OCR A Level Chemistry A H432 Specification
... Module 1 of the specification content relates to the practical skills learners are expected to gain throughout the course, which are assessed throughout the written examinations and also through the Practical Endorsement (see Section 5). Practical activities are embedded within the learning outcomes ...
... Module 1 of the specification content relates to the practical skills learners are expected to gain throughout the course, which are assessed throughout the written examinations and also through the Practical Endorsement (see Section 5). Practical activities are embedded within the learning outcomes ...
006 Thermochemistry
... 56. The enthalpy change when a strong acid is neutralized by strong base is -56.1 kJ/mol. If 12.0 mL of 6.00 M HBr at 21.30C is mixed with 300. mL of 0.250 M NaOH, also at 21.30C, what will the maximum temperature reached by the resulting solution? [Assume that there is no heat loss to the contain ...
... 56. The enthalpy change when a strong acid is neutralized by strong base is -56.1 kJ/mol. If 12.0 mL of 6.00 M HBr at 21.30C is mixed with 300. mL of 0.250 M NaOH, also at 21.30C, what will the maximum temperature reached by the resulting solution? [Assume that there is no heat loss to the contain ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... Strategy: Hydrogen displacement: Any metal above hydrogen in the activity series will displace it from water or from an acid. Metals below hydrogen will not react with either water or an acid. Solution: Only (b) Li and (d) Ca are above hydrogen in the activity series, so they are the only metals in ...
... Strategy: Hydrogen displacement: Any metal above hydrogen in the activity series will displace it from water or from an acid. Metals below hydrogen will not react with either water or an acid. Solution: Only (b) Li and (d) Ca are above hydrogen in the activity series, so they are the only metals in ...
Abdullah F. Eid
... The crystal structure of HPAs depends on the amount of hydration water. This water can be easily removed on heating, whereby the acid strength is increased due to the dehydration of protons. This is a reversible process accompanied by changing the volume of crystal cell. Unlike the rigid network str ...
... The crystal structure of HPAs depends on the amount of hydration water. This water can be easily removed on heating, whereby the acid strength is increased due to the dehydration of protons. This is a reversible process accompanied by changing the volume of crystal cell. Unlike the rigid network str ...
Chemical Equilibrium - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
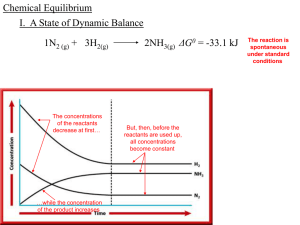
... Chemical Equilibrium which states, at a given ___________, temperature a chemical state in which a system may reach a _____ ratio of _______ reactant and particular _____ product ____________ concentrations has a constant _______ _______ value Cato Maximilian Guldberg ...
... Chemical Equilibrium which states, at a given ___________, temperature a chemical state in which a system may reach a _____ ratio of _______ reactant and particular _____ product ____________ concentrations has a constant _______ _______ value Cato Maximilian Guldberg ...
Chapter 5 Geochemical Weathering
... constant PCO2 and restrains pH to the circum-neutral range. As shown in the next section, this contrasts with carbonate dissolution under closed system conditions where the limited CO2 gained during infiltration through the soil precludes extensive weathering. Here, the PCO2 will evolve to very low ...
... constant PCO2 and restrains pH to the circum-neutral range. As shown in the next section, this contrasts with carbonate dissolution under closed system conditions where the limited CO2 gained during infiltration through the soil precludes extensive weathering. Here, the PCO2 will evolve to very low ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... MgCl2, an AgCl precipitate forms immediately. The precipitate is then filtered from the solution, dried, and weighed. If the recovered AgCl is found to have a mass of 0.1183 g, what as the concentration of magnesium ions in the original MgCl2 solution? A) 0.300 M D) 2.06 10–5 M B) 8.25 10–3 M E) ...
... MgCl2, an AgCl precipitate forms immediately. The precipitate is then filtered from the solution, dried, and weighed. If the recovered AgCl is found to have a mass of 0.1183 g, what as the concentration of magnesium ions in the original MgCl2 solution? A) 0.300 M D) 2.06 10–5 M B) 8.25 10–3 M E) ...
Specification and sample assessment material - Edexcel
... than 70 countries working to help people of all ages to make measurable progress in their lives through learning. We put the learner at the centre of everything we do, because wherever learning flourishes, so do people. Find out more about how we can help you and your learners at qualifications.pear ...
