Abstract poster Presentation
... chains using real-time atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopic (dynamical HRTEM) and the ab initio density functional total energy methods. By performing the experiments and theoretical study of LACs at different temperatures (150K and 300K), we have been able to get very precise informa ...
... chains using real-time atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopic (dynamical HRTEM) and the ab initio density functional total energy methods. By performing the experiments and theoretical study of LACs at different temperatures (150K and 300K), we have been able to get very precise informa ...
College Chemistry 1 Note Guide(free download)
... hence the year long course has been split into two separate courses to accommodate those needs. The second semester course is available under the title, College Chemistry II. The videos used for this course were made in the studios at Gulf Coast Community College by Dr. Sandra Etheridge and were des ...
... hence the year long course has been split into two separate courses to accommodate those needs. The second semester course is available under the title, College Chemistry II. The videos used for this course were made in the studios at Gulf Coast Community College by Dr. Sandra Etheridge and were des ...
Model Visualization of Atomic Quantum Numbers Three
... of the angular momentum of the electron to the nucleus. The number of the subshell electrons are dependent on the value of the principal quantum number (n). Azimuthal quantum number value from 0 to (n - 1). When n = 1, then there is only one subshell ie l = 0, while n = 2, then there are two sub-she ...
... of the angular momentum of the electron to the nucleus. The number of the subshell electrons are dependent on the value of the principal quantum number (n). Azimuthal quantum number value from 0 to (n - 1). When n = 1, then there is only one subshell ie l = 0, while n = 2, then there are two sub-she ...
Sample Chem 111 Final
... 1. A metal sample weighing 30.9232 grams was added to a graduated cylinder containing 23.20 mL of water. The volume of the water plus the sample was 24.80 mL. What is the density of the metal? a) 19.3 g/mL b) 19.33 g/mL c) 19.327 g/mL d) 2.0 x 10‚ g/mL e) 19. g/mL 2. About the year 1910 Rutherford a ...
... 1. A metal sample weighing 30.9232 grams was added to a graduated cylinder containing 23.20 mL of water. The volume of the water plus the sample was 24.80 mL. What is the density of the metal? a) 19.3 g/mL b) 19.33 g/mL c) 19.327 g/mL d) 2.0 x 10‚ g/mL e) 19. g/mL 2. About the year 1910 Rutherford a ...
Static Electricity - Kania´s Science Page
... • Recall that fundamental particles carry something called electric charge – protons have exactly one unit of positive charge – electrons have exactly one unit of negative charge ...
... • Recall that fundamental particles carry something called electric charge – protons have exactly one unit of positive charge – electrons have exactly one unit of negative charge ...
Lecture Trends in the Periodic Table - NGHS
... The number of orbitals in a shell is the square of the principal quantum number: 12 = 1, 22 = 4, 32 = 9. There is one orbital in an s subshell (l = 0), three orbitals in a p subshell (l = 1), and five orbitals in a d subshell (l = 2). The number of orbitals in a subshell is therefore 2(l) + 1. Befo ...
... The number of orbitals in a shell is the square of the principal quantum number: 12 = 1, 22 = 4, 32 = 9. There is one orbital in an s subshell (l = 0), three orbitals in a p subshell (l = 1), and five orbitals in a d subshell (l = 2). The number of orbitals in a subshell is therefore 2(l) + 1. Befo ...
Chapter 7 Statistical physics in equilibrium
... In general, for systems with one particle in one dimension, the phase trajectory is a closed curve. For d > 1, closed trajectories happen only if there are more conserved quantities than just energy such as, for instance, the Runge-Lenz vector in the Kepler problem. Most of the examples we will cons ...
... In general, for systems with one particle in one dimension, the phase trajectory is a closed curve. For d > 1, closed trajectories happen only if there are more conserved quantities than just energy such as, for instance, the Runge-Lenz vector in the Kepler problem. Most of the examples we will cons ...
Honors Physics Electrostatics Worksheet #2
... a) Find the electrostatic force between the charges. b) If the charges are brought together and touched, what would be the charge on each one? c) These spheres are then moved 3 cm apart. What would be the force between them? 2. Two equal charges experience a repulsive force between them of 1 x 102 N ...
... a) Find the electrostatic force between the charges. b) If the charges are brought together and touched, what would be the charge on each one? c) These spheres are then moved 3 cm apart. What would be the force between them? 2. Two equal charges experience a repulsive force between them of 1 x 102 N ...
