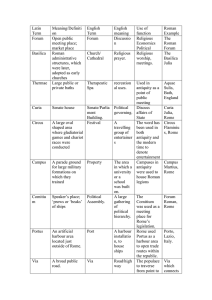
3 Branches of Early Roman Government
... (1) ___________________ Instead of a king, the Romans preferred having these at the head of their government. (2) ___________________ A “republic” is a type of government in which representatives of the people make the laws. Was Rome a republic? (yes or no) (3) ___________________ They were rich lan ...
... (1) ___________________ Instead of a king, the Romans preferred having these at the head of their government. (2) ___________________ A “republic” is a type of government in which representatives of the people make the laws. Was Rome a republic? (yes or no) (3) ___________________ They were rich lan ...
Rome Geography Worksheet
... Rome, Ostia, Syracuse, Carthage, Pompeii, Brindisium, Tarentum peoples [purple ink]: Latins, Gauls, Etruscans, Greeks other [black ink]: Magna Graecia 2. What natural/geographic advantages did the city of Rome have? 3. How was Rome's geography different from that of Greece? How was it similar? 4. Wh ...
... Rome, Ostia, Syracuse, Carthage, Pompeii, Brindisium, Tarentum peoples [purple ink]: Latins, Gauls, Etruscans, Greeks other [black ink]: Magna Graecia 2. What natural/geographic advantages did the city of Rome have? 3. How was Rome's geography different from that of Greece? How was it similar? 4. Wh ...
3.1 Early Rome
... The Etruscans lived North on Tiber River and had the biggest influence on the early Romans. Many things we think of as being Roman were adopted from the Etruscans. They enjoyed chariot races and gladiator fights, built aches, aquaducts and sewers. They were also important in shaping the government i ...
... The Etruscans lived North on Tiber River and had the biggest influence on the early Romans. Many things we think of as being Roman were adopted from the Etruscans. They enjoyed chariot races and gladiator fights, built aches, aquaducts and sewers. They were also important in shaping the government i ...
THE GREAT QUESTIONS FROM HISTORY – Term 1 Ancient Rome
... 22. Rome fought against which civilisation in the two Punic wars? 23. What does the adjective Punic mean? 24. Who was the famous leader who fought against Rome in the second Punic War? 25. What was the name given to the period of peace during the first and second centuries AD when the empire was sta ...
... 22. Rome fought against which civilisation in the two Punic wars? 23. What does the adjective Punic mean? 24. Who was the famous leader who fought against Rome in the second Punic War? 25. What was the name given to the period of peace during the first and second centuries AD when the empire was sta ...
Name: Date - MrDowling.com
... The Patricians and the Plebeians Sometime before the first surviving written historical account, Rome was controlled by the Etruscans, a brutal civilization from the northern part of the Italian peninsula. Etruscans kings rained terror for more than a century until the Romans rebelled and expelled t ...
... The Patricians and the Plebeians Sometime before the first surviving written historical account, Rome was controlled by the Etruscans, a brutal civilization from the northern part of the Italian peninsula. Etruscans kings rained terror for more than a century until the Romans rebelled and expelled t ...
The Patricians and the Plebeians
... The Patricians and the Plebeians Sometime before the first surviving written historical account, Rome was controlled by the Etruscans, a brutal civilization from the northern part of the Italian peninsula. Etruscans kings rained terror for more than a century until the Romans rebelled and expelled t ...
... The Patricians and the Plebeians Sometime before the first surviving written historical account, Rome was controlled by the Etruscans, a brutal civilization from the northern part of the Italian peninsula. Etruscans kings rained terror for more than a century until the Romans rebelled and expelled t ...
Rome`s Creation of a Mediterranean Empire
... Some credit the greed and aggression for the propelled expansion Romans were quick to seize an opportunity to present themselves Conquest to Italy sparked by friction between Apennines Apennines, whose livelihood depended on their ability to drive their herds to seasonal grazing grounds Had rose to ...
... Some credit the greed and aggression for the propelled expansion Romans were quick to seize an opportunity to present themselves Conquest to Italy sparked by friction between Apennines Apennines, whose livelihood depended on their ability to drive their herds to seasonal grazing grounds Had rose to ...
The engineering of ancient Roman roads
... to think, that the legionary troop train was made up entirely of pack-animals, and that wagons were used only between campaigns by the army train”. (J. P. Roth: The Logistics of the Roman ...
... to think, that the legionary troop train was made up entirely of pack-animals, and that wagons were used only between campaigns by the army train”. (J. P. Roth: The Logistics of the Roman ...
The Government of Rome and the Cursus Honorum_edited
... walls of the city and killed his own brother for crossing them without permission. Indeed, the name Rome is said to have come from Romulus, who became the first king of Rome. A line of kings then ruled Rome, though whether or not they truly existed, and how exaggerated are their deeds, is unknown. T ...
... walls of the city and killed his own brother for crossing them without permission. Indeed, the name Rome is said to have come from Romulus, who became the first king of Rome. A line of kings then ruled Rome, though whether or not they truly existed, and how exaggerated are their deeds, is unknown. T ...
