Measurement of An Electron's Electric Dipole Moment Using Cesium Atoms Trapped in Optical Lattices.
... better than ⌬ P⫽⌬ / coll⫽3⫻10⫺6 upon static electric field ES reversal, if the atoms were allowed to collide. If individual atoms are isolated at separate sites of a 3D optical lattice, however, these collisional effects can be greatly suppressed. For the configuration described above, only L⫽1/ ...
... better than ⌬ P⫽⌬ / coll⫽3⫻10⫺6 upon static electric field ES reversal, if the atoms were allowed to collide. If individual atoms are isolated at separate sites of a 3D optical lattice, however, these collisional effects can be greatly suppressed. For the configuration described above, only L⫽1/ ...
Probing a scattering resonance in Rydberg molecules with a Bose
... with a detuning in this range are not shifted as much as the theory predicts, leading to an underestimated theory signal between -40 and 0 MHz. There are several simplifications in the model, which could lead to these discrepancies at intermediate detunings. All atoms are treated as point-like parti ...
... with a detuning in this range are not shifted as much as the theory predicts, leading to an underestimated theory signal between -40 and 0 MHz. There are several simplifications in the model, which could lead to these discrepancies at intermediate detunings. All atoms are treated as point-like parti ...
Hall Effect, AC Conductivity and Thermal Conductivity
... very good explanation of DC and AC conductivity in metals, the Hall effect, and thermal conductivity (due to electrons) in metals. The model also explains the Wiedemann-Franz law of 1853. "However, the Drude model greatly overestimates the electronic heat capacities of metals. In reality, metals and ...
... very good explanation of DC and AC conductivity in metals, the Hall effect, and thermal conductivity (due to electrons) in metals. The model also explains the Wiedemann-Franz law of 1853. "However, the Drude model greatly overestimates the electronic heat capacities of metals. In reality, metals and ...
1 Assignment 5 Hydrogen – The Unique Element
... Current research surrounding the chemistry of hydrogen As mentioned earlier in this essay, there is immense interest in hydrogen fuel cells as a source of clean energy. In November 2010, Mitch Jacoby wrote a short report in a chemical newspaper on a nickel complex that could boost hydrogen oxidation ...
... Current research surrounding the chemistry of hydrogen As mentioned earlier in this essay, there is immense interest in hydrogen fuel cells as a source of clean energy. In November 2010, Mitch Jacoby wrote a short report in a chemical newspaper on a nickel complex that could boost hydrogen oxidation ...
Lecture 25 - Black Hole Firewall
... • Eventually, energy of photon emitted would be larger than mass-energy of black hole. – About a Planck mass ...
... • Eventually, energy of photon emitted would be larger than mass-energy of black hole. – About a Planck mass ...
Lecture5
... How much more light gathering power does a 10m telescope have than an 0.5 m telescope? Answer: The light gathering power is proportional to the square of the mirror’s diameter. (10m)2/(0.5m)2 = 100m / 0.25m = 400 So you can see objects about 400 times fainter with the 10m telescope in the same amou ...
... How much more light gathering power does a 10m telescope have than an 0.5 m telescope? Answer: The light gathering power is proportional to the square of the mirror’s diameter. (10m)2/(0.5m)2 = 100m / 0.25m = 400 So you can see objects about 400 times fainter with the 10m telescope in the same amou ...
chem100c1f
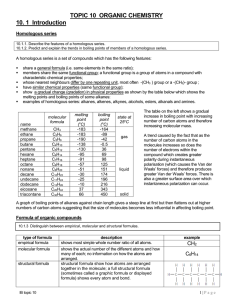
... • A change in the state of matter. It does not involve a change in the substances. E.g. melting of wax and water. • Chemical change: • A change involving at least one of the substances making the matter. E.g. Electrolysis of water, formation of rust: reaction of iron and oxygen to from iron oxide. ...
... • A change in the state of matter. It does not involve a change in the substances. E.g. melting of wax and water. • Chemical change: • A change involving at least one of the substances making the matter. E.g. Electrolysis of water, formation of rust: reaction of iron and oxygen to from iron oxide. ...