Pressure and mass conservation
... Composition of the atmosphere • Air is a mixture of various gases • Particularly, nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide • We can assume air behaves like an ideal gas ...
... Composition of the atmosphere • Air is a mixture of various gases • Particularly, nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide • We can assume air behaves like an ideal gas ...
Slide 1
... Ketterle (MIT) experiment Cooled some hundred times more atoms (Na23) , and was able to demonstrate quantum mechanical interference between two BEC. ...
... Ketterle (MIT) experiment Cooled some hundred times more atoms (Na23) , and was able to demonstrate quantum mechanical interference between two BEC. ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... g) The first energy level is nearest to the centre and can take a maximum of two electrons. h) The second and third energy levels can take a maximum of eight electrons each. i) The first level is filled with electrons first and then the second and third ones. j) When atoms bond with other atoms, the ...
... g) The first energy level is nearest to the centre and can take a maximum of two electrons. h) The second and third energy levels can take a maximum of eight electrons each. i) The first level is filled with electrons first and then the second and third ones. j) When atoms bond with other atoms, the ...
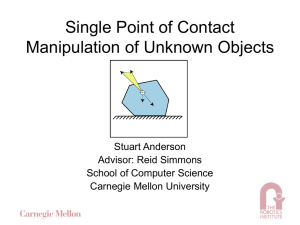
Single Point of Contact Manipulation of Unknown Objects
... Everything else is sort of compliant What if we worked on a rubber mat? ...
... Everything else is sort of compliant What if we worked on a rubber mat? ...
Department of Chemistry - The City College of New York
... chemistry, including atomic and molecular structure, quantum chemistry, chemical bonding, stoichiometry, kinetics and mechanisms, equilibria, thermochemistry and thermodynamics, molecular structure and function, electrochemistry, and the periodic chemical properties of the elements. Apply the fundam ...
... chemistry, including atomic and molecular structure, quantum chemistry, chemical bonding, stoichiometry, kinetics and mechanisms, equilibria, thermochemistry and thermodynamics, molecular structure and function, electrochemistry, and the periodic chemical properties of the elements. Apply the fundam ...
Homework No. 07 (Spring 2015) PHYS 530A: Quantum Mechanics II
... 4. (20 points.) (Schwinger’s QM book, Prob. 3-4a.) Iso(topic) spin T : The nucleon is a particle of isospin T = 21 ; the state with T3 = 21 is the proton (p), the state with T3 = − 12 is the neutron (n). Electric charge of a nucleon is given by Q = 21 + T3 . The π meson, or pion, has isospin T = 1, ...
... 4. (20 points.) (Schwinger’s QM book, Prob. 3-4a.) Iso(topic) spin T : The nucleon is a particle of isospin T = 21 ; the state with T3 = 21 is the proton (p), the state with T3 = − 12 is the neutron (n). Electric charge of a nucleon is given by Q = 21 + T3 . The π meson, or pion, has isospin T = 1, ...
Document
... degeneracy, so that secular determinants of that order must be solved. In addition, while the perturbation splits some of the degenerate levels, the brute force diagonalization of the secular determinant does not give the physical reason for the nature of the splitting. Thus, the n = 2 level of the ...
... degeneracy, so that secular determinants of that order must be solved. In addition, while the perturbation splits some of the degenerate levels, the brute force diagonalization of the secular determinant does not give the physical reason for the nature of the splitting. Thus, the n = 2 level of the ...
Chapter 3 Magnetism of the Electron
... is not relativistically invariant because the operators "/"t and "/"x do not appear to the same power. We need to use a 4-vector X = (ct, x, y, z) with derivatives "/"X. Dirac discovered the relativistic quantum mechanical theory of the electron, which involves the Pauli spin operators# :I, with cou ...
... is not relativistically invariant because the operators "/"t and "/"x do not appear to the same power. We need to use a 4-vector X = (ct, x, y, z) with derivatives "/"X. Dirac discovered the relativistic quantum mechanical theory of the electron, which involves the Pauli spin operators# :I, with cou ...
AP Chemistry - Oak Park Unified School District
... Write the number next to the word that fits the paragraph. Measurement in Chemistry Science knowledge is advanced by observing patterns, (1), and constructing explanations, (2); which are supported by repeatable (3) evidence. Measurements are made using the metric system, where the standard units ar ...
... Write the number next to the word that fits the paragraph. Measurement in Chemistry Science knowledge is advanced by observing patterns, (1), and constructing explanations, (2); which are supported by repeatable (3) evidence. Measurements are made using the metric system, where the standard units ar ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.