General chemistry laboratory activities, Lorentz
... Reaction flasks (see Figure 2) are usually spherical (i.e. round-bottom flask) and are accompanied by their necks, at the ends of which are ground glass joints to quickly and tightly connect to the rest of the apparatus (such as a reflux condenser or dropping funnel). The reaction flask is usually m ...
... Reaction flasks (see Figure 2) are usually spherical (i.e. round-bottom flask) and are accompanied by their necks, at the ends of which are ground glass joints to quickly and tightly connect to the rest of the apparatus (such as a reflux condenser or dropping funnel). The reaction flask is usually m ...
Osmium(VIII) Catalyzed Oxidation of 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid
... conditions, it has been shown [13] that metal ions act as catalysts by one of these different paths such as the formation of complexes with reactants or oxidation of the substrate itself or through the formation of free radicals. In earlier report [14], it has been observed that Os(VIII) forms a com ...
... conditions, it has been shown [13] that metal ions act as catalysts by one of these different paths such as the formation of complexes with reactants or oxidation of the substrate itself or through the formation of free radicals. In earlier report [14], it has been observed that Os(VIII) forms a com ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... TOK: The early discoverers of the elements allowed chemistry to make great steps with limited apparatus, often derived from the pseudoscience of alchemy. Lavoisier’s work with oxygen, which overturned the phlogiston theory of heat, could be discussed as an example of a paradigm shift. Int: The disco ...
... TOK: The early discoverers of the elements allowed chemistry to make great steps with limited apparatus, often derived from the pseudoscience of alchemy. Lavoisier’s work with oxygen, which overturned the phlogiston theory of heat, could be discussed as an example of a paradigm shift. Int: The disco ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... TOK: The early discoverers of the elements allowed chemistry to make great steps with limited apparatus, often derived from the pseudoscience of alchemy. Lavoisier’s work with oxygen, which overturned the phlogiston theory of heat, could be discussed as an example of a paradigm shift. Int: The disco ...
... TOK: The early discoverers of the elements allowed chemistry to make great steps with limited apparatus, often derived from the pseudoscience of alchemy. Lavoisier’s work with oxygen, which overturned the phlogiston theory of heat, could be discussed as an example of a paradigm shift. Int: The disco ...
Slide 1
... Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium • Le Châtelier’s principle states that if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that relieves the stress. • For example, consider the equilibrium system • If an additional amount of reactant (NO or Br2) is added to t ...
... Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium • Le Châtelier’s principle states that if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that relieves the stress. • For example, consider the equilibrium system • If an additional amount of reactant (NO or Br2) is added to t ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... values of substances in their standard states. • Standard entropies tend to increase with increasing molar mass. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... values of substances in their standard states. • Standard entropies tend to increase with increasing molar mass. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chemistry Unit Outcomes
... List the names of the first persons to recognize that it would be convenient to represent chemical substances using symbols? 2. Outline what John Dalton, an English chemist, did in 1808. 3. Explain how Dalton represented element and why there was a problem with Dalton’s system. 4. Define the term ch ...
... List the names of the first persons to recognize that it would be convenient to represent chemical substances using symbols? 2. Outline what John Dalton, an English chemist, did in 1808. 3. Explain how Dalton represented element and why there was a problem with Dalton’s system. 4. Define the term ch ...
Exam 961-1st Name___________________________________
... A) a compound can contain different numbers of atoms as long as it has the same kinds of atoms. B) atoms of different element combine to form compounds. C) all atoms are different. D) all matter is made up of tiny particles called electrons. E) atoms are created and destroyed during a chemical react ...
... A) a compound can contain different numbers of atoms as long as it has the same kinds of atoms. B) atoms of different element combine to form compounds. C) all atoms are different. D) all matter is made up of tiny particles called electrons. E) atoms are created and destroyed during a chemical react ...
Photosynthesis in Hydrogen-Dominated Atmospheres
... relate directly to standard electrode potentials or other, energetic measures of redox state. It is simply a convenient classification based on chemical structure alone. A sample set of 2275 molecules were randomly selected from the chemical space to provide up to 30 examples of all of the Rr values ...
... relate directly to standard electrode potentials or other, energetic measures of redox state. It is simply a convenient classification based on chemical structure alone. A sample set of 2275 molecules were randomly selected from the chemical space to provide up to 30 examples of all of the Rr values ...
Basic Concepts - Department of Chemistry
... pressures are substituted into the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction. • When equilibrium concentrations are not given the equilibrium concentrations can be obtained from the initial concentrations of the reactants and the balanced equation for the reaction, as long as the equilibrium ...
... pressures are substituted into the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction. • When equilibrium concentrations are not given the equilibrium concentrations can be obtained from the initial concentrations of the reactants and the balanced equation for the reaction, as long as the equilibrium ...
