Feudalism - Bibb County Schools
... In return for his services, the lord granted his vassal land and permission to rule the people who lived on it. This grant was known as a fief. These fiefs of land were called manors. A manor consisted of the manor house or castle, the surrounding fields, and a peasant village. Vassals were knights ...
... In return for his services, the lord granted his vassal land and permission to rule the people who lived on it. This grant was known as a fief. These fiefs of land were called manors. A manor consisted of the manor house or castle, the surrounding fields, and a peasant village. Vassals were knights ...
Constructing the Pyramid Feudal Power
... • An economic system in the Middle Ages that was built around large estates called manors • Included a village and the land surrounding it ...
... • An economic system in the Middle Ages that was built around large estates called manors • Included a village and the land surrounding it ...
The Rise of Europe - Swampscott High School
... Charlemagne were short lived • After his death his sons battled for power and later his grandsons split the empire into three parts • His heirs faced invasion by Muslims, Magyars and Vikings which led to death and destruction throughout western Europe ...
... Charlemagne were short lived • After his death his sons battled for power and later his grandsons split the empire into three parts • His heirs faced invasion by Muslims, Magyars and Vikings which led to death and destruction throughout western Europe ...
Feudal Hierarchy - 8th Grade Social Studies Page
... • either a king or a queen which was typically in power based on lineage • powerful noblemen and women who owned large tracts of land • a person who is given a manor from a lord or king • a specially trained soldier who fights for a lord and vassal • men who learned from a relative how to produce a ...
... • either a king or a queen which was typically in power based on lineage • powerful noblemen and women who owned large tracts of land • a person who is given a manor from a lord or king • a specially trained soldier who fights for a lord and vassal • men who learned from a relative how to produce a ...
TCI 2 - Development of Feudalism
... D. How Peasants Earned a Living 12. Serfs were required to A. grind their own grain at home. B. fight against the king's enemies. C. move to nearby cities and towns. D. stay on the land that they worked. 13. Suppose a knight is known for his chivalry. What does that suggest about him? A. He fought w ...
... D. How Peasants Earned a Living 12. Serfs were required to A. grind their own grain at home. B. fight against the king's enemies. C. move to nearby cities and towns. D. stay on the land that they worked. 13. Suppose a knight is known for his chivalry. What does that suggest about him? A. He fought w ...
The Feudal System - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... • In the Early Middle Ages and well into the High Middle Ages there was little difference between a king and a lord • The king was only as powerful as the lords who protected him • In this period some lords would become more rich and powerful than the king they served • This could often result in ci ...
... • In the Early Middle Ages and well into the High Middle Ages there was little difference between a king and a lord • The king was only as powerful as the lords who protected him • In this period some lords would become more rich and powerful than the king they served • This could often result in ci ...
As the Roman Empire crumbled, and Charlemagne`s
... protect the vassal, give military aid, and guard his children. At the bottom of the feudal society were the serfs. Although not technically a slave, a serf was bound to a lord for life. He could own no property and needed the lord's permission to marry. Serfs would often have to work three or four d ...
... protect the vassal, give military aid, and guard his children. At the bottom of the feudal society were the serfs. Although not technically a slave, a serf was bound to a lord for life. He could own no property and needed the lord's permission to marry. Serfs would often have to work three or four d ...
My Social Studies Teacher
... • Typically, siege warfare took place with an army surrounding a castle and cutting off food and supplies in attempt to capture it. • If the people refused to surrender, they would assault the castle using a variety of weapons, such as catapults, battering rams, ballistas and ...
... • Typically, siege warfare took place with an army surrounding a castle and cutting off food and supplies in attempt to capture it. • If the people refused to surrender, they would assault the castle using a variety of weapons, such as catapults, battering rams, ballistas and ...
Feudalism
... Origins of Feudalism •Feudalism originated partly as result of Viking, Magyar, Muslim invasions •Kings unable to defend their lands, lands of their nobles •Nobles had to find way to defend own lands •Built castles, often on hills •Not elaborate structures; built of wood, used as place of shelter in ...
... Origins of Feudalism •Feudalism originated partly as result of Viking, Magyar, Muslim invasions •Kings unable to defend their lands, lands of their nobles •Nobles had to find way to defend own lands •Built castles, often on hills •Not elaborate structures; built of wood, used as place of shelter in ...
Feudalism in Europe
... Vikings attacked and moved into a section of France that came to be known as Normandy Rulers found it more difficult to defend their subjects Feudalism, a system of governing and landholding came about as an agreement between rulers and warriors A powerful lord offered protection in return f ...
... Vikings attacked and moved into a section of France that came to be known as Normandy Rulers found it more difficult to defend their subjects Feudalism, a system of governing and landholding came about as an agreement between rulers and warriors A powerful lord offered protection in return f ...
Feudalism Handout - John Bowne High School
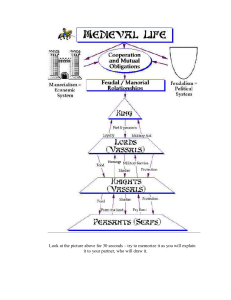
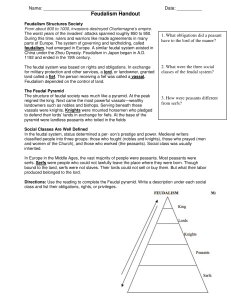
... Social Classes Are Well Defined In the feudal system, status determined a per- son’s prestige and power. Medieval writers classified people into three groups: those who fought (nobles and knights), those who prayed (men and women of the Church), and those who worked (the peasants). Social class was ...
