CHAPTER 5 General discussion - UvA-DARE
... suggestingg that genetically diverse regions were present. 2) We observed that fusion productss initially contained both hph and ble genes, but eventually lost the phleomycin markerr (Chapter 4, Fig. 3A). The loss of the ble marker might be the result of nondisjunctionall haploidization. Sincee hapl ...
... suggestingg that genetically diverse regions were present. 2) We observed that fusion productss initially contained both hph and ble genes, but eventually lost the phleomycin markerr (Chapter 4, Fig. 3A). The loss of the ble marker might be the result of nondisjunctionall haploidization. Sincee hapl ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... A PCR-based approach was developed to detect ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) form I large-subunit genes (cbbL) as a functional marker of autotrophic bacteria that fix carbon dioxide via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle. We constructed two different primer sets, targeting the ...
... A PCR-based approach was developed to detect ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) form I large-subunit genes (cbbL) as a functional marker of autotrophic bacteria that fix carbon dioxide via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle. We constructed two different primer sets, targeting the ...
ppt_E4ch02_Biotechnology_3e
... most of the insects, but a few bugs will survive because of random mutations that make them resistant. They'll not only survive, but they'll gain a reproductive edge, breeding with each other to create strains of Bt-resistant bugs that could dominate an area. To forestall this catastrophe, farmers c ...
... most of the insects, but a few bugs will survive because of random mutations that make them resistant. They'll not only survive, but they'll gain a reproductive edge, breeding with each other to create strains of Bt-resistant bugs that could dominate an area. To forestall this catastrophe, farmers c ...
Real-time Quantification of HER2/neu Gene Amplification by
... The techniques used to evaluate the HER2/neu gene status have included gene-based assays such as Southern and slot blotting, in-situ hybridization (fluorescent and nonfluorescent) and PCR methods [7]. Each of the techniques mentioned has its advantages and disadvantages. In order to perform a fast p ...
... The techniques used to evaluate the HER2/neu gene status have included gene-based assays such as Southern and slot blotting, in-situ hybridization (fluorescent and nonfluorescent) and PCR methods [7]. Each of the techniques mentioned has its advantages and disadvantages. In order to perform a fast p ...
Chapter 18
... What causes a temperate phage like lambda to switch from lysogenic to lytic? We observed the switch to be caused by environmental factors like radiation or certain chemicals causing DNA damage, which would promote the lytic phase as the bacterial cell will likely die soon and the phage needs to get ...
... What causes a temperate phage like lambda to switch from lysogenic to lytic? We observed the switch to be caused by environmental factors like radiation or certain chemicals causing DNA damage, which would promote the lytic phase as the bacterial cell will likely die soon and the phage needs to get ...
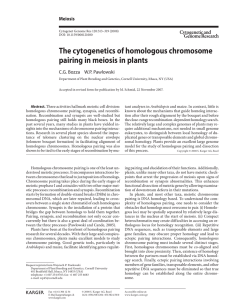
The cytogenetics of homologous chromosome pairing in meiosis in plants Meiosis
... meiotic prophase I and coincides with two other major meiotic processes: recombination and synapsis. Recombination starts by formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in chromosomal DNA, which are later repaired, leading to crossovers between a single sister chromatid of each homologous chromosome. S ...
... meiotic prophase I and coincides with two other major meiotic processes: recombination and synapsis. Recombination starts by formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in chromosomal DNA, which are later repaired, leading to crossovers between a single sister chromatid of each homologous chromosome. S ...
The cytogenetics of homologous chromosome pairing in meiosis in
... meiotic prophase I and coincides with two other major meiotic processes: recombination and synapsis. Recombination starts by formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in chromosomal DNA, which are later repaired, leading to crossovers between a single sister chromatid of each homologous chromosome. S ...
... meiotic prophase I and coincides with two other major meiotic processes: recombination and synapsis. Recombination starts by formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in chromosomal DNA, which are later repaired, leading to crossovers between a single sister chromatid of each homologous chromosome. S ...
Genetics - Michael
... at a computer as they do working at a research bench. For example, once a molecular geneticist has generated a sequence of DNA from an automated sequencer (which contains elaborate computer software itself), they often utilize complex algorithms and statistical packages to examine the structure of t ...
... at a computer as they do working at a research bench. For example, once a molecular geneticist has generated a sequence of DNA from an automated sequencer (which contains elaborate computer software itself), they often utilize complex algorithms and statistical packages to examine the structure of t ...
PDF
... is effective for contaminant removal (Pel et al., 2009) and generates purified and concentrated DNA suitable for PCR or metagenomic analysis (Engel et al., 2012), yet requires specialized equipment. We have found that for library construction, humic acids can simply be allowed to run off the gel dur ...
... is effective for contaminant removal (Pel et al., 2009) and generates purified and concentrated DNA suitable for PCR or metagenomic analysis (Engel et al., 2012), yet requires specialized equipment. We have found that for library construction, humic acids can simply be allowed to run off the gel dur ...
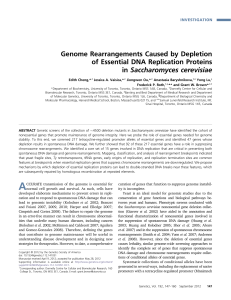
Genome Rearrangements Caused by Depletion of Essential DNA
... cycle following gene-product depletion by promoter shut off (Yu et al. 2006). Spontaneous DNA damage was measured by the relocalization of the DNA damage checkpoint protein Ddc2 from a diffuse nuclear pattern to discrete subnuclear foci (Figure 1A) (Melo et al. 2001; Lisby et al. 2004). Following gr ...
