10 - Parkway C-2
... An early example is the room that gives its name to the Villa of Mysteries at Pompeii. Many scholars believe this was a chamber used for private celebrations of the rites of the Greek god Dionysos (Roman Bacchus). Dionysos was the focus of an unofficial mystery religion among women in Italy at the t ...
... An early example is the room that gives its name to the Villa of Mysteries at Pompeii. Many scholars believe this was a chamber used for private celebrations of the rites of the Greek god Dionysos (Roman Bacchus). Dionysos was the focus of an unofficial mystery religion among women in Italy at the t ...
Plebeians win victory for the rule of law in Ancient Rome, 449 BCE
... nostalgic for the form of government they had been so hasty in replacing. Eventually, the two new tables of law were added to the original ten, and if it could be brought to a vote in the centuries’ assembly, the decemvirate could be retired. But the decemvirs never called for the election. When the ...
... nostalgic for the form of government they had been so hasty in replacing. Eventually, the two new tables of law were added to the original ten, and if it could be brought to a vote in the centuries’ assembly, the decemvirate could be retired. But the decemvirs never called for the election. When the ...
Section Two: Africa`s Carthage
... nearly touched the water. Only a handful of men could march side by side. The mist from the lake was thick, and the Romans did not see Hannibal’s men hiding behind the mountain slopes. They saw only the enemy troops ahead of them. The Romans charged. They thought it was an enemy camp they were about ...
... nearly touched the water. Only a handful of men could march side by side. The mist from the lake was thick, and the Romans did not see Hannibal’s men hiding behind the mountain slopes. They saw only the enemy troops ahead of them. The Romans charged. They thought it was an enemy camp they were about ...
Julius Caesar - powayusd.com
... Caesar was now master of Rome and made himself consul and dictator. He used his power to carry out muchneeded reform, relieving debt, enlarging the senate, building the Forum and revising the calendar. Dictatorship was always regarded a temporary position but in 44 BC, Caesar took it for life. His s ...
... Caesar was now master of Rome and made himself consul and dictator. He used his power to carry out muchneeded reform, relieving debt, enlarging the senate, building the Forum and revising the calendar. Dictatorship was always regarded a temporary position but in 44 BC, Caesar took it for life. His s ...
Explaining the Change from Republic to Principle in Rome
... theories are without any specific merits and that they do not contribute in any way to the explanation of the great change in the Roman world. But they are not aiming, it must be said, at the basic and crucial processes, which led from Republic to Monarchy. To take my first example, which is represe ...
... theories are without any specific merits and that they do not contribute in any way to the explanation of the great change in the Roman world. But they are not aiming, it must be said, at the basic and crucial processes, which led from Republic to Monarchy. To take my first example, which is represe ...
Introduction
... “wicked” emperors (at least by the senatorial class, which has provided us with most of our source material and which suffered most from his paranoia and cruelty; the general population seemed generally indifferent to him). He is one to whom Pliny refers when he speaks of a “bad prince”. Domitian wa ...
... “wicked” emperors (at least by the senatorial class, which has provided us with most of our source material and which suffered most from his paranoia and cruelty; the general population seemed generally indifferent to him). He is one to whom Pliny refers when he speaks of a “bad prince”. Domitian wa ...
PDF sample
... a. It became stronger and well-protected. b. It lasted for 500 more years. c. It was destroyed and all of its treasures were taken. d. It was soon divided into 3 smaller parts. 11. Which of these tribes did not invade Rome? a. the Huns b. the Aryans c. the Visigoths d. the Vandals C. True or False. ...
... a. It became stronger and well-protected. b. It lasted for 500 more years. c. It was destroyed and all of its treasures were taken. d. It was soon divided into 3 smaller parts. 11. Which of these tribes did not invade Rome? a. the Huns b. the Aryans c. the Visigoths d. the Vandals C. True or False. ...
- SAS
... placed on both descent and antiquity in the traditional societies of the ancient world, and on a familiar tactic through which the movements and acts of key individuals – heroes, kings, founders, ancestors – were made to stand proxy for the history of entire peoples who claimed them. This wide lay-b ...
... placed on both descent and antiquity in the traditional societies of the ancient world, and on a familiar tactic through which the movements and acts of key individuals – heroes, kings, founders, ancestors – were made to stand proxy for the history of entire peoples who claimed them. This wide lay-b ...
Zenobia and the Rebellion of The Palmyrene Empire
... fact is apparent to historians, then it was probably apparent to enemies of Rome at the time (ie) other powers saw that Rome was not as mighty as it used to be. Finally, since Zenobia's rebellion, she has been held up as an example of a powerful female leader during a time when it was very difficult ...
