Feudal Europe - TeacherV.net
... The Serfs - Manorialism ▫ The right to rent certain strips was inherited by a peasant’s children. ▫ Not all got the same area. Some peasants had 20 acres, and some had 2. ▫ Among these strips was demesne (rhymes with reign) land belonging to a lord. Peasants farmed that for him and his family as ...
... The Serfs - Manorialism ▫ The right to rent certain strips was inherited by a peasant’s children. ▫ Not all got the same area. Some peasants had 20 acres, and some had 2. ▫ Among these strips was demesne (rhymes with reign) land belonging to a lord. Peasants farmed that for him and his family as ...
Feudalism in Europe - school search home
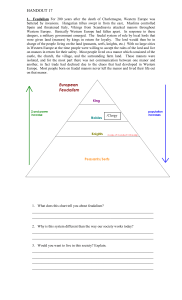
... made life in western Europe difficult. People suffered and feared for their futures. With no strong central government, they went to local leaders for protection. 1. Why did the people need to turn to local leaders for help? ...
... made life in western Europe difficult. People suffered and feared for their futures. With no strong central government, they went to local leaders for protection. 1. Why did the people need to turn to local leaders for help? ...
Feudalism and Manorialism Power Point
... › After proving himself in battle a squire would become a knight in an elaborate ceremony ...
... › After proving himself in battle a squire would become a knight in an elaborate ceremony ...
The Medieval Period *The Middle Ages*
... What did being “self-sufficient” mean for a Medieval Manor? What do they mean when they say the Manors were isolated? ...
... What did being “self-sufficient” mean for a Medieval Manor? What do they mean when they say the Manors were isolated? ...
handout 17 - Spring Branch ISD
... 1. Lords: In feudal Europe a lord was someone that was given land by a local king or queen. A person who controlled land and could therefore give land to vassals (which were the people that lived on the land that they controlled). Usually they were given this power by a local king. And they were the ...
... 1. Lords: In feudal Europe a lord was someone that was given land by a local king or queen. A person who controlled land and could therefore give land to vassals (which were the people that lived on the land that they controlled). Usually they were given this power by a local king. And they were the ...
Feudalism
... 15-30 Families Lived in the Community Serfs, Peasants, and Nobleman lived together. Daily Life consisted of Farming and church Serfs and Peasants produced nearly all that everyone needed to live on. Peasants had no say in Manor laws and government unlike Greek or even Roman Times ...
... 15-30 Families Lived in the Community Serfs, Peasants, and Nobleman lived together. Daily Life consisted of Farming and church Serfs and Peasants produced nearly all that everyone needed to live on. Peasants had no say in Manor laws and government unlike Greek or even Roman Times ...
Feudalism in Medieval Europe
... Lived by a code of chivalry – (expected to obey his lord, be brave, show respect to women of noble birth, to honor the church, and to help people) ...
... Lived by a code of chivalry – (expected to obey his lord, be brave, show respect to women of noble birth, to honor the church, and to help people) ...
What was the feudal system?
... worked directly for the knights, who paid rents and taxes to him and who fought for him in time of war. The knights also provided for law and order and justice through the manorial courts. Most peasants were serfs (villeins) who were ‘owned’ by the knights. It was common for a peasant to have a smal ...
... worked directly for the knights, who paid rents and taxes to him and who fought for him in time of war. The knights also provided for law and order and justice through the manorial courts. Most peasants were serfs (villeins) who were ‘owned’ by the knights. It was common for a peasant to have a smal ...
Name: -____ - cloudfront.net
... the Middle Ages. Many people wonder why they were built and what everyday life was like in a castle. Early castles were built of timber and earth, but later ones were built of stone. Kings and lords built castles to serve as their homes and fortresses. From a castle a lord could defend his lands. Us ...
... the Middle Ages. Many people wonder why they were built and what everyday life was like in a castle. Early castles were built of timber and earth, but later ones were built of stone. Kings and lords built castles to serve as their homes and fortresses. From a castle a lord could defend his lands. Us ...
The feudal system
... Knights generally had to provide 40 -60 days service each year. If there was no war, they did 40 days of training at the Lord’s castle. ...
... Knights generally had to provide 40 -60 days service each year. If there was no war, they did 40 days of training at the Lord’s castle. ...
Ch 7 Notes on Feudalism
... • The person who granted land was called a lord. • The person that received the land was a vassal. • The grant of land was a fief. • The fief could not be broken up, and became hereditary. It was given to the first born male heir. Primogeniture. • Women could influence but had little real power. The ...
... • The person who granted land was called a lord. • The person that received the land was a vassal. • The grant of land was a fief. • The fief could not be broken up, and became hereditary. It was given to the first born male heir. Primogeniture. • Women could influence but had little real power. The ...