Basic Concepts
... pressures are substituted into the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction. • When equilibrium concentrations are not given the equilibrium concentrations can be obtained from the initial concentrations of the reactants and the balanced equation for the reaction, as long as the equilibrium ...
... pressures are substituted into the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction. • When equilibrium concentrations are not given the equilibrium concentrations can be obtained from the initial concentrations of the reactants and the balanced equation for the reaction, as long as the equilibrium ...
stoichiometry - einstein classes
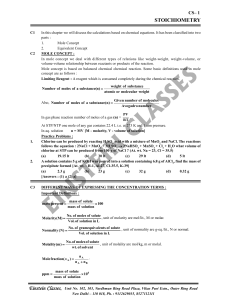
... It is based on law of equivalence which is explained as follows : Law of chemical equivalents : In a chemical reaction the equivalents of all the species (reactants or products) are equal to each other provided none of these compounds is in excess. N1V1 = N2V2 (when normalities and volumes are given ...
... It is based on law of equivalence which is explained as follows : Law of chemical equivalents : In a chemical reaction the equivalents of all the species (reactants or products) are equal to each other provided none of these compounds is in excess. N1V1 = N2V2 (when normalities and volumes are given ...
Unit 7 Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Notes
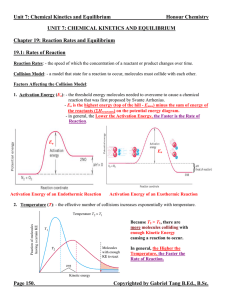
... 19.2A: Reversible Reactions Reversible Reactions: - reactions that can go from the right hand side of the equation (products) to the left hand side of the equation (reactants). Chemical Equilibrium: - the state at which the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with time (the ...
... 19.2A: Reversible Reactions Reversible Reactions: - reactions that can go from the right hand side of the equation (products) to the left hand side of the equation (reactants). Chemical Equilibrium: - the state at which the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with time (the ...
The reaction pathways of hydrogen peroxide in
... elucidates the formation and breakdown of an intermediate formed during the reaction. Sodium pyruvate is a potential base for the creation of a peroxide scavenger. It readily reacts with H2O2 to yield sodium acetate, carbon dioxide and water as final products. A low temperature nuclear magnetic reso ...
... elucidates the formation and breakdown of an intermediate formed during the reaction. Sodium pyruvate is a potential base for the creation of a peroxide scavenger. It readily reacts with H2O2 to yield sodium acetate, carbon dioxide and water as final products. A low temperature nuclear magnetic reso ...
Chapter 7 - NordoniaHonorsChemistry
... CH4 and O2 are the reactants, and CO2 and H2O are the products. The (g) after the formulas tells us the state of the chemical. The number in front of each substance tells us the numbers of those molecules in the reaction. ...
... CH4 and O2 are the reactants, and CO2 and H2O are the products. The (g) after the formulas tells us the state of the chemical. The number in front of each substance tells us the numbers of those molecules in the reaction. ...
sch103manual - university of nairobi staff profiles
... state as ice, liquid state as water and in the gaseous state as steam. The physical properties of a substance often depend on the state of the substance. In this section, we will review the states of matter and then look at the behavior of gases. Gases are much simpler than liquids or solids. Molecu ...
... state as ice, liquid state as water and in the gaseous state as steam. The physical properties of a substance often depend on the state of the substance. In this section, we will review the states of matter and then look at the behavior of gases. Gases are much simpler than liquids or solids. Molecu ...
Stoichiometry
... 3. If necessary multiply the whole equation by a factor to clear the fractional coefficients 4. Verify that the equation is balanced and the coefficients are the smallest whole numbers 5. Specify physical states ...
... 3. If necessary multiply the whole equation by a factor to clear the fractional coefficients 4. Verify that the equation is balanced and the coefficients are the smallest whole numbers 5. Specify physical states ...
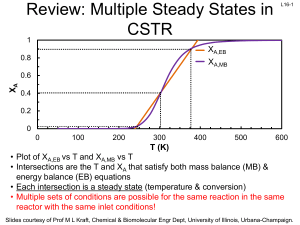
Review: SS Nonisothermal Reactors - University of Illinois Urbana
... Instead of feeding coolant to the reactor, a solvent with a low boiling point is added (component D). The solvent has a heat of vaporization of 1000 Btu/lb mol, and initially 25 lb mol of A are placed in the tank. The reactor is wellinsulated. What is the rate of solvent evaporation after 2 h if T i ...
... Instead of feeding coolant to the reactor, a solvent with a low boiling point is added (component D). The solvent has a heat of vaporization of 1000 Btu/lb mol, and initially 25 lb mol of A are placed in the tank. The reactor is wellinsulated. What is the rate of solvent evaporation after 2 h if T i ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.