投影片 - 中正大學化生系
... over 1000 times lighter than the hydrogen atom, but also that their mass was the same whatever type of atom they came from. 2. He concluded that the rays were composed of very light, negatively charged particles which were a universal building block of atoms. 3. He determined the charge-to-mass rati ...
... over 1000 times lighter than the hydrogen atom, but also that their mass was the same whatever type of atom they came from. 2. He concluded that the rays were composed of very light, negatively charged particles which were a universal building block of atoms. 3. He determined the charge-to-mass rati ...
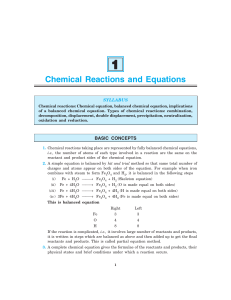
Chemical Reactions
... Combustion Reactions • Rapid reactions that produce a flame • Most often involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen in the air ...
... Combustion Reactions • Rapid reactions that produce a flame • Most often involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen in the air ...
File
... acid and nitrogen monoxide. What are the states of matter of nitrogen dioxide, nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide? ...
... acid and nitrogen monoxide. What are the states of matter of nitrogen dioxide, nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide? ...
Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced
... A. Balanced equations • Used to find how much reactant is needed • Used to predict how much product will be made • You can use amount of one substance to find the amounts of the other substances • Quantity usually in moles or grams • Stoichiometry: calculations of quantities involved in a chemical r ...
... A. Balanced equations • Used to find how much reactant is needed • Used to predict how much product will be made • You can use amount of one substance to find the amounts of the other substances • Quantity usually in moles or grams • Stoichiometry: calculations of quantities involved in a chemical r ...
Test 2 Guide Key
... 10) The minimum energy required to get a chemical reaction going is called a catalyst. False: it’s called activation energy. 11) The heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction is called enthalpy. True 12) If 2.5 moles of H2 are added to 2.1 moles of CO to form CH3CH2OH, the limiting reagen ...
... 10) The minimum energy required to get a chemical reaction going is called a catalyst. False: it’s called activation energy. 11) The heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction is called enthalpy. True 12) If 2.5 moles of H2 are added to 2.1 moles of CO to form CH3CH2OH, the limiting reagen ...
Thermodynamics and kinetics
... • At equilibrium, no further change as long as external conditions are constant • Change in external conditions can change equilibrium A stressed system at equilibrium will shift to reduce stress concentration, pressure, temperature • N2 + 3 H2 <--> 2 NH3 + 22 kcal What is the shift due to Inc ...
... • At equilibrium, no further change as long as external conditions are constant • Change in external conditions can change equilibrium A stressed system at equilibrium will shift to reduce stress concentration, pressure, temperature • N2 + 3 H2 <--> 2 NH3 + 22 kcal What is the shift due to Inc ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry
... ΔH can be calculated for any reaction, using quantities known as enthalpies of formation. Meaning = Δ H0f ΔH0f , standard molar enthalpy of formation of a compound is equal to the enthalpy change when one mole of the compound is formed at a constant pressure of 1 atm and a fixed temperature (250C) f ...
... ΔH can be calculated for any reaction, using quantities known as enthalpies of formation. Meaning = Δ H0f ΔH0f , standard molar enthalpy of formation of a compound is equal to the enthalpy change when one mole of the compound is formed at a constant pressure of 1 atm and a fixed temperature (250C) f ...
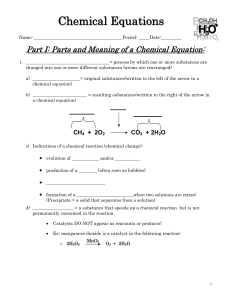
Chemical Equations
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
Sec. 12.3: Molecular Composition of Gases 1) Boyle`s Law: a
... 18) Ratios of __________ __________ will be the same as __________ __________ of gases in _______________ _______________. a) Avogadro’s law shows that the __________ __________ of two gases at the same temperature and pressure is the same as the _____________ ratio of the two gases. 19) For example ...
... 18) Ratios of __________ __________ will be the same as __________ __________ of gases in _______________ _______________. a) Avogadro’s law shows that the __________ __________ of two gases at the same temperature and pressure is the same as the _____________ ratio of the two gases. 19) For example ...
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... Describe petroleum as a mixture of hydrocarbons and its separation into useful fractions by fractional distillation. ...
... Describe petroleum as a mixture of hydrocarbons and its separation into useful fractions by fractional distillation. ...
Dec. 15 , 2012, 9:00 am – noon - Dr. K. Brown
... Use the available space to answer the following questions. B1. (8 marks) Mg (s) will react with aqueous HCl to generate H2 gas and magnesium chloride. (a) Write the balanced equation for this reaction (2 marks). ...
... Use the available space to answer the following questions. B1. (8 marks) Mg (s) will react with aqueous HCl to generate H2 gas and magnesium chloride. (a) Write the balanced equation for this reaction (2 marks). ...
IB:Enthalpy Review Questions
... b. Calculate ∆S0 for the reaction and state the meaning of the sign of ∆S0 obtained. c. Identify a thermodynamic function that can be used to predict reaction spontaneity, at 25 OC. Determine the value of this function, stating its units, and state the meaning of the sign obtained. Is CuSO4. 5H2O(s) ...
... b. Calculate ∆S0 for the reaction and state the meaning of the sign of ∆S0 obtained. c. Identify a thermodynamic function that can be used to predict reaction spontaneity, at 25 OC. Determine the value of this function, stating its units, and state the meaning of the sign obtained. Is CuSO4. 5H2O(s) ...
chapter 9: aqueous solutions
... 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ((s) usually), (aq) for ions on the right) Example 1: Solid Sodium carbonate dissolves in water ...
... 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ((s) usually), (aq) for ions on the right) Example 1: Solid Sodium carbonate dissolves in water ...
Chemistry Test Ch 11 Stoichiometry
... A. If 6.52 L of H2 react with excess nitrogen what volume of NH3 is produced? B. In order to produce 6.52 L of NH3 how many liters of nitrogen are needed? C. If 2.35 x 1024 molecules of NH3 is formed how many grams of hydrogen was used? 2. Use the following equation answer these questions: Mg + 2 HN ...
... A. If 6.52 L of H2 react with excess nitrogen what volume of NH3 is produced? B. In order to produce 6.52 L of NH3 how many liters of nitrogen are needed? C. If 2.35 x 1024 molecules of NH3 is formed how many grams of hydrogen was used? 2. Use the following equation answer these questions: Mg + 2 HN ...
Ch06 BalancingChemRxns
... Electrical current through water. Electrolysis of water into its elements. 1. Write the skeleton equation ...
... Electrical current through water. Electrolysis of water into its elements. 1. Write the skeleton equation ...
2 - Montville.net
... find, the unknown. The given and the unknown may be expressed in grams or moles. The masses in the reaction are usually expressed in grams. ...
... find, the unknown. The given and the unknown may be expressed in grams or moles. The masses in the reaction are usually expressed in grams. ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.