chemistry: A Conceptual Approach, 3rd ed. (1975)) A pretty good way to determine the electronic con gurations of the elements is to imagine adding one electron at a time to the energy levels of an atom. ...
Practice Exam-1A Fall 2016
... A) Color of carpet faded (by sun light) B) Zinc strip dissolves in vinegar (to produce hydrogen gas) C) Burn a wood block D) Water freezes E) Iron rusts 9. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are there in 79Br- (bromide anion)? Isotopes with number on front top represent mass number. Mass # = ...
... A) Color of carpet faded (by sun light) B) Zinc strip dissolves in vinegar (to produce hydrogen gas) C) Burn a wood block D) Water freezes E) Iron rusts 9. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are there in 79Br- (bromide anion)? Isotopes with number on front top represent mass number. Mass # = ...
Electric Charge
... • In certain cases, conductors can allow charges to move within the conductor without actually gaining an imbalance of positive or negative charge • The nature of conductors is responsible for this ability ...
... • In certain cases, conductors can allow charges to move within the conductor without actually gaining an imbalance of positive or negative charge • The nature of conductors is responsible for this ability ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.