Physics 571 Lecture #27 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... too much at how arcane this appears to be. This stuff really is helpful. Every atom has an infinite ...
... too much at how arcane this appears to be. This stuff really is helpful. Every atom has an infinite ...
SOLID STATE QUANTUM COMPUTING USING SPECTRAL HOLES
... This method is analogous to a scheme proposed by Pellizzari, et al.4 that uses adiabatic transfer to move quantum information coherently from one particle to another, then performs quantum logic by inducing single-particle Raman transitions. Consider a situation where each atom has a Λ-type transiti ...
... This method is analogous to a scheme proposed by Pellizzari, et al.4 that uses adiabatic transfer to move quantum information coherently from one particle to another, then performs quantum logic by inducing single-particle Raman transitions. Consider a situation where each atom has a Λ-type transiti ...
Stoichiometry
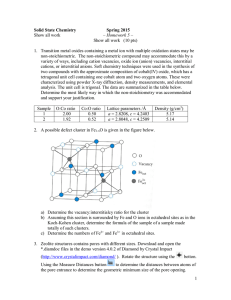
... Dalton’s law of partial pressure: The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases, that do not interact, equals sum of partial pressures of all gases, if each gas occupies the container on its own. P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + ………… ...
... Dalton’s law of partial pressure: The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases, that do not interact, equals sum of partial pressures of all gases, if each gas occupies the container on its own. P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + ………… ...
Anderson localization of ultra
... Quantum Field Theory are well imitated by certain Condensed Matter systems… He thought that there should be a certain class of quantum mechanical systems which would simulate any other system, a ...
... Quantum Field Theory are well imitated by certain Condensed Matter systems… He thought that there should be a certain class of quantum mechanical systems which would simulate any other system, a ...
Arc Attack - Society for the Performing Arts
... our musical performance, but also lays the foundation for the understanding of the basic scientific principles that compose modern day technology and promote it’s advancement. It is geared towards use for multiple grade levels including the high school physics classroom; however, most of the concept ...
... our musical performance, but also lays the foundation for the understanding of the basic scientific principles that compose modern day technology and promote it’s advancement. It is geared towards use for multiple grade levels including the high school physics classroom; however, most of the concept ...
Electric Fields File
... powder) is dusted onto the drum. The toner consists of fine toner particles (negative) stuck to larger iron particles (positive). There is a magnetic roller (near the main drum) attracts the iron carrier particles containing the toner to its surface. As the positive charge is much larger on the sele ...
... powder) is dusted onto the drum. The toner consists of fine toner particles (negative) stuck to larger iron particles (positive). There is a magnetic roller (near the main drum) attracts the iron carrier particles containing the toner to its surface. As the positive charge is much larger on the sele ...
Feb. 17, 2006
... has zero rotational energy according to eq. 13-8. Thus, there is no zero-point energy. This does not violate the uncertainty principle because, although we know the angular momentum exactly, we don't know anything about the angular "position" (how the molecule is oriented in space, if you will). The ...
... has zero rotational energy according to eq. 13-8. Thus, there is no zero-point energy. This does not violate the uncertainty principle because, although we know the angular momentum exactly, we don't know anything about the angular "position" (how the molecule is oriented in space, if you will). The ...
1357750568.
... 5. A mass of 0.2 kg produces an extension of 8 cm in a spring. The force required to produce an extension of 6 cm is. A. 0.75N B. 1.50N C. 2.70N D. 24.00N 6. Brownian motion experiment shows that molecules of gases are A. stationary B. in motion in one direction only C. in constant random motion D. ...
... 5. A mass of 0.2 kg produces an extension of 8 cm in a spring. The force required to produce an extension of 6 cm is. A. 0.75N B. 1.50N C. 2.70N D. 24.00N 6. Brownian motion experiment shows that molecules of gases are A. stationary B. in motion in one direction only C. in constant random motion D. ...
127 - Chimica
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Brochure
... by veteran professor and scientist, Brian W. Pfennig, Principles of Inorganic Chemistry is composed of eclectic sources from Dr. Pfennig s many years of teaching and built on a principles–based, group and molecular orbital theory approach. Covering a variety of topics from the Composition of Matter, ...
