C. - Knights of The Periodic Table
... A. CH2 1(12) + 2(1) = 14 g B. C3H6 3(12) + 6(1) = 42 g C. C2H4 2(12) + 4(1) = 28 g D. C2H18 2(12) + 18(1) = 42 g The molar mass was 42 and there are two answers that are 42 but C2H18 is a formula that is not possible carbon only forms 4 bonds! Therefore B is the correct answer. ...
... A. CH2 1(12) + 2(1) = 14 g B. C3H6 3(12) + 6(1) = 42 g C. C2H4 2(12) + 4(1) = 28 g D. C2H18 2(12) + 18(1) = 42 g The molar mass was 42 and there are two answers that are 42 but C2H18 is a formula that is not possible carbon only forms 4 bonds! Therefore B is the correct answer. ...
Atomic Physics
... neutral, it also has 3 electrons. Bohr’s model is not applicable. If two electrons are stripped away, one ends up with the ion Li2+ . What is the ionization energy of Li2+ ? Solution: Since one has only one electron left, the Bohr’s model can be used. The ionization energy is found by putting n = 1 ...
... neutral, it also has 3 electrons. Bohr’s model is not applicable. If two electrons are stripped away, one ends up with the ion Li2+ . What is the ionization energy of Li2+ ? Solution: Since one has only one electron left, the Bohr’s model can be used. The ionization energy is found by putting n = 1 ...
Lectures 6-7
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
Chapter 21 The Electric Field 1: Discrete Charge Distributions
... to find the distribution of the charge that maximizes this force. Using Coulomb’s law, express the force that either charge exerts on the ...
... to find the distribution of the charge that maximizes this force. Using Coulomb’s law, express the force that either charge exerts on the ...
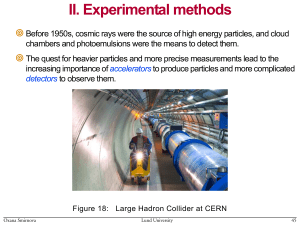
Accelerators - Particle Physics, Lund University
... Here q is electric charge of a particle, velocity v/c , Lorentz factor (1-2)-1/2, and is the radius of the orbit. For relativistic particles E/mc2 energy loss increases as E4/m4 , becoming very significant for high-energy light particles (electrons) Radio-frequency power is limited ...
... Here q is electric charge of a particle, velocity v/c , Lorentz factor (1-2)-1/2, and is the radius of the orbit. For relativistic particles E/mc2 energy loss increases as E4/m4 , becoming very significant for high-energy light particles (electrons) Radio-frequency power is limited ...
zeeman effect
... Filled shells have no net spin, so only consider valence electrons. Since electrons have spin 1/2, not possible to obtain S = 0 from atoms with odd number of valence electrons. ...
... Filled shells have no net spin, so only consider valence electrons. Since electrons have spin 1/2, not possible to obtain S = 0 from atoms with odd number of valence electrons. ...
Scheme for a coherently controlled pulsed electron gun F. Robicheaux
... electron will leave the region near the nucleus and travel downfield. (3) If the initial angle is larger than the separatrix angle, the electron will be trapped forever in the region near the nucleus because this system separates in parabolic coordinates. However, the presence of core electrons in a ...
... electron will leave the region near the nucleus and travel downfield. (3) If the initial angle is larger than the separatrix angle, the electron will be trapped forever in the region near the nucleus because this system separates in parabolic coordinates. However, the presence of core electrons in a ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... 4. Check your work by counting atoms of each element , they should be the same on both sides of the equation. 5. If you cannot balance an equation, you have probably written a formula incorrectly, Check and try again. Hints for balancing and writing chemical equations: * Remember the seven elements ...
... 4. Check your work by counting atoms of each element , they should be the same on both sides of the equation. 5. If you cannot balance an equation, you have probably written a formula incorrectly, Check and try again. Hints for balancing and writing chemical equations: * Remember the seven elements ...
Lab 1
... You should get either 500,000 or 5 105 and either is correct. IF YOU DID NOT GET THAT ANSWER THEN…….read on………. DO NOT’s of Scientific calculators. 1. DO NOT USE the 10X key. DO NOT enter the above numbers as 1 times 102 times 5 times 103 even though you get the same answer….IT IS A WASTE OF KEY S ...
... You should get either 500,000 or 5 105 and either is correct. IF YOU DID NOT GET THAT ANSWER THEN…….read on………. DO NOT’s of Scientific calculators. 1. DO NOT USE the 10X key. DO NOT enter the above numbers as 1 times 102 times 5 times 103 even though you get the same answer….IT IS A WASTE OF KEY S ...
Fundamental Definitions - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Newton’s second law is a relationship between acceleration, forces, and mass. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration a that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the accelera ...
... Newton’s second law is a relationship between acceleration, forces, and mass. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration a that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the accelera ...
Ch. 7 & 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) teacher
... left side of the arrow, and the right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
... left side of the arrow, and the right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
p211c08
... dt dt example: A 50.0 kg woman walks from one end of 5m, 40.0 kg canoe to the other. Both the canoe and the woman are initially at rest. If the friction between the water and the canoe is negligible, how far does the woman move relative to shore? How far does the boat move relative to shore? ...
