Julius Caesar biography
... chaotic. The tribune (Roman official) had been murdered, and his death was followed by great disorder in Rome. Caesar had crossed the Alps to watch the changing conditions in Rome. When the news of revolt in Gaul reached him, he recrossed the Alps and rallied his divided army. Caesar's forces lost s ...
... chaotic. The tribune (Roman official) had been murdered, and his death was followed by great disorder in Rome. Caesar had crossed the Alps to watch the changing conditions in Rome. When the news of revolt in Gaul reached him, he recrossed the Alps and rallied his divided army. Caesar's forces lost s ...
part one caius octavius (thurinus) 63–44 bc
... This brief mention in the Christmas story must have been the first time I heard of Augustus, and although it is hard to be precise with such early memories I must have been very young. Like most people who hear or read these words, I doubt that I thought much of them, and it was only later that my l ...
... This brief mention in the Christmas story must have been the first time I heard of Augustus, and although it is hard to be precise with such early memories I must have been very young. Like most people who hear or read these words, I doubt that I thought much of them, and it was only later that my l ...
CHAPTER X The Emperors Decius, Gallus, Aemilianus, Valerian
... inhabitants of Sweden were masters of a sufficient number of large vessels, with oars (Tacit. Germ. c. 44), and the distance is little more than one hundred miles from Cariscrona to the nearest ports of Pomerania and Prussia. Here, at length, we land on firm and historic ground. At least as early as ...
... inhabitants of Sweden were masters of a sufficient number of large vessels, with oars (Tacit. Germ. c. 44), and the distance is little more than one hundred miles from Cariscrona to the nearest ports of Pomerania and Prussia. Here, at length, we land on firm and historic ground. At least as early as ...
Sample Chapter 4 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... might receive from the Senate. There were two other assemblies, the more important being the Assembly of Tribes (Comitia Tributa), which was divided into thirty-five large voting blocs called tribes. Membership in a specific tribe was determined by a man’s residence. This tribal assembly elected off ...
... might receive from the Senate. There were two other assemblies, the more important being the Assembly of Tribes (Comitia Tributa), which was divided into thirty-five large voting blocs called tribes. Membership in a specific tribe was determined by a man’s residence. This tribal assembly elected off ...
File
... the collapse of the Roman Empire. During his 20 years as Emperor, he governed as an autocrat, without either advice or consent from the Senate. ...
... the collapse of the Roman Empire. During his 20 years as Emperor, he governed as an autocrat, without either advice or consent from the Senate. ...
Ancient Rome - Lesson Corner
... Italy. It looked as if Caesar was about to invade Rome. The consul Marcellus named Pompey the defender of the city. The Senate demanded that Caesar give up his post. Caesar answered by leading his army across the Rubicon River into Italy. This “crossing of the Rubicon” was an act of war. It was agai ...
... Italy. It looked as if Caesar was about to invade Rome. The consul Marcellus named Pompey the defender of the city. The Senate demanded that Caesar give up his post. Caesar answered by leading his army across the Rubicon River into Italy. This “crossing of the Rubicon” was an act of war. It was agai ...
The Praetorian Guard
... praetorian cohorts, in imitation of the select troop which attended the person of the praetor or Roman general. Augustus originally stationed only three thousand of them, three cohorts, at Rome, and dispersed the remainder in the adjacent Italian towns. Under Tiberius they were all assembled at Rome ...
... praetorian cohorts, in imitation of the select troop which attended the person of the praetor or Roman general. Augustus originally stationed only three thousand of them, three cohorts, at Rome, and dispersed the remainder in the adjacent Italian towns. Under Tiberius they were all assembled at Rome ...
Humanities 3 IV. Skepticism and Self-Knowledge
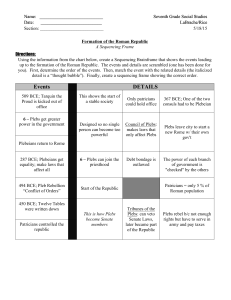
... History of the Roman Republic • Founded in 509 BC, after defeat of last king • Republic governed by two consuls, elected annually, and the senate • Power divided between the patricians (ancient noble families) and the plebeians (including property owners who lack noble status) • Throughout the hist ...
... History of the Roman Republic • Founded in 509 BC, after defeat of last king • Republic governed by two consuls, elected annually, and the senate • Power divided between the patricians (ancient noble families) and the plebeians (including property owners who lack noble status) • Throughout the hist ...