... by veteran professor and scientist, Brian W. Pfennig, Principles of Inorganic Chemistry is composed of eclectic sources from Dr. Pfennig s many years of teaching and built on a principles–based, group and molecular orbital theory approach. Covering a variety of topics from the Composition of Matter, ...
Matter and Change
... • Substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in fixed (constant) proportions • Can be separated into elements by chemical change • Types: covalent or ionic http://cwis.nyu.edu/pages/mathmol/modules/water/water.html ...
... • Substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in fixed (constant) proportions • Can be separated into elements by chemical change • Types: covalent or ionic http://cwis.nyu.edu/pages/mathmol/modules/water/water.html ...
An Introduction to Redox
... individual quiz (labeled Quiz 4.3 at the end of the lesson plan) so that their progress can be assessed more formally by the instructor in the event that additional review or follow‐up activities are necessary. ...
... individual quiz (labeled Quiz 4.3 at the end of the lesson plan) so that their progress can be assessed more formally by the instructor in the event that additional review or follow‐up activities are necessary. ...
letters - Atomcool
... atoms have a negative s-wave scattering length a, indicating that for a sufficiently cold and dilute gas the interatomic interactions are effectively attractive. Attractive interactions are thought to prevent BEC from occurring at all in a spatially homogeneous (i.e., untrapped) gas [3,4], and as re ...
... atoms have a negative s-wave scattering length a, indicating that for a sufficiently cold and dilute gas the interatomic interactions are effectively attractive. Attractive interactions are thought to prevent BEC from occurring at all in a spatially homogeneous (i.e., untrapped) gas [3,4], and as re ...
SiO 2 - Wits Structural Chemistry
... Example is tungsten carbide (WC) which is used for cutting tools and also high-pressure apparatus. Cementite, Fe3C is a major constituent of steel and cast iron. Silicides: silicon-metal compounds contain isolated Si, tetrahedral or Si4, or hexagonal nets of Si atom. Examples are Fe3Si and K4Si4. ...
... Example is tungsten carbide (WC) which is used for cutting tools and also high-pressure apparatus. Cementite, Fe3C is a major constituent of steel and cast iron. Silicides: silicon-metal compounds contain isolated Si, tetrahedral or Si4, or hexagonal nets of Si atom. Examples are Fe3Si and K4Si4. ...
7 Problems Chapter 7: Coulomb Blockade and the Single Elec! tron
... changes don’t lead to additional states. For the case of periodic BCs, sign is important, and so we are interested in the total number of states NT having energy less than some value (but with E E1 ). This is approximately the volume of the sphere NT = ...
... changes don’t lead to additional states. For the case of periodic BCs, sign is important, and so we are interested in the total number of states NT having energy less than some value (but with E E1 ). This is approximately the volume of the sphere NT = ...
Quantum Field Theory I
... The aim of the quantum field theory is to come up with a formalism which is completely equivalent to multi-body Schrödinger equations but just better: it allows you to consider a variable number of particles all within the same framework and can even describe the change in the number of particles. ...
... The aim of the quantum field theory is to come up with a formalism which is completely equivalent to multi-body Schrödinger equations but just better: it allows you to consider a variable number of particles all within the same framework and can even describe the change in the number of particles. ...
coherent interaction of atoms and molecules with laser radiation
... ground or excited state and mJ – the corresponding magnetic quantum number or projection of rotation momentum on quantization axis, and ξ describes all the remaining quantum numbers, which in the framework of chosen transition remain unchanged. When describing a molecular system in such basis, it is ...
... ground or excited state and mJ – the corresponding magnetic quantum number or projection of rotation momentum on quantization axis, and ξ describes all the remaining quantum numbers, which in the framework of chosen transition remain unchanged. When describing a molecular system in such basis, it is ...
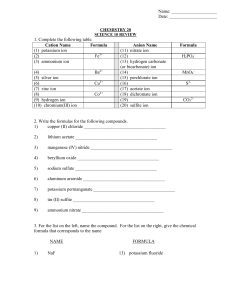
NAME
... b) aluminum bromide solution and chlorine gas react to form aluminum chloride and bromine gas. ...
... b) aluminum bromide solution and chlorine gas react to form aluminum chloride and bromine gas. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.