UNIT: Cell Growth and reproduction
... 1. Use your two red pieces of licorice to assemble a strand of DNA with the following nucleotide sequence A-T-C-G. You will use the toothpicks to attach the nitrogen bases (gummy bears) to the sugar-phosphate backbones (licorice). 2. Attach the complementary nucleotides to the other side of the toot ...
... 1. Use your two red pieces of licorice to assemble a strand of DNA with the following nucleotide sequence A-T-C-G. You will use the toothpicks to attach the nitrogen bases (gummy bears) to the sugar-phosphate backbones (licorice). 2. Attach the complementary nucleotides to the other side of the toot ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 1. One of the reasons most scientists believed proteins were the carriers of genetic information was that c. proteins were much more complex and heterogeneous molecules than nucleic acids. (pg. 293) 2. Transformation involves a. the uptake of external genetic material, often from one bacterial strai ...
... 1. One of the reasons most scientists believed proteins were the carriers of genetic information was that c. proteins were much more complex and heterogeneous molecules than nucleic acids. (pg. 293) 2. Transformation involves a. the uptake of external genetic material, often from one bacterial strai ...
Chapter 16.
... T.H. Morgan working with fruit flies Determined: genes are on chromosomes The question then was: is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes that are the genes? ...
... T.H. Morgan working with fruit flies Determined: genes are on chromosomes The question then was: is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes that are the genes? ...
as a PDF
... 14. List some characteristics that viruses share with living organisms and explain why viruses do not fit our usual definition of life. 15. Provide evidence that viruses probably evolved from fragments of cellular nucleic acid. 16. Describe the structure of a bacterial chromosome. 17. Describe the p ...
... 14. List some characteristics that viruses share with living organisms and explain why viruses do not fit our usual definition of life. 15. Provide evidence that viruses probably evolved from fragments of cellular nucleic acid. 16. Describe the structure of a bacterial chromosome. 17. Describe the p ...
o Discovers DNA • Albrecht Kosse
... DNA, RNA, & Proteins – Inactivate one at a time & infect bacteria Transformation only occurs when DNA is left active Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase (1952) o Phages grown in two different media Radioactive sulfur labeled proteins Radioactive phosphorus labeled DNA o Phages infect new bacteri ...
... DNA, RNA, & Proteins – Inactivate one at a time & infect bacteria Transformation only occurs when DNA is left active Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase (1952) o Phages grown in two different media Radioactive sulfur labeled proteins Radioactive phosphorus labeled DNA o Phages infect new bacteri ...
Chapter 9. Pg 189 DNA: The Genetic Material
... • As DNA polymerases are adding nucleotides, they can only move on to the next one if the previous one is correctly paired to its complementary base. If there is a mismatch, then the DNA polymerases can move backwards and make the correction. ...
... • As DNA polymerases are adding nucleotides, they can only move on to the next one if the previous one is correctly paired to its complementary base. If there is a mismatch, then the DNA polymerases can move backwards and make the correction. ...
History of DNA
... human. They believed that plants and animals had been specifically designed by a creator. ...
... human. They believed that plants and animals had been specifically designed by a creator. ...
Influenza virus:
... can occur due to mutation in sequence of amino acids in proteins of H and N . The mutation leads to change in antigenic nature of H or N or both ...
... can occur due to mutation in sequence of amino acids in proteins of H and N . The mutation leads to change in antigenic nature of H or N or both ...
English_Virus dan peranannya2005-01
... healthy tobacco plant and it was infected. It can be cncluded that the cause of this pest is because the size of it is smaller than that of bacteria so that it can slip out from the filter. Martinus W. Beijerinck( Belanda,1897) stated that yelow pest causing agents can breed in creatures. Wendel ...
... healthy tobacco plant and it was infected. It can be cncluded that the cause of this pest is because the size of it is smaller than that of bacteria so that it can slip out from the filter. Martinus W. Beijerinck( Belanda,1897) stated that yelow pest causing agents can breed in creatures. Wendel ...
Methods to Detect Microbes in the Environment ENVR 133 – Lecture
... • In the DNA double helix, purines and pyrimidines face each other • The two polynucleotide chains in the double helix are connected by hydrogen bonds between the bases • Watson-Crick base-pairing rules •A T •G C • GC base pairs (bps)have more energy than AT bps • Since one strand of DNA is compleme ...
