Viruses – Invisible Invaders, Amazing Allies
... ssRNA may be plus (+) or minus (-) sense (+)RNA genome can serve as mRNA and directly translated into protein (-)RNA genome cannot serve as mRNA and cannot be translated directly into protein ...
... ssRNA may be plus (+) or minus (-) sense (+)RNA genome can serve as mRNA and directly translated into protein (-)RNA genome cannot serve as mRNA and cannot be translated directly into protein ...
Structure, replication and repair of DNA
... discovered the structure of DNA Nearly beaten to the discovery by Rosalind Franklin (she would have won if she had not been socially isolated) Chemical make up had been known for 30 years, but not the three-dimensional structure, which would give a clue as to how it worked. Nucleotides - sugar ...
... discovered the structure of DNA Nearly beaten to the discovery by Rosalind Franklin (she would have won if she had not been socially isolated) Chemical make up had been known for 30 years, but not the three-dimensional structure, which would give a clue as to how it worked. Nucleotides - sugar ...
Viral capsid proteins bind to receptors on host cell membrane (outer
... bind to receptors on host cell membrane (outer part of host cell) ...
... bind to receptors on host cell membrane (outer part of host cell) ...
Viral Diseases and Human Evolution
... of Africa and coevolved with distinct human ethnic groups ever since. Herpes are also slow evolving DNA viruses with large genomes (White & Fenner 1986). Herpes viruses were shown to coevolve with distinct vertebrate lineages, possibly since the Devonian (McGeogh et al. 1995). Moreover, several pres ...
... of Africa and coevolved with distinct human ethnic groups ever since. Herpes are also slow evolving DNA viruses with large genomes (White & Fenner 1986). Herpes viruses were shown to coevolve with distinct vertebrate lineages, possibly since the Devonian (McGeogh et al. 1995). Moreover, several pres ...
REN Ee Chee
... HBV replication efficiency (Ng et al, PLoS Med 2:e163, 2005). By accurately describing both viral and host components that contribute to viral replication, this combined approach will provide elucidation of pathways and specific genes that will form targets for the development of anti-HBV therapy. A ...
... HBV replication efficiency (Ng et al, PLoS Med 2:e163, 2005). By accurately describing both viral and host components that contribute to viral replication, this combined approach will provide elucidation of pathways and specific genes that will form targets for the development of anti-HBV therapy. A ...
Chp 18 Viruses and Bacteria
... 14. List some characteristics that viruses share with living organisms, and explain why viruses do not fit our usual definition of life. 15. Provide evidence that viruses probably evolved from fragments of cellular nucleic acid. 16. Describe the structure of a bacterial chromosome. 17. Describe the ...
... 14. List some characteristics that viruses share with living organisms, and explain why viruses do not fit our usual definition of life. 15. Provide evidence that viruses probably evolved from fragments of cellular nucleic acid. 16. Describe the structure of a bacterial chromosome. 17. Describe the ...
DNA-independent ATPase activity of the Trichoplusia ni
... Autographa californica (Ac)MNPV in cells and larvae of T. ni. However, changes in only one or a few amino acids in the helicase (P143) of AcMNPV enable this virus to replicate in cells and larvae of Bombyx mori, where its replication is normally restricted (Maeda et al., 1993 ; Croizier et al., 1994 ...
... Autographa californica (Ac)MNPV in cells and larvae of T. ni. However, changes in only one or a few amino acids in the helicase (P143) of AcMNPV enable this virus to replicate in cells and larvae of Bombyx mori, where its replication is normally restricted (Maeda et al., 1993 ; Croizier et al., 1994 ...
Lecture 6 Quiz
... 4. Which of the correct functions defined in the previous exercise is the fastest? Hint. You will need to generate a very large string to test them on, and the function clock() from the time module to time each function. ...
... 4. Which of the correct functions defined in the previous exercise is the fastest? Hint. You will need to generate a very large string to test them on, and the function clock() from the time module to time each function. ...