ANCIENT ROME REVIEW 1. Who were the major powers struggling
... Paving the way for a change from a republic to an empire 18. Why was Augustus considered to be one of the most capable of all Rome’s Emperors? He forced Rome into a powerful Empire; he expanded the empire and made it bigger than ever; he shared some of his absolute powers with the senate. 19. What i ...
... Paving the way for a change from a republic to an empire 18. Why was Augustus considered to be one of the most capable of all Rome’s Emperors? He forced Rome into a powerful Empire; he expanded the empire and made it bigger than ever; he shared some of his absolute powers with the senate. 19. What i ...
End of the Empire
... Upon his death, the empire was divided between his two sons, Arcadius (East) and Honorius (West) ...
... Upon his death, the empire was divided between his two sons, Arcadius (East) and Honorius (West) ...
Ancient Greece - Calaveras Unified School District
... l. He was murdered by a group of senators on March 15, 44 BC, “Ides of March”. 4. The Republic dies after Caesar’s death. a. A third civil war creates a great leader, Octavian (Augustus). b. He is part of a 2nd Triumvirate, Octavian (grandson of Caesar), Lepidus (powerful politician) and Marc Antony ...
... l. He was murdered by a group of senators on March 15, 44 BC, “Ides of March”. 4. The Republic dies after Caesar’s death. a. A third civil war creates a great leader, Octavian (Augustus). b. He is part of a 2nd Triumvirate, Octavian (grandson of Caesar), Lepidus (powerful politician) and Marc Antony ...
Section Summary Key Terms and People
... displayed in the forum, Rome’s public meeting place. Although the Romans continued to make laws, the Law of the Twelve Tables remained as the basis of Roman law. THE ROMAN FORUM The forum was the heart of Rome. All the important government buildings and religious temples were there. It was also the ...
... displayed in the forum, Rome’s public meeting place. Although the Romans continued to make laws, the Law of the Twelve Tables remained as the basis of Roman law. THE ROMAN FORUM The forum was the heart of Rome. All the important government buildings and religious temples were there. It was also the ...
6.2 – The Roman Empire
... • Religion – The Romans were polytheistic, and like the Greeks, had gods and goddesses for just about everything. Religion was closely linked to politics, and the gods and goddesses were seen as symbols of the state. • Society – The Roman elite lived extravagantly and the poor lived miserably. The R ...
... • Religion – The Romans were polytheistic, and like the Greeks, had gods and goddesses for just about everything. Religion was closely linked to politics, and the gods and goddesses were seen as symbols of the state. • Society – The Roman elite lived extravagantly and the poor lived miserably. The R ...
The Daily Life of Ancient Romans
... – Romance languages (French, Spanish, Italian, English, etc.) ...
... – Romance languages (French, Spanish, Italian, English, etc.) ...
Ancient Rome Notes
... Executive (Two Consuls) similar to kings, they commanded the army and directed the government; power was limited because their term was only one year long and the a consul could not be re-elected for ten years; one consul could always override, or veto, the other’s decisions Legislative a. Senate ...
... Executive (Two Consuls) similar to kings, they commanded the army and directed the government; power was limited because their term was only one year long and the a consul could not be re-elected for ten years; one consul could always override, or veto, the other’s decisions Legislative a. Senate ...
Roman Empire: Guided Notes
... and conquered the western half. They were more or less forced into Rome because all the Germanic tribes were deathly afraid of the _____________. Their great leader_____________________, was on his way to conquering possibly all of the Empire but was stopped in his tracks by ________________. Histor ...
... and conquered the western half. They were more or less forced into Rome because all the Germanic tribes were deathly afraid of the _____________. Their great leader_____________________, was on his way to conquering possibly all of the Empire but was stopped in his tracks by ________________. Histor ...
Romans and dacians
... The roman art has in vew not only the one put in shape on the italian gronds, but also the one that the romans have borown from the lads they conquerd: Asia Minor, Germany, Dacia and others. The romans have taken very much from the originality that other people have developed. After the conquest of ...
... The roman art has in vew not only the one put in shape on the italian gronds, but also the one that the romans have borown from the lads they conquerd: Asia Minor, Germany, Dacia and others. The romans have taken very much from the originality that other people have developed. After the conquest of ...
The Roman Republic
... has a tripartite system. The U.S. system of checks and balances makes sure that one branch of the government doesn’t have too much power. This system is like the veto, which limited the power of Roman consuls. In addition, like Rome, the United States has a written constitution on which its governme ...
... has a tripartite system. The U.S. system of checks and balances makes sure that one branch of the government doesn’t have too much power. This system is like the veto, which limited the power of Roman consuls. In addition, like Rome, the United States has a written constitution on which its governme ...
C H A P T E R 4: Classical Civilization in the Mediterranean: Greece
... Despite the efforts of emperors like Diocletian and Constantine, the ensuing 250 years brought a slow but decisive fall. Greek and Roman Political Institutions Greece and Rome featured an important variety of political forms. Both tended to emphasize aristocratic rule, but there were significant ...
... Despite the efforts of emperors like Diocletian and Constantine, the ensuing 250 years brought a slow but decisive fall. Greek and Roman Political Institutions Greece and Rome featured an important variety of political forms. Both tended to emphasize aristocratic rule, but there were significant ...