... than 70 countries working to help people of all ages to make measurable progress in their lives through learning. We put the learner at the centre of everything we do, because wherever learning flourishes, so do people. Find out more about how we can help you and your learners at qualifications.pear ...
BRIEF ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS APPENDIX G
... only one type of atom in an element. 2.4(a) The presence of more than one element makes pure calcium chloride a compound. (b) There is only one kind of atom, so sulfur is an element. (c) The presence of more than one compound makes baking powder a mixture. (d) The presence of more than one type of a ...
... only one type of atom in an element. 2.4(a) The presence of more than one element makes pure calcium chloride a compound. (b) There is only one kind of atom, so sulfur is an element. (c) The presence of more than one compound makes baking powder a mixture. (d) The presence of more than one type of a ...
Chapter 15 Calculations in chemistry: stoichiometry
... Copper metal can be recovered from a solution of copper(II) sulfate by the addition of scrap metal iron to the solution. The equation for the reaction is: Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) What mass of copper would be obtained if 1.0 kg of scrap iron was added to enough copper sulfate to react ...
... Copper metal can be recovered from a solution of copper(II) sulfate by the addition of scrap metal iron to the solution. The equation for the reaction is: Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) What mass of copper would be obtained if 1.0 kg of scrap iron was added to enough copper sulfate to react ...
Answers to Problem-Solving Practice Problems
... (4) Check your answer: Because the density is a little less than 1.00 g/mL, the volume in milliliters should be a little larger than the mass in grams. The calculated answer, 4.92 mL, is a little larger than the mass, 4.33 g. 1.2 Substance A must be a mixture since some of it dissolves and some, sub ...
... (4) Check your answer: Because the density is a little less than 1.00 g/mL, the volume in milliliters should be a little larger than the mass in grams. The calculated answer, 4.92 mL, is a little larger than the mass, 4.33 g. 1.2 Substance A must be a mixture since some of it dissolves and some, sub ...
BS Chemistry - Government College University Faisalabad
... Relation of entropy and energy with equilibrium constant and their dependence on temperature. Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Chemical potential. Partial molar quantities. Laws of thermodynamics and their applications. Thermodynamic functions internal energy, enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Relation ...
... Relation of entropy and energy with equilibrium constant and their dependence on temperature. Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Chemical potential. Partial molar quantities. Laws of thermodynamics and their applications. Thermodynamic functions internal energy, enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Relation ...
Chapter 4 FULL PPT - Westminster Public Schools
... a. 0.250 M NaOH from 1.00 M NaOH stock solution Add 500 mL of the 1.00 M NaOH stock solution to a 2L volumetric flask; fill to the mark with water ...
... a. 0.250 M NaOH from 1.00 M NaOH stock solution Add 500 mL of the 1.00 M NaOH stock solution to a 2L volumetric flask; fill to the mark with water ...
08 Redox Reactions
... 5 to 3 and that of ‘Zn’ increases from 0 to + 4. Hence, N is an oxidizing agent and is itself reduced by the gain of electrons. ‘Zn’ acts as a reducing agent and is itself oxidized by loss of electrons. ...
... 5 to 3 and that of ‘Zn’ increases from 0 to + 4. Hence, N is an oxidizing agent and is itself reduced by the gain of electrons. ‘Zn’ acts as a reducing agent and is itself oxidized by loss of electrons. ...
Specification – AS/A Level Chemistry A
... (ii) molecular formula as the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule; (d) calculate empirical and molecular formulae, ...
... (ii) molecular formula as the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule; (d) calculate empirical and molecular formulae, ...
master ap chemistry - NelnetSolutions.com
... For more information, contact Peterson’s, 2000 Lenox Drive, Lawrenceville, NJ 08648; 800-338-3282; or find us on the World Wide Web at: www.petersons.com/about. © 2007 Peterson’s, a Nelnet company Previous edition © 2005 Editor: Wallie Walker Hammond; Production Editor: Mark D. Snider; Composition M ...
... For more information, contact Peterson’s, 2000 Lenox Drive, Lawrenceville, NJ 08648; 800-338-3282; or find us on the World Wide Web at: www.petersons.com/about. © 2007 Peterson’s, a Nelnet company Previous edition © 2005 Editor: Wallie Walker Hammond; Production Editor: Mark D. Snider; Composition M ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.