24 Hour Fluorescent Virus Titration Assay (96
... Now remove medium from Row D 1-6 up to Row A 1-6; then add the virus from the dilution plate. Use the same tips to add the virus when moving up from Row H 1-6 to Row A 1-6, then change tips for Row H 7-12 through Row A 7-12. Take note of the time the plate is put back into the incubator. Incubate th ...
... Now remove medium from Row D 1-6 up to Row A 1-6; then add the virus from the dilution plate. Use the same tips to add the virus when moving up from Row H 1-6 to Row A 1-6, then change tips for Row H 7-12 through Row A 7-12. Take note of the time the plate is put back into the incubator. Incubate th ...
DNA Structure and history10
... – purified DNA & proteins from Streptococcus bacteria – injected protein into bacteria ...
... – purified DNA & proteins from Streptococcus bacteria – injected protein into bacteria ...
Document
... protooncogene. A normal cellular copy goes bad, which mutates it, that does something to the gene and now converts the cell to cancer. The protooncogene goes out of control and converts to cancer. That’s the history of RNA tumor viruses. There are other RNA viruses that are thought to have some invo ...
... protooncogene. A normal cellular copy goes bad, which mutates it, that does something to the gene and now converts the cell to cancer. The protooncogene goes out of control and converts to cancer. That’s the history of RNA tumor viruses. There are other RNA viruses that are thought to have some invo ...
recombinant dna technology
... • FIRST, THE PLASMID IS TREATED WITH THE SAME RESTRICTION ENZYME AS WAS USED TO CREATE THE DNA FRAGMENT • THE RESTRICTION ENZYME WILL CUT THE PLASMID AT THE SAME RECOGNITION SEQUENCES, PRODUCING THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PA ...
... • FIRST, THE PLASMID IS TREATED WITH THE SAME RESTRICTION ENZYME AS WAS USED TO CREATE THE DNA FRAGMENT • THE RESTRICTION ENZYME WILL CUT THE PLASMID AT THE SAME RECOGNITION SEQUENCES, PRODUCING THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PA ...
Sequence analysis of selected nucleotide sequences of abortogenic
... Sections of the genome of the field isolate coding for the main surface glycoproteins of EHV-1 were selected for surveying the Prostejov field isolate and for determining the stability of the isolated virus during the passaging in the cell culture. These glycoproteins are crucial both for the proper ...
... Sections of the genome of the field isolate coding for the main surface glycoproteins of EHV-1 were selected for surveying the Prostejov field isolate and for determining the stability of the isolated virus during the passaging in the cell culture. These glycoproteins are crucial both for the proper ...
ViRUSES AND PRiONS
... and certain cells within those hosts An important characteristic of a virus is its host range—the spectrum of hosts that it is able to infect. Some viruses infect only animals, while others infect only plants, fungi, and so forth. Even within a group such as animal viruses, however, a given virus ca ...
... and certain cells within those hosts An important characteristic of a virus is its host range—the spectrum of hosts that it is able to infect. Some viruses infect only animals, while others infect only plants, fungi, and so forth. Even within a group such as animal viruses, however, a given virus ca ...
No Slide Title
... 7. Final report: 30 points Assignment 1 Pick an enzyme/organism combination • Try to convince the group in 5-10 minutes why yours is best ...
... 7. Final report: 30 points Assignment 1 Pick an enzyme/organism combination • Try to convince the group in 5-10 minutes why yours is best ...
Solving the Structure of DNA
... 7. Complete the table by estimating the percentages of each based on Chargaff’s rule DNA sample ...
... 7. Complete the table by estimating the percentages of each based on Chargaff’s rule DNA sample ...
Recombinant DNA Technology for the non
... Geneticists have known for a long time how to isolate DNA from cells. Geneticists have known for a long time how to chop DNA into small pieces. What geneticists did not know how to do until the early 1970s was to replicate small fragments of DNA. ...
... Geneticists have known for a long time how to isolate DNA from cells. Geneticists have known for a long time how to chop DNA into small pieces. What geneticists did not know how to do until the early 1970s was to replicate small fragments of DNA. ...