... fact is apparent to historians, then it was probably apparent to enemies of Rome at the time (ie) other powers saw that Rome was not as mighty as it used to be. Finally, since Zenobia's rebellion, she has been held up as an example of a powerful female leader during a time when it was very difficult ...
The Lost Legions of Augustus
... what kind of military leader Varus really was, some have defended him, but most ancient Romans have blasted his abilities. It is difficult to determine the true nature of the man, Varus. Velleius Paterculus, who knew Varus personally, had only bad words for him, suggesting he was incompetent as a m ...
... what kind of military leader Varus really was, some have defended him, but most ancient Romans have blasted his abilities. It is difficult to determine the true nature of the man, Varus. Velleius Paterculus, who knew Varus personally, had only bad words for him, suggesting he was incompetent as a m ...
The Torch Bearer and the Tutor: Prevalent
... Cromer, for example, thought that the notion of imperialism, ‘’as we understand, and as the Romans, with many notable differences, understood the term” was in essence the same24. In Ancient and Modern Imperialism he proceeds to argue that Britain’s situation regarding its imperial role resembled Rom ...
... Cromer, for example, thought that the notion of imperialism, ‘’as we understand, and as the Romans, with many notable differences, understood the term” was in essence the same24. In Ancient and Modern Imperialism he proceeds to argue that Britain’s situation regarding its imperial role resembled Rom ...
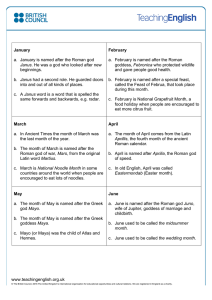
www.teachingenglish.org.uk January a. January is named after the
... the emperor had won eight great battles in c. July is anti-boredom month when people are his lifetime. encouraged to do things to stop getting bored. c. In English, august also means respected. September ...
... the emperor had won eight great battles in c. July is anti-boredom month when people are his lifetime. encouraged to do things to stop getting bored. c. In English, august also means respected. September ...
Option 1 - The origins of Rome - The kings - Translations
... help from the famously strong Etruscans and their king Mezentius who was ruling in Caere, which was a wealthy city then. Ever since the start of the new city being built, Mezentius was not happy and he thought that the Trojans’ power was growing much too fast to be safe for the neighbours so gladly ...
... help from the famously strong Etruscans and their king Mezentius who was ruling in Caere, which was a wealthy city then. Ever since the start of the new city being built, Mezentius was not happy and he thought that the Trojans’ power was growing much too fast to be safe for the neighbours so gladly ...
Western Civ. IE
... of Italy, on the other side of the Tiber River from the Latins. Because they were civilized and the Latins were not, they were able to conquer and to rule some of the Latins for a brief time. Around 575 B.C., one band of Etruscans crossed the Tiber and took over the Latin village overlooking the riv ...
... of Italy, on the other side of the Tiber River from the Latins. Because they were civilized and the Latins were not, they were able to conquer and to rule some of the Latins for a brief time. Around 575 B.C., one band of Etruscans crossed the Tiber and took over the Latin village overlooking the riv ...
Military service and cultural identity in the auxilia. In
... them (Apul., Met. 9.41). The sacrarnentum is known to have been repeated on 3 January and on the anniversary of the emperor's accession, and may even have been taken daily (Davies 1989, 47). It was therefore a sacred and constant reminder of the soldier's special r61e in society. Irrespective of his ...
... them (Apul., Met. 9.41). The sacrarnentum is known to have been repeated on 3 January and on the anniversary of the emperor's accession, and may even have been taken daily (Davies 1989, 47). It was therefore a sacred and constant reminder of the soldier's special r61e in society. Irrespective of his ...
Lesson I ideal citizen of a republic In the beginning Rome, too, was
... painting in vivid colors the brutal lust of Sextus, the rape of the innocent Lucretia and her pitiful death, and the sadness of her father, for whom the cause of her death was even worse than the death itself. ...
... painting in vivid colors the brutal lust of Sextus, the rape of the innocent Lucretia and her pitiful death, and the sadness of her father, for whom the cause of her death was even worse than the death itself. ...
Ancient Roman Clothing
... Children wore a special locket around their neck, given to them at birth, called a bulla. It contained an amulet as a protection against evil and was worn on a chain, cord, or strap. ...
... Children wore a special locket around their neck, given to them at birth, called a bulla. It contained an amulet as a protection against evil and was worn on a chain, cord, or strap. ...
World History Connections to Today
... center of Italy but are not too rugged. Fertile plains supported a growing population. ...
... center of Italy but are not too rugged. Fertile plains supported a growing population. ...