... • In the DNA double helix, purines and pyrimidines face each other • The two polynucleotide chains in the double helix are connected by hydrogen bonds between the bases • Watson-Crick base-pairing rules •A T •G C • GC base pairs (bps)have more energy than AT bps • Since one strand of DNA is compleme ...
Molecular Determinants of Alphavirus Neurovirulence: Nucleotide
... Nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding the 26S RNA of TC-83 virus D N A complementary to the 26S region of viral 42S RNA was prepared for cloning into pUC18 by priming at the T-end of the genome, as previously described (Kinney et al., 1986). Restriction fragments of the cloned cDNA, designated pTC-5, ...
... Nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding the 26S RNA of TC-83 virus D N A complementary to the 26S region of viral 42S RNA was prepared for cloning into pUC18 by priming at the T-end of the genome, as previously described (Kinney et al., 1986). Restriction fragments of the cloned cDNA, designated pTC-5, ...
Common Antiviral Agents Common Antiviral Agents
... (epitope) recognizes the receptor site on the cell (sialic acid or N-acetyl-neuraminic acid, NANA). An antibody will block the epitope. Without immunity, epitope binds with receptor and the virus will subsequently enter the cell. The 16 different H structures all have a similar polypeptide compositi ...
... (epitope) recognizes the receptor site on the cell (sialic acid or N-acetyl-neuraminic acid, NANA). An antibody will block the epitope. Without immunity, epitope binds with receptor and the virus will subsequently enter the cell. The 16 different H structures all have a similar polypeptide compositi ...
10 Restriction Analysis of Genomic DNA
... over 1 billion (109) base pairs. This is far too big to be analyzed at one time in its entirety. Deoxyribonucleic acids can, however, be analyzed in a variety of ways. The general strategy is to break up the DNA into fragments of manageable size. One very useful means by which this is done is to dig ...
... over 1 billion (109) base pairs. This is far too big to be analyzed at one time in its entirety. Deoxyribonucleic acids can, however, be analyzed in a variety of ways. The general strategy is to break up the DNA into fragments of manageable size. One very useful means by which this is done is to dig ...
DNA, RNA, and Proteins - Tri-City
... • DNA is considered to be a relatively stable molecule. What gives it this stability, even though the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases are easily broken? • Hint: Hydrogen bonds hold the c ...
... • DNA is considered to be a relatively stable molecule. What gives it this stability, even though the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases are easily broken? • Hint: Hydrogen bonds hold the c ...
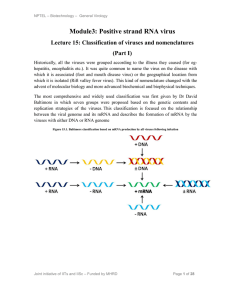
Module3: Positive strand RNA virus
... Group 1, dsDNA viruses – Replicating through DNA Group 2, ss DNA viruses- Replicating through DNA Group 3, ds RNA viruses- Replicating through RNA Group 4, ssRNA viruses (+) polarity, (sense to mRNAs) - Replicating through RNA Group 5, ssRNA viruses (-) polarity, (antisense to mRNAs) - Replicating t ...
... Group 1, dsDNA viruses – Replicating through DNA Group 2, ss DNA viruses- Replicating through DNA Group 3, ds RNA viruses- Replicating through RNA Group 4, ssRNA viruses (+) polarity, (sense to mRNAs) - Replicating through RNA Group 5, ssRNA viruses (-) polarity, (antisense to mRNAs) - Replicating t ...
DNA Structure Notes PPT
... • In 1953, Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made of two chains of sugar and phosphate held together by nitrogenous bases. • Watson and Crick also proposed that DNA is shaped like a long zipper that is twisted into a coil like a spring. ...
... • In 1953, Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made of two chains of sugar and phosphate held together by nitrogenous bases. • Watson and Crick also proposed that DNA is shaped like a long zipper that is twisted into a coil like a spring. ...
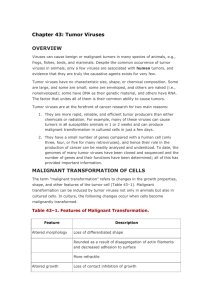
43. Tumor Viruses
... Although it has been demonstrated that viral oncogenes can cause malignant transformation, it has not been directly shown that cellular oncogenes can do so. However, as described in Table 43–2, the following evidence suggests that they do: 1. DNA containing cellular oncogenes isolated from certain t ...