View/Open
... Shaping the Dioceses of Asiana and Africa in Late Antiquity there is only contemporary evidence for the itemisation of the provinces, however, not for the creation of the dioceses.12 Although in Lactantius‘s De mortibus persecutorum, a vicarii praefectorum is mentioned, there is no suggestion that ...
... Shaping the Dioceses of Asiana and Africa in Late Antiquity there is only contemporary evidence for the itemisation of the provinces, however, not for the creation of the dioceses.12 Although in Lactantius‘s De mortibus persecutorum, a vicarii praefectorum is mentioned, there is no suggestion that ...
Julius Caesar Executive Summary
... Without a doubt the most significant figure in the history of Rome, Julius Caesar paved the way both for the end of the republic and the creation of the empire under his nephew Octavian, or Augustus Caesar. As a general he led military operations in Britain and elsewhere, and as dictator of Rome, he ...
... Without a doubt the most significant figure in the history of Rome, Julius Caesar paved the way both for the end of the republic and the creation of the empire under his nephew Octavian, or Augustus Caesar. As a general he led military operations in Britain and elsewhere, and as dictator of Rome, he ...
etruscans and romans
... In 616 B.C., Lucius Tarquinius became the first Etruscan ruler of Rome. No one is certain whether Tarquinius took the throne from the Latin king by force or by cleverness. Nevertheless, his dynasty ruled Rome for more than 100 years. The Etruscans were more culturally advanced than the Latins. They ...
... In 616 B.C., Lucius Tarquinius became the first Etruscan ruler of Rome. No one is certain whether Tarquinius took the throne from the Latin king by force or by cleverness. Nevertheless, his dynasty ruled Rome for more than 100 years. The Etruscans were more culturally advanced than the Latins. They ...
Images of Rome in the Eighteenth Century
... 1968), 36 indicates that Cato’s Letters, rather than Locke or Montesquieu, were the most widely read and most cited authorities in Colonial America.. ...
... 1968), 36 indicates that Cato’s Letters, rather than Locke or Montesquieu, were the most widely read and most cited authorities in Colonial America.. ...
Chapter Six - The Roman Republic
... Romans ever had. The most famous incident in these wars is the Roman surrender at the Caudine Forks. A Roman army, in a hurry to help allies on the far side of the Samnite country, rushed headlong into a trap almost as soon as they had crossed the Samnite border. They had to go through one mountain ...
... Romans ever had. The most famous incident in these wars is the Roman surrender at the Caudine Forks. A Roman army, in a hurry to help allies on the far side of the Samnite country, rushed headlong into a trap almost as soon as they had crossed the Samnite border. They had to go through one mountain ...
Rummler Karl Rummler Ms. Bergen English 10
... as “Poor Uncle Claudius” (Graves 3), but as a great emperor who widely expanded the Roman Empire. Claudius Caesar used the money from the conquests into rebuilding Rome. He rebuilt roads, aqueducts, temples, and the Theatre of Pompey. In addition to rebuilding, Claudius had built many victory monume ...
... as “Poor Uncle Claudius” (Graves 3), but as a great emperor who widely expanded the Roman Empire. Claudius Caesar used the money from the conquests into rebuilding Rome. He rebuilt roads, aqueducts, temples, and the Theatre of Pompey. In addition to rebuilding, Claudius had built many victory monume ...
The Nobility under Augustus Spencer Williams
... Republic shifted. The culture of Republican nobility with its themes of balance, mutual celebration, and cooperation, yielded to the force of Augustus. In the new culture that emerged in its place, the nobility were dependent on a princeps, “the first man.” While the scholarship on this transition p ...
... Republic shifted. The culture of Republican nobility with its themes of balance, mutual celebration, and cooperation, yielded to the force of Augustus. In the new culture that emerged in its place, the nobility were dependent on a princeps, “the first man.” While the scholarship on this transition p ...
CHAPTER 5 The Roman Empire
... In Res gestae divi Augusti (The Achievements of the Divine Augustus), a docu ment composed shortly before his death and left to be published with his will, Augustus gave an account of those achievements for which he wanted to be re membered. A careful reading reveals the image Augustus chose to pr ...
... In Res gestae divi Augusti (The Achievements of the Divine Augustus), a docu ment composed shortly before his death and left to be published with his will, Augustus gave an account of those achievements for which he wanted to be re membered. A careful reading reveals the image Augustus chose to pr ...