A Quantum Mechanical Model for Vibration and Rotation of Molecules
... diatomic molecule (relative motions of atoms). Also – of interest kinetic and potential energy of the diatomic molecule during the oscillatory motion. Not necessarily the energies of individual atoms of the molecule. The ultimate goal is to find the (eigen) energies and the eigen functions (wavefunc ...
... diatomic molecule (relative motions of atoms). Also – of interest kinetic and potential energy of the diatomic molecule during the oscillatory motion. Not necessarily the energies of individual atoms of the molecule. The ultimate goal is to find the (eigen) energies and the eigen functions (wavefunc ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... 1. Determine the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the reaction. 2. Determine which atom is being oxidized and which is being reduced. 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (los ...
... 1. Determine the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the reaction. 2. Determine which atom is being oxidized and which is being reduced. 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (los ...
The Representative Elements: Group 5A Through 8A
... Elements of Group 5A overwhelmingly form covalent compounds. Whereas nitrogen can form a maximum of four covalent bonds, other elements in the group can form more than four covalent bonds by utilizing one or more of the nd orbitals. Nitrogen and phosphorus form simple anion with “-3” charge when rea ...
... Elements of Group 5A overwhelmingly form covalent compounds. Whereas nitrogen can form a maximum of four covalent bonds, other elements in the group can form more than four covalent bonds by utilizing one or more of the nd orbitals. Nitrogen and phosphorus form simple anion with “-3” charge when rea ...
Cloud Chamber - Wabash College
... some of the events (See Figure 4), but we analyzed the formation of the clouds as well. We wanted to find a lower bound for the speed of the particles that were entering the chamber. It makes sense that the speed of the cloud formation would be less than the actual speed of the particle. Because the ...
... some of the events (See Figure 4), but we analyzed the formation of the clouds as well. We wanted to find a lower bound for the speed of the particles that were entering the chamber. It makes sense that the speed of the cloud formation would be less than the actual speed of the particle. Because the ...
Hartree-Fock Theory
... It is not consistent with variational principle (that does better without this constraint). ...
... It is not consistent with variational principle (that does better without this constraint). ...
Ontological Status of Molecular Structure - HYLE-
... claim that the whole physical world is nothing but ‘atoms and quanta’ is as untenable as the claim that airplanes, tractors, cars, trains, bridges, etc., are but the materials of which they are made. That is to say, a given collection of atoms and quanta – or indeed of fundamental particles – can in ...
... claim that the whole physical world is nothing but ‘atoms and quanta’ is as untenable as the claim that airplanes, tractors, cars, trains, bridges, etc., are but the materials of which they are made. That is to say, a given collection of atoms and quanta – or indeed of fundamental particles – can in ...
Homework No. 09 (Spring 2014) PHYS 530A: Quantum Mechanics II
... and using the lowering operator to construct the |1, 0i and |1, −1i states. The state |0, 0i was then constructed (to within a phase factor) as the state orthogonal to |1, 0i. (a) Repeat this exercise by beginning with the total angular momentum state |1, −1i and using the raising operator to constr ...
... and using the lowering operator to construct the |1, 0i and |1, −1i states. The state |0, 0i was then constructed (to within a phase factor) as the state orthogonal to |1, 0i. (a) Repeat this exercise by beginning with the total angular momentum state |1, −1i and using the raising operator to constr ...
Reheating and Preheating after Inflation : an Introduction
... more visual terms a violation of condition (56) also means that the intrinsic width of the inflaton mass eigenstate has become broader than the first resonance band around k ' m. A realistic treatment of preheating beyond our toy model faces further complications. The expansion of the Universe, for ...
... more visual terms a violation of condition (56) also means that the intrinsic width of the inflaton mass eigenstate has become broader than the first resonance band around k ' m. A realistic treatment of preheating beyond our toy model faces further complications. The expansion of the Universe, for ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.