When did the Roman Empire fall? Lezing door Tom Holland (BBC
... Lezing door Tom Holland (BBC & University of Cambridge) In AD 476, Romulus Augustulus, emperor in line to Augustus, Trajan and Constantine, was deposed by a German chieftain. It is an event that in most history books is identified as marking the end of the Roman Empire. But did it? Tom Holland explo ...
... Lezing door Tom Holland (BBC & University of Cambridge) In AD 476, Romulus Augustulus, emperor in line to Augustus, Trajan and Constantine, was deposed by a German chieftain. It is an event that in most history books is identified as marking the end of the Roman Empire. But did it? Tom Holland explo ...
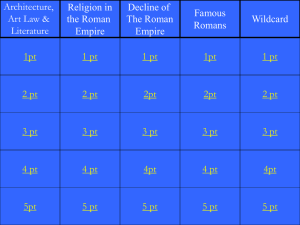
Jeopardy Example
... that the Roman Empire would be neutral with regard to religious worship and officially removed all obstacles to the practice of religions ...
... that the Roman Empire would be neutral with regard to religious worship and officially removed all obstacles to the practice of religions ...
The Decline of Rome - Christian Brothers High School
... Christians because they saw him as punishment from God for their sins. Weakened by internal and external problems, the Roman Empire gave away some of their lands to ...
... Christians because they saw him as punishment from God for their sins. Weakened by internal and external problems, the Roman Empire gave away some of their lands to ...
The Fall of the Roman Empire
... The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BCE. Law Rome's greatest achievement was its system of laws. Some of the features of this system include, men being equal under the law, having the right to face their accusers, and being considered innocent until proven guilty. Later, these laws were written do ...
... The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BCE. Law Rome's greatest achievement was its system of laws. Some of the features of this system include, men being equal under the law, having the right to face their accusers, and being considered innocent until proven guilty. Later, these laws were written do ...
Rome Notes Roman Values and Virtues • Greeks vs. Romans
... Spread into Eastern Med. –because many Greek states supported Carthage, the Romans justified their conquest of most of Greece and then Asia Minor ca 180-120 ...
... Spread into Eastern Med. –because many Greek states supported Carthage, the Romans justified their conquest of most of Greece and then Asia Minor ca 180-120 ...
TESTREVIEWANSWERKEYe..
... 5. What is the port city on the Bay of Naples? PUTEOLI 6. What were large farming estates worked by enslaved people? LATIFUNDIA 7. Who were the artisans, shopkeepers, and owners of small farms in ancient Rome? PLEBEIANS 8. What included Crassus, Pompey, and Julius Caesar? FIRST TRIUMVIRATE 9. What i ...
... 5. What is the port city on the Bay of Naples? PUTEOLI 6. What were large farming estates worked by enslaved people? LATIFUNDIA 7. Who were the artisans, shopkeepers, and owners of small farms in ancient Rome? PLEBEIANS 8. What included Crassus, Pompey, and Julius Caesar? FIRST TRIUMVIRATE 9. What i ...
Roman World Takes Shape
... A. Romans hated monarchy (rule by a king) B. In 509 BCE- the Roman Republic is ...
... A. Romans hated monarchy (rule by a king) B. In 509 BCE- the Roman Republic is ...
Roman Society
... answer the following questions 1. Describe the early settlements of Rome 2. How did the patricians control the Roman Republic 3. Why did Marcus feel that Lucius and the other patricians had taken advantage of them? 4. What changes did Marcus and the other plebeians want to make in Roman government 5 ...
... answer the following questions 1. Describe the early settlements of Rome 2. How did the patricians control the Roman Republic 3. Why did Marcus feel that Lucius and the other patricians had taken advantage of them? 4. What changes did Marcus and the other plebeians want to make in Roman government 5 ...
Chapter 38 The Legacy of Rome in the Modern World To what
... Chapter 38 The Legacy of Rome in the Modern World ...
... Chapter 38 The Legacy of Rome in the Modern World ...
The Fall of Rome
... Stoicism was particularly popular. They also took inspiration from Greek literature. Epics were popular, and a way for the Romans to promote their own themes and values. The poet Virgil wrote the Aeneid, the most famous piece of Latin literature. On a less serious note, the poet Ovid was famous ...
... Stoicism was particularly popular. They also took inspiration from Greek literature. Epics were popular, and a way for the Romans to promote their own themes and values. The poet Virgil wrote the Aeneid, the most famous piece of Latin literature. On a less serious note, the poet Ovid was famous ...
Western Civilization I Exam Review II
... Explain the factors involved in the spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire both before and after the conversion of Constantine. One historian has said that “Romans became Christians and Christianity became Roman.” How did both Christianity and Rome change as it became the official religion of th ...
... Explain the factors involved in the spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire both before and after the conversion of Constantine. One historian has said that “Romans became Christians and Christianity became Roman.” How did both Christianity and Rome change as it became the official religion of th ...
