Vocabulary Review for Chapter 8 – The Rise of Rome
... Draw lines between terms that connect and explain the connection between those terms on the lines you use to connect them. Multiple terms may connect to one another. ...
... Draw lines between terms that connect and explain the connection between those terms on the lines you use to connect them. Multiple terms may connect to one another. ...
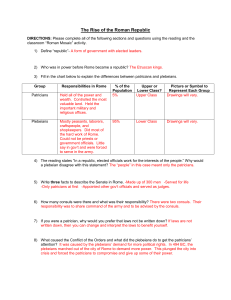
The Rise of the Roman Republic DIRECTIONS: Please complete all
... 9) In four sentences, explain how the conflict changed things for the plebeians. Make sure you use the words or phrases tribunes, veto, Council of the Plebs, and laws being written down. Due to the crisis, the patricians agreed to allow the plebeians to elect officials to the Tribunes of the Plebs, ...
... 9) In four sentences, explain how the conflict changed things for the plebeians. Make sure you use the words or phrases tribunes, veto, Council of the Plebs, and laws being written down. Due to the crisis, the patricians agreed to allow the plebeians to elect officials to the Tribunes of the Plebs, ...
complex roman numerals
... a. 1976 (year of Mr. Chang’s birth) b. 2005 (the year this document was made) c. 2046 (title of a movie) d. 1776 (signing of the Declaration of Independence) e. 753 (founding of Rome as a monarchy, i.e. rule by kings, BC) f. 509 (end of Monarchy; beginning of the Roman Republic, BC) g. 49 (Caesar cr ...
... a. 1976 (year of Mr. Chang’s birth) b. 2005 (the year this document was made) c. 2046 (title of a movie) d. 1776 (signing of the Declaration of Independence) e. 753 (founding of Rome as a monarchy, i.e. rule by kings, BC) f. 509 (end of Monarchy; beginning of the Roman Republic, BC) g. 49 (Caesar cr ...
2013 njcl Roman History
... 42. What military colony protected Campania from the Samnites? a. Arpinum b. Sentinum c. Fregellae d. Rhegium 43. Which historian determined the date of 753 B.C. for the founding of Rome? a .Eratosthenes b. Livy c. Terentius Varro d. Cato the Elder 44. Which king established the cult of Diana on the ...
... 42. What military colony protected Campania from the Samnites? a. Arpinum b. Sentinum c. Fregellae d. Rhegium 43. Which historian determined the date of 753 B.C. for the founding of Rome? a .Eratosthenes b. Livy c. Terentius Varro d. Cato the Elder 44. Which king established the cult of Diana on the ...
AP World History
... The Army of Rome • The Imperial Roman Legion at full strength was comprised of 6,000 men. • The cohorts each had 480 men. • Each of these was broken down further into 6 "centuries" of 80 men. • There was a 120 man cavalry unit attached to the legion. • Possibly as much as 60 artillery pieces. ...
... The Army of Rome • The Imperial Roman Legion at full strength was comprised of 6,000 men. • The cohorts each had 480 men. • Each of these was broken down further into 6 "centuries" of 80 men. • There was a 120 man cavalry unit attached to the legion. • Possibly as much as 60 artillery pieces. ...
Chapter 5 and 6 Outline
... rule by themselves, so they divided the empire into three equal parts. XXI The Legacy of Alexander A. Across his enormous empire, Alexander founded many new cities and named most of them after him. B. Gradually, a blending of eastern and western cultures occurred. C. At the very heart of the Helleni ...
... rule by themselves, so they divided the empire into three equal parts. XXI The Legacy of Alexander A. Across his enormous empire, Alexander founded many new cities and named most of them after him. B. Gradually, a blending of eastern and western cultures occurred. C. At the very heart of the Helleni ...
Rome Chapter 10 packet
... about the early life of Spartacus, but he may have been a nomad. Spartacus served in the Roman army, but seems to have left the army to form a bandit group. Spartacus led the group on raids of their own. Eventually Spartacus was captured by the Romans. The Romans made him a slave and trained him to ...
... about the early life of Spartacus, but he may have been a nomad. Spartacus served in the Roman army, but seems to have left the army to form a bandit group. Spartacus led the group on raids of their own. Eventually Spartacus was captured by the Romans. The Romans made him a slave and trained him to ...
Roman Architecture
... Tile covered concrete quickly supplanted marble as the primary building material and more daring buildings soon followed, with great pillars supporting broad arches and domes rather than dense lines of columns suspending flat architraves. The freedom of concrete also inspired the colonnade screen, a ...
