COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... intermediates in drug synthesis. The quaternary ammonium salts derived from long chain aliphatic tertiary amines are widely used as detergents. Aromatic amines e.g. aniline and its derivatives, are used for the production of dyes, drugs and photographic developers. 1,4-Diaminobenzene is the main ing ...
... intermediates in drug synthesis. The quaternary ammonium salts derived from long chain aliphatic tertiary amines are widely used as detergents. Aromatic amines e.g. aniline and its derivatives, are used for the production of dyes, drugs and photographic developers. 1,4-Diaminobenzene is the main ing ...
Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
... Answer: (a) Qc = 6.45 × 103, shifts right. (b) Qc = 0.12, shifts left. (c) Qc = 0, shifts right ...
... Answer: (a) Qc = 6.45 × 103, shifts right. (b) Qc = 0.12, shifts left. (c) Qc = 0, shifts right ...
Teacher Edition Calculations
... Perform a first-hand investigation to meas ure and identify the mass ratios of metal to non metal(s) in a common compound and calculate its empirical formula Describe the contribution of Gay-Lussac to the understanding of gaseous reactions and apply this to an understanding of the mole concept Recou ...
... Perform a first-hand investigation to meas ure and identify the mass ratios of metal to non metal(s) in a common compound and calculate its empirical formula Describe the contribution of Gay-Lussac to the understanding of gaseous reactions and apply this to an understanding of the mole concept Recou ...
KCET – CHEMISTRY – 2016 - Medicine.careers360.com
... The correct statement regarding entropy is, 1) At absolute zero temperature, entropy of a perfectly crystalline solid is zero 2) At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is +Ve 3) At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of all crystalline substance is zero 4) ...
... The correct statement regarding entropy is, 1) At absolute zero temperature, entropy of a perfectly crystalline solid is zero 2) At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is +Ve 3) At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of all crystalline substance is zero 4) ...
Signs of Reaction - Calderglen High School
... The atoms of a compound are joined together. The substances in a mixture are NOT joined and can be easily separated. Calderglen High School ...
... The atoms of a compound are joined together. The substances in a mixture are NOT joined and can be easily separated. Calderglen High School ...
Brief Contents - Educhimica.it
... 7. a. 56.0 + 3.44 = 59.44. The first number stops its significant figure in the tenths place after the decimal, and the second number stops its significant figure in the hundredths place after the decimal. Hence, we limit our final answer to the tenths place after the decimal. The final answer is 59.4. b. ...
... 7. a. 56.0 + 3.44 = 59.44. The first number stops its significant figure in the tenths place after the decimal, and the second number stops its significant figure in the hundredths place after the decimal. Hence, we limit our final answer to the tenths place after the decimal. The final answer is 59.4. b. ...
2. Solution Guide to Supplementary Exercises
... X reacts with water while Z does not. Therefore X is more reactive than Z. 40 C Option A — Both iron and lead exist as compounds in the Earth’s crust. Hence X probably exists as compounds in the Earth’s crust. Option B — Both iron and lead form oxide when heated in air. Hence X probably forms an oxi ...
... X reacts with water while Z does not. Therefore X is more reactive than Z. 40 C Option A — Both iron and lead exist as compounds in the Earth’s crust. Hence X probably exists as compounds in the Earth’s crust. Option B — Both iron and lead form oxide when heated in air. Hence X probably forms an oxi ...
Electrospun Polyaniline Fibers as Highly Sensitive Room
... All experiments were conducted with a constant total gas flow rate of 200 sccm. For NH3 sensing, a certified premixed gas containing 1000 ppm of NH3 in dry nitrogen was diluted with additional dry nitrogen gas by MFC’s to a concentration in the range of 10 to 700 ppm of NH3; for NO2 sensing, a cert ...
... All experiments were conducted with a constant total gas flow rate of 200 sccm. For NH3 sensing, a certified premixed gas containing 1000 ppm of NH3 in dry nitrogen was diluted with additional dry nitrogen gas by MFC’s to a concentration in the range of 10 to 700 ppm of NH3; for NO2 sensing, a cert ...
Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... the solvent3. An aqueous solution4 is a solution in which the solvent is water, whereas in a nonaqueous solution, the solvent is a substance other than water. Familiar examples of nonaqueous solvents are ethyl acetate, used in nail polish removers, and turpentine, used to clean paint brushes. In thi ...
... the solvent3. An aqueous solution4 is a solution in which the solvent is water, whereas in a nonaqueous solution, the solvent is a substance other than water. Familiar examples of nonaqueous solvents are ethyl acetate, used in nail polish removers, and turpentine, used to clean paint brushes. In thi ...
Amines - ncert
... hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, solubility decreases with increase in molar mass of amines due to increase in size of the hydrophobic alkyl part. Higher amines are essentially insoluble in water. Considering the electronegativity of nitrogen of amine and oxygen of alcohol as 3.0 and 3. ...
... hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, solubility decreases with increase in molar mass of amines due to increase in size of the hydrophobic alkyl part. Higher amines are essentially insoluble in water. Considering the electronegativity of nitrogen of amine and oxygen of alcohol as 3.0 and 3. ...
THESE DOCTORAT DE L`UNIVERSITE DE TOULOUSE ET
... other hand, a reversible reaction gives rise to a simple Cp*WVI ligand exchange product. The corresponding reaction for thioglycolic acid resulted in an adduct having the same stoichiometry at low substrate/W ratio, but containing a 5-membered cycle in an asymmetric [Cp*WO(OH)(SCH2COO)] structure. H ...
... other hand, a reversible reaction gives rise to a simple Cp*WVI ligand exchange product. The corresponding reaction for thioglycolic acid resulted in an adduct having the same stoichiometry at low substrate/W ratio, but containing a 5-membered cycle in an asymmetric [Cp*WO(OH)(SCH2COO)] structure. H ...
CHAPTER 3 STOICHIOMETRY
... Solution: Let's first calculate the number of N atoms in 1.68 10 g of urea. First, we must convert grams of urea to number of molecules of urea. This calculation is similar to Problem 3.26. The molecular formula of urea shows there are two N atoms in one urea molecule, which will allow us to conve ...
... Solution: Let's first calculate the number of N atoms in 1.68 10 g of urea. First, we must convert grams of urea to number of molecules of urea. This calculation is similar to Problem 3.26. The molecular formula of urea shows there are two N atoms in one urea molecule, which will allow us to conve ...
Document
... To study the energy changes in reactions under conditions of constant volume, a “bomb calorimeter” (Fig. 6.6) is used. For a constant-volume process, the change in volume ΔV is equal to zero, so work (which is -PΔV) is also equal to zero. 歐亞書局 ...
... To study the energy changes in reactions under conditions of constant volume, a “bomb calorimeter” (Fig. 6.6) is used. For a constant-volume process, the change in volume ΔV is equal to zero, so work (which is -PΔV) is also equal to zero. 歐亞書局 ...
Chapter 3 Solutions - Bremerton School District
... unit) of a compound. The empirical formula tells only the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a molecule. The molecular formula is a whole number multiple of the empirical formula. If that multiplier is one, the molecular and empirical formulas are the same. For example, both the ...
... unit) of a compound. The empirical formula tells only the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a molecule. The molecular formula is a whole number multiple of the empirical formula. If that multiplier is one, the molecular and empirical formulas are the same. For example, both the ...
chemistry-resource
... Students’ common errors, un-attempted questions and their remediation. Reviewed Support Materials of the previous year. In order to ensure that the participants come well-prepared for the Workshop, the topics/chapters were distributed among them well in advance. During the Workshop the materials pre ...
... Students’ common errors, un-attempted questions and their remediation. Reviewed Support Materials of the previous year. In order to ensure that the participants come well-prepared for the Workshop, the topics/chapters were distributed among them well in advance. During the Workshop the materials pre ...
DOE Chemistry 1
... their reactor-specific content, DOE Category A reactor training managers also reviewed and commented on the content. On the basis of feedback from these sources, information that applied to two or more DOE nuclear facilities was considered generic and was included. The final draft of each of the han ...
... their reactor-specific content, DOE Category A reactor training managers also reviewed and commented on the content. On the basis of feedback from these sources, information that applied to two or more DOE nuclear facilities was considered generic and was included. The final draft of each of the han ...
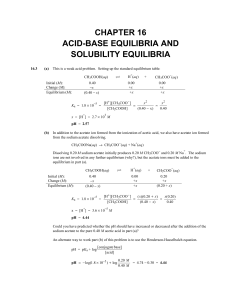
CHAPTER 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA AND SOLUBILITY
... The charges of the M and X ions are +3 and −2, respectively (are other values possible?). We first calculate the number of moles of M2X3 that dissolve in 1.0 L of water 1 mol ...
... The charges of the M and X ions are +3 and −2, respectively (are other values possible?). We first calculate the number of moles of M2X3 that dissolve in 1.0 L of water 1 mol ...
Modern Chemistry
... shows that 2 molecules (made of 4 atoms) of hydrogen and 1 molecule (made of 2 atoms) of oxygen produce 2 molecules of water. The total mass of the product, water, is equal to the sum of the masses of each of the reactants, hydrogen and oxygen. What parts of Dalton’s atomic theory are illustrated by ...
... shows that 2 molecules (made of 4 atoms) of hydrogen and 1 molecule (made of 2 atoms) of oxygen produce 2 molecules of water. The total mass of the product, water, is equal to the sum of the masses of each of the reactants, hydrogen and oxygen. What parts of Dalton’s atomic theory are illustrated by ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.