Ancient Rome - WordPress.com
... Not ruled by one person No final choice on what – may have evil to do intentions The money for being in Though it may not be government is spread spread evenly out ...
... Not ruled by one person No final choice on what – may have evil to do intentions The money for being in Though it may not be government is spread spread evenly out ...
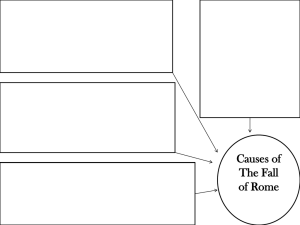
The Fall of the Roman Empire
... • Decline in trade and small industry • Labor shortage created by plague (fast spreading, deadly disease) • Decline in farm production • Roman money began to lose its value (inflation) ...
... • Decline in trade and small industry • Labor shortage created by plague (fast spreading, deadly disease) • Decline in farm production • Roman money began to lose its value (inflation) ...
Ancient Rome - Early Peoples
... had little say. Angry about their lack of representation, in 471 B.C.E. the common people refused to work. ...
... had little say. Angry about their lack of representation, in 471 B.C.E. the common people refused to work. ...
Study Guide
... 8. Carthage 9. Punic Wars 10. Ibes of March 11. Pax Romana 12. Colosseum 13. Gospels 14. Diaspora 15. Edict of Milan 16. Inflation 17. Constantinople ...
... 8. Carthage 9. Punic Wars 10. Ibes of March 11. Pax Romana 12. Colosseum 13. Gospels 14. Diaspora 15. Edict of Milan 16. Inflation 17. Constantinople ...
The glory that was Greece
... These Latins were the ancestors to the Romans Their villages grew into Rome, the city on 7 hills ...
... These Latins were the ancestors to the Romans Their villages grew into Rome, the city on 7 hills ...
Ancient Rome
... legacy- took idea that a written law can protect one person from another- put it into practice- Because it’s the laws means something to us- not necessarily in other cultures. tried to appeal to people through argument- idea of people deciding magistrates important in Rome- e.g. of Apostle Paul ...
... legacy- took idea that a written law can protect one person from another- put it into practice- Because it’s the laws means something to us- not necessarily in other cultures. tried to appeal to people through argument- idea of people deciding magistrates important in Rome- e.g. of Apostle Paul ...
THE RISE OF ROME
... • Raised by a female wolf • Found by a shepard and his wife • When grown killed the King and put real grandfather on throne • Brothers set up city of Rome on edge of Tiber • Brothers fight/Romulus kills Remus • Rome is born! ...
... • Raised by a female wolf • Found by a shepard and his wife • When grown killed the King and put real grandfather on throne • Brothers set up city of Rome on edge of Tiber • Brothers fight/Romulus kills Remus • Rome is born! ...
Fall of Rome
... • The use of slavery led to high unemployment • High taxes & Inflation • No more war plunder ...
... • The use of slavery led to high unemployment • High taxes & Inflation • No more war plunder ...
VI. Roman Citizenship - Mr Dombrowski`s Social Studies Class
... 4. Could hold approx. 50,000 spectators or more 5. Gladiators fought for glory, slaves for their lives 6. It was an absolute spectacle: violence, blood, brutality... all those things dudes like 7. What did this influence today? ...
... 4. Could hold approx. 50,000 spectators or more 5. Gladiators fought for glory, slaves for their lives 6. It was an absolute spectacle: violence, blood, brutality... all those things dudes like 7. What did this influence today? ...
Roman agriculture

Agriculture in ancient Rome was not only a necessity, but was idealized among the social elite as a way of life. Cicero considered farming the best of all Roman occupations. In his treatise On Duties, he declared that ""of all the occupations by which gain is secured, none is better than agriculture, none more profitable, none more delightful, none more becoming to a free man."" When one of his clients was derided in court for preferring a rural lifestyle, Cicero defended country life as ""the teacher of economy, of industry, and of justice"" (parsimonia, diligentia, iustitia). Cato, Columella, Varro and Palladius wrote handbooks on farming practice.The staple crop was spelt, and bread was the mainstay of every Roman table. In his treatise De agricultura (""On Farming"", 2nd century BC), Cato wrote that the best farm was a vineyard, followed by an irrigated garden, willow plantation, olive orchard, meadow, grain land, forest trees, vineyard trained on trees, and lastly acorn woodlands.Though Rome relied on resources from its many provinces acquired through conquest and warfare, wealthy Romans developed the land in Italy to produce a variety of crops. ""The people living in the city of Rome constituted a huge market for the purchase of food produced on Italian farms.""Land ownership was a dominant factor in distinguishing the aristocracy from the common person, and the more land a Roman owned, the more important he would be in the city. Soldiers were often rewarded with land from the commander they served. Though farms depended on slave labor, free men and citizens were hired at farms to oversee the slaves and ensure that the farms ran smoothly.