... Tile covered concrete quickly supplanted marble as the primary building material and more daring buildings soon followed, with great pillars supporting broad arches and domes rather than dense lines of columns suspending flat architraves. The freedom of concrete also inspired the colonnade screen, a ...
TEST THREE NOTES
... • Between 750 and 600 BC established colonies in southern Italy and Sicily. • Influenced Roman culture – Literature – Myths – Alphabet – Architecture - arch ...
... • Between 750 and 600 BC established colonies in southern Italy and Sicily. • Influenced Roman culture – Literature – Myths – Alphabet – Architecture - arch ...
Freshmen Midterm Review Sheet
... Greece is a mountainous peninsula. The Greeks developed city-states (small independent cities) because of the mountains. Minoan civilization was on Crete. Myceneaens fought the Trojan War. The story of the Trojan War is told in the Iliad and the Odyssey orally retold by the blind poet Homer. Sparta ...
... Greece is a mountainous peninsula. The Greeks developed city-states (small independent cities) because of the mountains. Minoan civilization was on Crete. Myceneaens fought the Trojan War. The story of the Trojan War is told in the Iliad and the Odyssey orally retold by the blind poet Homer. Sparta ...
Conflict Between Classes
... concerns to the government. Tribunes could also veto government decisions. Later, plebeians were even allowed to become consuls, and marriages between plebeians and patricians were made legal. In 287 b.c., the plebeians won another important political victory. The Council of the Plebs was given the ...
... concerns to the government. Tribunes could also veto government decisions. Later, plebeians were even allowed to become consuls, and marriages between plebeians and patricians were made legal. In 287 b.c., the plebeians won another important political victory. The Council of the Plebs was given the ...
document
... 1. What are the dates for the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire? 2. Explain the meaning of the Latin phrase ...
... 1. What are the dates for the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire? 2. Explain the meaning of the Latin phrase ...
The Punic Wars
... responded Rome had built a larger navy and controlled the sea even though the Carthigininas were better sailors, decided to cross the Alps w/ war elephants and force Rome to recall all of their troops, Hannibal croosed the Alps w/ 26,000 infantry, 4,000 calvary and 20 of 60 war elephants, aided by t ...
... responded Rome had built a larger navy and controlled the sea even though the Carthigininas were better sailors, decided to cross the Alps w/ war elephants and force Rome to recall all of their troops, Hannibal croosed the Alps w/ 26,000 infantry, 4,000 calvary and 20 of 60 war elephants, aided by t ...
Document
... cross into the city. With the help of two officers, and a pile of corpses to hide behind, Horatius defended the bridge. Just as the bridge fell behind him, leaving Horatius facing the Etruscans, he was shot with an arrow in his behind, and dove, in full armor, into the water and swam to safety on th ...
... cross into the city. With the help of two officers, and a pile of corpses to hide behind, Horatius defended the bridge. Just as the bridge fell behind him, leaving Horatius facing the Etruscans, he was shot with an arrow in his behind, and dove, in full armor, into the water and swam to safety on th ...
Rome Notes
... 1. Spread of slavery into agricultural system: pushed farmers into cities: too many Plebeians, not enough jobs 2. Migration of small farmers into cities-unemployment 3. Civil War over the power of Julius Caesar 4. Inflation: devaluation of Roman currency- didn’t have enough money to buy things they ...
... 1. Spread of slavery into agricultural system: pushed farmers into cities: too many Plebeians, not enough jobs 2. Migration of small farmers into cities-unemployment 3. Civil War over the power of Julius Caesar 4. Inflation: devaluation of Roman currency- didn’t have enough money to buy things they ...
Chapter 4: Classical Civilization in the Mediterranean: Greece and
... people who took over the Balkan Peninsula by 1700 BCE • Early kingdom of Mycenaeans around 1400s – Kingdom in Homer’s epics about the Trojan War ...
... people who took over the Balkan Peninsula by 1700 BCE • Early kingdom of Mycenaeans around 1400s – Kingdom in Homer’s epics about the Trojan War ...
Rome and Byzantine Lessons of Power
... Rome - The World’s First Republic A republic is a government where political powers are vested in the hands of representatives elected by citizens. Elected leaders, called Consuls ruled the city with the help of the elected Senate. • Consuls – The 2 Elected Rulers of Rome • Senators – The 300 Electe ...
... Rome - The World’s First Republic A republic is a government where political powers are vested in the hands of representatives elected by citizens. Elected leaders, called Consuls ruled the city with the help of the elected Senate. • Consuls – The 2 Elected Rulers of Rome • Senators – The 300 Electe ...