... Social Classes Are Well Defined In the feudal system, status determined a per- son’s prestige and power. Medieval writers classified people into three groups: those who fought (nobles and knights), those who prayed (men and women of the Church), and those who worked (the peasants). Social class was ...
Feudalism Notes - Prep World History I
... military or economic or both; the vassal was required to provide some form of service to the lord, which could also be military or economic or both. For example, the king granted lands known as fiefs (and the peasants that went with them) to his nobles in exchange for their loyalty, military service ...
... military or economic or both; the vassal was required to provide some form of service to the lord, which could also be military or economic or both. For example, the king granted lands known as fiefs (and the peasants that went with them) to his nobles in exchange for their loyalty, military service ...
Name
... Medieval society was a network of mutual duties. Even kings and nobles exchanged vows of service and loyalty. These vows were part of a new political and legal system called feudalism, which was the basis of European life during the Middle Ages. Feudalism was a structure of lords and lesser lords, c ...
... Medieval society was a network of mutual duties. Even kings and nobles exchanged vows of service and loyalty. These vows were part of a new political and legal system called feudalism, which was the basis of European life during the Middle Ages. Feudalism was a structure of lords and lesser lords, c ...
Feudalism
... What was the relationship between the lord and the serfs (peasants tied to land)? Serfs worked the land for the lord in exchange for housing, land and protection Serfs also had to pay several different kinds of taxes to the lord Serfs provided lord with share of crops and provide labor to the l ...
... What was the relationship between the lord and the serfs (peasants tied to land)? Serfs worked the land for the lord in exchange for housing, land and protection Serfs also had to pay several different kinds of taxes to the lord Serfs provided lord with share of crops and provide labor to the l ...
II. Feudalism
... 1. Lords possessed large amounts of land 2. Feudalism developed as a military, political, and economic system based on the holding of land 3. Lords would give small pieces of land (fief) to vassals in exchange for military service 4. Vassals could become lords by further dividing their land and givi ...
... 1. Lords possessed large amounts of land 2. Feudalism developed as a military, political, and economic system based on the holding of land 3. Lords would give small pieces of land (fief) to vassals in exchange for military service 4. Vassals could become lords by further dividing their land and givi ...
Feudalism in Europe A New Social Order Feudalism Structures
... • Kings served by ________ who are served by _______; peasants at the bottom • Knights - _______________ - defend their lord’s land in exchange for fiefs Feudal system- people into 3 social groups: • Those who ___________: nobles & knights • Those who __________: monks, nuns, clergy • Those who ____ ...
... • Kings served by ________ who are served by _______; peasants at the bottom • Knights - _______________ - defend their lord’s land in exchange for fiefs Feudal system- people into 3 social groups: • Those who ___________: nobles & knights • Those who __________: monks, nuns, clergy • Those who ____ ...
CH 10-2 Lesson 1
... After Charlemagne Kings lost power. Land-owning nobles raised armies, collected taxes & imposed laws. Nobles protected people in return for service. Fighting in the army or farming. This social order - Feudalism. By the 1000’s – hundreds of feudal territories. ...
... After Charlemagne Kings lost power. Land-owning nobles raised armies, collected taxes & imposed laws. Nobles protected people in return for service. Fighting in the army or farming. This social order - Feudalism. By the 1000’s – hundreds of feudal territories. ...
FEUDALISM IN EUROPE The Vikings Invade from the North Vikings
... The serfs paid a tax to get married (after they had the permission of their lord to marry) The serfs paid a tithe or church tax They lived in crowded cottages They warmed their dirt-floor houses by bringing pigs in They slept on straw that often crawled with insects Their life expectancy was about 3 ...
... The serfs paid a tax to get married (after they had the permission of their lord to marry) The serfs paid a tithe or church tax They lived in crowded cottages They warmed their dirt-floor houses by bringing pigs in They slept on straw that often crawled with insects Their life expectancy was about 3 ...
Serfdom in Russia
.jpg?width=300)
The origins of serfdom in Russia are traced to Kievan Rus' in the 11th century. Legal documents of the epoch, such as Russkaya Pravda, distinguished several degrees of feudal dependency of peasants, the term for an unfree peasant in the Russian Empire, krepostnoi krestyanin (крепостной крестьянин), is translated as serf.Serfdom became the dominant form of relation between peasants and nobility in the 17th century. Serfdom only existed in central and southern areas of the Russian Empire. It was never established in the North, in the Urals, and in Siberia. Tsar Alexander I of Russia wanted to reform the system but was stymied. New laws allowed all classes (except the serfs) to own land, the privilege that was previously confined to the nobility. Finally, serfdom was abolished by a decree issued by Tsar Alexander II in 1861. Scholars have proposed multiple overlapping reasons to account for the abolition, including fear of a large-scale revolt by the serfs, the government's financial needs, evolving cultural sensibilities and the military's need for soldiers.