... Although it has been demonstrated that viral oncogenes can cause malignant transformation, it has not been directly shown that cellular oncogenes can do so. However, as described in Table 43–2, the following evidence suggests that they do: 1. DNA containing cellular oncogenes isolated from certain t ...
X – Ray Diffraction
... Hershey and Chase Cont. • Results – Group 1: Labeled viral DNA in bacteria – Group 2: Labeled proteins outside of bacteria cells ...
... Hershey and Chase Cont. • Results – Group 1: Labeled viral DNA in bacteria – Group 2: Labeled proteins outside of bacteria cells ...
Restriction Enzyme Digestion
... companion modification enzyme (DNA methyltransferasemethylase) that protects their own DNA from cleavage. • These enzymes recognize the same DNA sequence as the restriction enzyme they accompany, but instead of cleaving the sequence, they disguise it by methylating one of the bases in each DNA stran ...
... companion modification enzyme (DNA methyltransferasemethylase) that protects their own DNA from cleavage. • These enzymes recognize the same DNA sequence as the restriction enzyme they accompany, but instead of cleaving the sequence, they disguise it by methylating one of the bases in each DNA stran ...
Preservation of viral genomes in 700-y-old caribou feces from
... which extract both DNA and RNA viruses (17–19), in two different laboratories using new primers and reagents (Fig. 1A and Fig. S4). In both laboratories, we implemented standard protocols to isolate ancient materials (20), including multiple negative controls, sterile reagents, and working in isolat ...
... which extract both DNA and RNA viruses (17–19), in two different laboratories using new primers and reagents (Fig. 1A and Fig. S4). In both laboratories, we implemented standard protocols to isolate ancient materials (20), including multiple negative controls, sterile reagents, and working in isolat ...
Possible risks of GMO-s
... Guidelines for GMO creation and release • Early planning and design of GMO-s to reduce environmental risks (reduce risks of sterility, lower fitness, • The promoter should be inducible rather than constitutive • Selection markers should be removed before cultivation • Prevent large-scale or commerc ...
... Guidelines for GMO creation and release • Early planning and design of GMO-s to reduce environmental risks (reduce risks of sterility, lower fitness, • The promoter should be inducible rather than constitutive • Selection markers should be removed before cultivation • Prevent large-scale or commerc ...
Curr. Opin. Virol. v2-SFE140709
... Indeed, this solution provides a single stable equilibrium in which both populations coexist. (ii) If parameters satisfy the condition R < T and S < P, then mutual defection is the dominant strategy, which also corresponds to a stable equilibrium in which, in the long term, only one of the populatio ...
... Indeed, this solution provides a single stable equilibrium in which both populations coexist. (ii) If parameters satisfy the condition R < T and S < P, then mutual defection is the dominant strategy, which also corresponds to a stable equilibrium in which, in the long term, only one of the populatio ...
notes File - selu moodle
... Round one: all DNA medium density (between light and heavy) Round two: half DNA medium density; half DNA light density Explanation: initially all DNA was heavy, after first replication DNA is medium because it has a heavy and a light strand, after second replication half DNA is medium (heavy and lig ...
... Round one: all DNA medium density (between light and heavy) Round two: half DNA medium density; half DNA light density Explanation: initially all DNA was heavy, after first replication DNA is medium because it has a heavy and a light strand, after second replication half DNA is medium (heavy and lig ...
Zika Virus Division of Infectious Disease Department of Internal Medicine
... About 1 in 5 people infected with ZikV become ill The most common symptoms of ZikV are fever, maculopapular rash, joint pain, conjunctivitis. Other common symptoms include muscle pain and headache. The illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting for several days to a week. Zika virus usu ...
... About 1 in 5 people infected with ZikV become ill The most common symptoms of ZikV are fever, maculopapular rash, joint pain, conjunctivitis. Other common symptoms include muscle pain and headache. The illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting for several days to a week. Zika virus usu ...
DNA virus

A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but may also be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses. Single-stranded DNA is usually expanded to double-stranded in infected cells. Although Group VII viruses such as hepatitis B contain a DNA genome, they are not considered DNA viruses according to the Baltimore classification, but rather reverse transcribing viruses because they replicate through an RNA intermediate. Notable diseases like smallpox, herpes, and chickenpox are caused by such DNA viruses.