Chapter 24 Feudal Society
... • From their fiefs, the soldiers got the income they needed to buy horses and battle ...
... • From their fiefs, the soldiers got the income they needed to buy horses and battle ...
Feudalism in Medieval Europe
... Lived by a code of chivalry – (expected to obey his lord, be brave, show respect to women of noble birth, to honor the church, and to help people) ...
... Lived by a code of chivalry – (expected to obey his lord, be brave, show respect to women of noble birth, to honor the church, and to help people) ...
Feudalism Pyramid of Power Manoralism
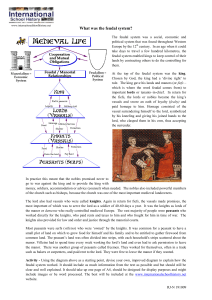
... Remember: a fief was all of a Lord’s land. The Manor was the part of the fief where the peasants farmed and lived. In your book finish this sentence: In the Middle Ages, a fief was … A manor, in the Middle Ages, is … ...
... Remember: a fief was all of a Lord’s land. The Manor was the part of the fief where the peasants farmed and lived. In your book finish this sentence: In the Middle Ages, a fief was … A manor, in the Middle Ages, is … ...
FEUDALISM
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
Medieval Times-1 - Kenwood Academy High School
... The church was the main focus of community life. Priest was appointed by the lord – kept up the church – provided hospitality to travelers. – The priest officiated at church services, weddings, baptisms, funerals, and visited the ill. – Earned income for parish lands, fees for services, and tithe mo ...
... The church was the main focus of community life. Priest was appointed by the lord – kept up the church – provided hospitality to travelers. – The priest officiated at church services, weddings, baptisms, funerals, and visited the ill. – Earned income for parish lands, fees for services, and tithe mo ...
FEUDALISM
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
Feudalism and manor is the back bone of medieval Europe Why did
... ◦Woodland (used for lumber and hunting-only for The Lord) ...
... ◦Woodland (used for lumber and hunting-only for The Lord) ...
feudalism - TriciaWood
... – Manor lords gave the peasants protection and plots of land for themselves and their families – In return, the peasants had to farm the lord’s land, along with other services • Most of the peasants were serfs – Serfs = peasants who are legally bound to the land, the manor on which they serve – They ...
... – Manor lords gave the peasants protection and plots of land for themselves and their families – In return, the peasants had to farm the lord’s land, along with other services • Most of the peasants were serfs – Serfs = peasants who are legally bound to the land, the manor on which they serve – They ...
The Middle Ages - Smyrna Middle School
... Europe had no central government or system of defense. Many invading groups set up kingdoms throughout western Europe. Kingdoms were often at war with each other. Most powerful rulers controlled the most land and had the best warriors. ...
... Europe had no central government or system of defense. Many invading groups set up kingdoms throughout western Europe. Kingdoms were often at war with each other. Most powerful rulers controlled the most land and had the best warriors. ...
THE FEUDAL MODEL Definition
... a. Slaves and peasants took agricultural tasks and frequently intermarried b. Free peasants often turned themselves and their lands over to a lord for protection c. Serfs as an intermediate category emerged about the mid-seventh century 2. Serfs' obligations a. Labor service and rents in kind b. Cou ...
... a. Slaves and peasants took agricultural tasks and frequently intermarried b. Free peasants often turned themselves and their lands over to a lord for protection c. Serfs as an intermediate category emerged about the mid-seventh century 2. Serfs' obligations a. Labor service and rents in kind b. Cou ...
Manorial System
... middle ages. -Feudalism only occurs when there is a weak central government because the king ends up giving away some of his land ...
... middle ages. -Feudalism only occurs when there is a weak central government because the king ends up giving away some of his land ...
Serfdom in Russia
.jpg?width=300)
The origins of serfdom in Russia are traced to Kievan Rus' in the 11th century. Legal documents of the epoch, such as Russkaya Pravda, distinguished several degrees of feudal dependency of peasants, the term for an unfree peasant in the Russian Empire, krepostnoi krestyanin (крепостной крестьянин), is translated as serf.Serfdom became the dominant form of relation between peasants and nobility in the 17th century. Serfdom only existed in central and southern areas of the Russian Empire. It was never established in the North, in the Urals, and in Siberia. Tsar Alexander I of Russia wanted to reform the system but was stymied. New laws allowed all classes (except the serfs) to own land, the privilege that was previously confined to the nobility. Finally, serfdom was abolished by a decree issued by Tsar Alexander II in 1861. Scholars have proposed multiple overlapping reasons to account for the abolition, including fear of a large-scale revolt by the serfs, the government's financial needs, evolving cultural sensibilities and the military's need for soldiers.