Complete Nucleotide Sequence of a South African Isolate of
... vector is present, and it is considered the most important viral pathogen of grapevine in Europe. In South Africa, GFLV infections occur predominantly in the Breede River Valley in the Western Cape, due to the prevalence of its nematode vector, Xiphinema index [2]. GFLV is classified in the genus Ne ...
... vector is present, and it is considered the most important viral pathogen of grapevine in Europe. In South Africa, GFLV infections occur predominantly in the Breede River Valley in the Western Cape, due to the prevalence of its nematode vector, Xiphinema index [2]. GFLV is classified in the genus Ne ...
Viral virulence genes
... Virions enter but encounter a block before RT RestricNon mediated by species-‐specific protein TRIM5α that acts on the viral capsid ...
... Virions enter but encounter a block before RT RestricNon mediated by species-‐specific protein TRIM5α that acts on the viral capsid ...
P.324doc
... proportions: 30% A, 15% T, 35% G, and 20% C, since bases are complementary. 28. The roles of the following enzymes in DNA replication are outlined below: DNA ligase: joins DNA fragments by catalyzing the formation of a bond between the 3' hydroxyl group and the 5' phosphate group on the sugar-phosph ...
... proportions: 30% A, 15% T, 35% G, and 20% C, since bases are complementary. 28. The roles of the following enzymes in DNA replication are outlined below: DNA ligase: joins DNA fragments by catalyzing the formation of a bond between the 3' hydroxyl group and the 5' phosphate group on the sugar-phosph ...
How did HIV evolve?
... 1. Scroll down until yu see a series of boxes. 2. Click on the box labeled Session Tools. Now look through the menu of the long rectangular box and select Start New Session. Name the ...
... 1. Scroll down until yu see a series of boxes. 2. Click on the box labeled Session Tools. Now look through the menu of the long rectangular box and select Start New Session. Name the ...
Whole genome assembly from next generation sequencing
... chromosome-sized assemblies from the typically short sequence reads obtained. These include large regions of repetitive DNA, paralogous gene families and interspersed retrotransposable elements, which together often comprise up to 70% of an organism’s genome (1). A number of long read technologies, ...
... chromosome-sized assemblies from the typically short sequence reads obtained. These include large regions of repetitive DNA, paralogous gene families and interspersed retrotransposable elements, which together often comprise up to 70% of an organism’s genome (1). A number of long read technologies, ...
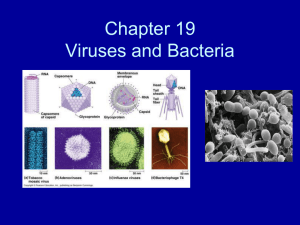
Viruses and Bacteria
... Viruses: Living or Non-living? • No cell membrane or other living cell components • Host cells required for reproduction • Do not metabolize or respond to stimuli • BUT, they do have genetic info and can change over time ...
... Viruses: Living or Non-living? • No cell membrane or other living cell components • Host cells required for reproduction • Do not metabolize or respond to stimuli • BUT, they do have genetic info and can change over time ...
Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
... uncoating, biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, maturation, and release. Knowledge of viral replication phases is important for drug development strategies, and for understanding disease pathology. © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. ...
... uncoating, biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, maturation, and release. Knowledge of viral replication phases is important for drug development strategies, and for understanding disease pathology. © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. ...
DNA
... • ribose instead of deoxyribose • uracil instead of thymine • single strand instead of double strand. The single strand forms double strand areas by twisting upon itself using the same rules of base complementarity (A complementary to U and G complementary to C) • RNA is transcribed off DNA and func ...
... • ribose instead of deoxyribose • uracil instead of thymine • single strand instead of double strand. The single strand forms double strand areas by twisting upon itself using the same rules of base complementarity (A complementary to U and G complementary to C) • RNA is transcribed off DNA and func ...
DNA virus

A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but may also be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses. Single-stranded DNA is usually expanded to double-stranded in infected cells. Although Group VII viruses such as hepatitis B contain a DNA genome, they are not considered DNA viruses according to the Baltimore classification, but rather reverse transcribing viruses because they replicate through an RNA intermediate. Notable diseases like smallpox, herpes, and chickenpox are caused by such DNA viruses.