... dt dt example: A 50.0 kg woman walks from one end of 5m, 40.0 kg canoe to the other. Both the canoe and the woman are initially at rest. If the friction between the water and the canoe is negligible, how far does the woman move relative to shore? How far does the boat move relative to shore? ...
The Quantum Theory of Atoms - Electrostatics and Vibrations
... The magnitude of the force between the particles is dependent on the medium in which the charges are situated, and this is taken into account by the factor ε which is known as the permittivity of the medium. The permittivity of a medium is ε = εr ε0 where ε0 is a fundamental constant known as the va ...
... The magnitude of the force between the particles is dependent on the medium in which the charges are situated, and this is taken into account by the factor ε which is known as the permittivity of the medium. The permittivity of a medium is ε = εr ε0 where ε0 is a fundamental constant known as the va ...
Document
... Rotation and Non-uniform Mass Distribution At the equator ac=v2/rE=3.4 cm/s2. Thus, the gravitational field strength at poles and equator is different by 3.4 cm/s2. Measurement, however, show that the difference is 5.2 cm/s2. Why disagree? Non-uniform mass distribution. If the Earth rotates very fas ...
... Rotation and Non-uniform Mass Distribution At the equator ac=v2/rE=3.4 cm/s2. Thus, the gravitational field strength at poles and equator is different by 3.4 cm/s2. Measurement, however, show that the difference is 5.2 cm/s2. Why disagree? Non-uniform mass distribution. If the Earth rotates very fas ...
How Einstein Swept Retrocausality Under the Rug
... different frames of reference. Einstein succeeded where others had failed by deriving the formula in a way that was consistent in all frames of reference. He did so in 1905 with his equation for Special Relativity, which adds momentum to the famous energy/mass equation (E2 = p2c2 + m2c4 , where E is ...
... different frames of reference. Einstein succeeded where others had failed by deriving the formula in a way that was consistent in all frames of reference. He did so in 1905 with his equation for Special Relativity, which adds momentum to the famous energy/mass equation (E2 = p2c2 + m2c4 , where E is ...
Atomistic simulations of field assisted evaporation in atom probe
... external fields are much stronger than the field due to a single elementary charge, and the evaporation events are rare. The full solution of the Laplace’s equation by the finite difference method employed currently in our code becomes a computationally expensive process for a large system with shar ...
... external fields are much stronger than the field due to a single elementary charge, and the evaporation events are rare. The full solution of the Laplace’s equation by the finite difference method employed currently in our code becomes a computationally expensive process for a large system with shar ...
Short questions from past papers
... 1. Define the moment of a force. [2006 OL][2003 OL][2011] The moment of a force is equal to the force multiplied by the distance between the force and the fulcrum. 2. What are the two conditions for the equilibrium of a set of co-planar forces? [2010][2011] Forces up = forces down // (algebraic) sum ...
... 1. Define the moment of a force. [2006 OL][2003 OL][2011] The moment of a force is equal to the force multiplied by the distance between the force and the fulcrum. 2. What are the two conditions for the equilibrium of a set of co-planar forces? [2010][2011] Forces up = forces down // (algebraic) sum ...
Energy-Angle Distribution of Thin Target Bremsstrahlung
... radiation from fast electrons in very thin targets. Targets thin enough for the present result to be directly applicable can be realized with linear accelerators, although probably not with betatrons or synchrotrons. This result may also prove to be of interest as a basis for further calculations on ...
... radiation from fast electrons in very thin targets. Targets thin enough for the present result to be directly applicable can be realized with linear accelerators, although probably not with betatrons or synchrotrons. This result may also prove to be of interest as a basis for further calculations on ...
2016 - Specimen Paper 2 - Cambridge International Examinations
... After the copper(II) sulfate had crystallised the students dried and weighed the crystals. Which student produced the highest percentage yield of hydrated copper(II) sulfate? mass of copper(II) oxide used / g ...
... After the copper(II) sulfate had crystallised the students dried and weighed the crystals. Which student produced the highest percentage yield of hydrated copper(II) sulfate? mass of copper(II) oxide used / g ...
heisenberg`s uncertainty principle in high school curriculum
... will increase (the position of particle is fuzzy) and we cannot pinpoint the position of particle. Werner Heisenberg noticed this fact and he formulated uncertainty principle in 1927: ”The more precisely the position is determined, the less precisely the momentum is known in this instant, and vice v ...
... will increase (the position of particle is fuzzy) and we cannot pinpoint the position of particle. Werner Heisenberg noticed this fact and he formulated uncertainty principle in 1927: ”The more precisely the position is determined, the less precisely the momentum is known in this instant, and vice v ...
Quantum Information Processing with Trapped Neutral Atoms
... neutrals are shallow compared to ion traps, and the atom/trap field interaction invariably perturbs the atomic internal state. In QIP one must balance an intrinsic conflict – qubits must interact with each other and with external control fields that drive the quantum algorithm, while at the same ti ...
... neutrals are shallow compared to ion traps, and the atom/trap field interaction invariably perturbs the atomic internal state. In QIP one must balance an intrinsic conflict – qubits must interact with each other and with external control fields that drive the quantum algorithm, while at the same ti ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.