2nd Semester Exam Review
... • How many grams of CaCl2 would be dissolved in 1.0 L of a 0.10 M solution of CaCl2? ...
... • How many grams of CaCl2 would be dissolved in 1.0 L of a 0.10 M solution of CaCl2? ...
Notes
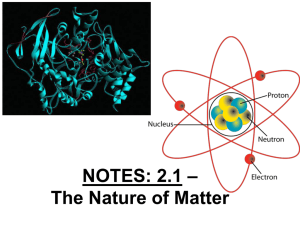
... • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
... • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
Enthalpy diagram relating the change for a reaction to enthalpies of
... Reaction rates decreases as reaction proceeds, because the concentration of reactants decreases. ...
... Reaction rates decreases as reaction proceeds, because the concentration of reactants decreases. ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
Chemical Equations PowerPoint
... of the following, predict the products and write a word equation. Next, write a formula equation and a balanced chemical equation. Finally, write the type of reaction represented by each chemical equation. ...
... of the following, predict the products and write a word equation. Next, write a formula equation and a balanced chemical equation. Finally, write the type of reaction represented by each chemical equation. ...
2014
... PCl5 (g) ⇆ PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) PCl5 (g) decomposes into PCl3 (g) and Cl2 (g) according to the equation above. A sample of PCl5 (g) is placed into a rigid, evacuated 1.00 L container. The initial pressure of the PCl5 (g) is 1.00 atm. The temperature is held constant until the PCl5 (g) reaches equilibr ...
... PCl5 (g) ⇆ PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) PCl5 (g) decomposes into PCl3 (g) and Cl2 (g) according to the equation above. A sample of PCl5 (g) is placed into a rigid, evacuated 1.00 L container. The initial pressure of the PCl5 (g) is 1.00 atm. The temperature is held constant until the PCl5 (g) reaches equilibr ...
Matter_and_Change2
... • Solid: definite shape and volume • Liquid: Takes on shape of container, definite volume • Gas: Fills any space; compressible ...
... • Solid: definite shape and volume • Liquid: Takes on shape of container, definite volume • Gas: Fills any space; compressible ...
Name - rwebbchem
... Solubility Rules: Use the solubility rules to complete the following: 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
... Solubility Rules: Use the solubility rules to complete the following: 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
2 - CronScience
... Solid iron (III) sulfide reacts with gaseous hydrogen chloride to form iron (III) chloride and hydrogen sulfide gas. Nitric acid dissolved in water reacts with solid sodium carbonate to form liquid water and carbon dioxide gas and sodium nitrate dissolved in water. ...
... Solid iron (III) sulfide reacts with gaseous hydrogen chloride to form iron (III) chloride and hydrogen sulfide gas. Nitric acid dissolved in water reacts with solid sodium carbonate to form liquid water and carbon dioxide gas and sodium nitrate dissolved in water. ...
Making Connections - SCH4U1-CCVI
... In a chemical reaction, the PE of the reactants and products results in the transfer of energy from the: 1) surroundings to the chemical system (ENDO) 2) chemical system to the surroundings (EXO) Enthalpy changes and Spontaneity Bond energy (BE): the minimum energy required to break one mole of bo ...
... In a chemical reaction, the PE of the reactants and products results in the transfer of energy from the: 1) surroundings to the chemical system (ENDO) 2) chemical system to the surroundings (EXO) Enthalpy changes and Spontaneity Bond energy (BE): the minimum energy required to break one mole of bo ...
EXAM 3
... The elements nitrogen and oxygen combine at high temperatures to form nitric oxide, NO. The balanced chemical equation is N2(g) + O2(g) ----------> 2NO(g) In a high temperature experiment, a chemist mixed 3.417 g of N2 with an excess of O2 and allowed the above reaction to take place. Assuming compl ...
... The elements nitrogen and oxygen combine at high temperatures to form nitric oxide, NO. The balanced chemical equation is N2(g) + O2(g) ----------> 2NO(g) In a high temperature experiment, a chemist mixed 3.417 g of N2 with an excess of O2 and allowed the above reaction to take place. Assuming compl ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of
... 2) Calculate the maximum heat evolved when 4.61 grams C2H5OH (46.0684 g/mol) and 9.24 g O2 (31.998 g/mol) are used in the reaction, C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l) ∆H = −1367 kJ 3) An unknown liquid was vaporized in an experiment in order to find its molar mass. Calculate the molar mass of ...
... 2) Calculate the maximum heat evolved when 4.61 grams C2H5OH (46.0684 g/mol) and 9.24 g O2 (31.998 g/mol) are used in the reaction, C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l) ∆H = −1367 kJ 3) An unknown liquid was vaporized in an experiment in order to find its molar mass. Calculate the molar mass of ...
Chemical Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reac ...
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reac ...
CH225h - Oregon State chemistry
... (a) What is the ratio of rms speeds of Ar and He atoms in a gas sample at 290 K and 0.8 atm? The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, ...
... (a) What is the ratio of rms speeds of Ar and He atoms in a gas sample at 290 K and 0.8 atm? The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, ...
Ch17-2 Driving Forces of Reactions
... What would the activation curve look like for a rapid reaction? What would happen if amount
... What would the activation curve look like for a rapid reaction? What would happen if amount
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... A formula equation is an equation in which the reactants and products are represented by symbols and formulas. It has only qualitative meaning, until the equation is balanced are given. Provide valuable information such as the number of moles or atoms of the elements or formulas contained in the equ ...
... A formula equation is an equation in which the reactants and products are represented by symbols and formulas. It has only qualitative meaning, until the equation is balanced are given. Provide valuable information such as the number of moles or atoms of the elements or formulas contained in the equ ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.