... cycle following gene-product depletion by promoter shut off (Yu et al. 2006). Spontaneous DNA damage was measured by the relocalization of the DNA damage checkpoint protein Ddc2 from a diffuse nuclear pattern to discrete subnuclear foci (Figure 1A) (Melo et al. 2001; Lisby et al. 2004). Following gr ...
Deciphering the role of DNA methylation in multiple sclerosis
... gene promoter, while hypomethylation to the transcription and usually to the expression of the subjected gene [22]. The demethylation of those regions can easily occur in either a passive or in an active way. The passive one is favored during DNA replication, while the active one is achieved by othe ...
... gene promoter, while hypomethylation to the transcription and usually to the expression of the subjected gene [22]. The demethylation of those regions can easily occur in either a passive or in an active way. The passive one is favored during DNA replication, while the active one is achieved by othe ...
MAK, a computational tool kit for automated MITE
... yielding a large copy number; type II elements (DNA elements) use a cut–paste–repair approach to transpose. However, numerous families of highly repetitive (hundreds or thousands), short (100–500 bp), elements that do not seem ...
... yielding a large copy number; type II elements (DNA elements) use a cut–paste–repair approach to transpose. However, numerous families of highly repetitive (hundreds or thousands), short (100–500 bp), elements that do not seem ...
DNA barcoding parasite organisms found in terrestrial
... may inhibit the transportation of parasite species in mammal scat, which may cause parasite populations to differ significantly on either side of these physical barriers. While out collecting, the majority of predator scat, coyote, wolf, and bear, were found out in the open; however, the scat of he ...
... may inhibit the transportation of parasite species in mammal scat, which may cause parasite populations to differ significantly on either side of these physical barriers. While out collecting, the majority of predator scat, coyote, wolf, and bear, were found out in the open; however, the scat of he ...
Fulltext PDF
... the collection. How do we distinguish between these possibilities? This is done using a technique called ‘complementation analysis’ (Figure 1). Without bothering about the technical nuances, this is done by creating a diploid cell by combining the haploid genomes of any two mutants and examining the ...
... the collection. How do we distinguish between these possibilities? This is done using a technique called ‘complementation analysis’ (Figure 1). Without bothering about the technical nuances, this is done by creating a diploid cell by combining the haploid genomes of any two mutants and examining the ...
Genome duplications and accelerated evolution of
... be established, but it does not allow for precise identification of their cluster affiliation, due to the limited number of variable amino acid positions in the homeobox. Furthermore, gene absence cannot be unambiguously confirmed due to the inherent problems of PCR template competition when amplify ...
... be established, but it does not allow for precise identification of their cluster affiliation, due to the limited number of variable amino acid positions in the homeobox. Furthermore, gene absence cannot be unambiguously confirmed due to the inherent problems of PCR template competition when amplify ...
Microbial Gene Transfer: An Ecological
... recent evidence from natural populations as well as genome research has indicated that this process may be a major driving force in microbial evolution. Studies with natural populations have taken two approacheseither adding a defined donor with a traceable gene to an indigenous community, and detec ...
... recent evidence from natural populations as well as genome research has indicated that this process may be a major driving force in microbial evolution. Studies with natural populations have taken two approacheseither adding a defined donor with a traceable gene to an indigenous community, and detec ...
Virus induced gene silencing, a post transcriptional gene silencing
... Therefore, a number of viral-derived vectors have been developed (Table 1) and many procedures have been optimized by the researchers. TRV system was efficiently optimized for efficient silencing of Solanaceous plants [14; 15], and the system was also applied for tomato to study role of fruit ripeni ...
... Therefore, a number of viral-derived vectors have been developed (Table 1) and many procedures have been optimized by the researchers. TRV system was efficiently optimized for efficient silencing of Solanaceous plants [14; 15], and the system was also applied for tomato to study role of fruit ripeni ...
What is a GO term? - NDSU Computer Science
... Cross-products: The existence of several ontologies will also allow us to create 'cross-products' that maximize the utility of each ontology while avoiding redundancy. For example, by combining the developmental terms in the GO process ontology with a second ontology that describes Drosophila anato ...
... Cross-products: The existence of several ontologies will also allow us to create 'cross-products' that maximize the utility of each ontology while avoiding redundancy. For example, by combining the developmental terms in the GO process ontology with a second ontology that describes Drosophila anato ...
The Mobile Genetic Element Alu in the Human Genome
... repetitive elements When the DNA double helix of higher organisms (species other than bacteria and viruses) is split open or denatured into two single strands by heat and left to spontaneously reanneal, the entire DNA is not likely to become double-stranded at the same rate. In contrast, all parts o ...
... repetitive elements When the DNA double helix of higher organisms (species other than bacteria and viruses) is split open or denatured into two single strands by heat and left to spontaneously reanneal, the entire DNA is not likely to become double-stranded at the same rate. In contrast, all parts o ...
Use of QTL analysis in physiological research
... allelic variation is present in genes encoding for biosynthetic enzymes, analyzing enzyme activity as a quantitative trait in a segregating population is expected to point towards the genes encoding the enzyme under investigation. Here, the advantage of using Arabidopsis is clear: the genome has bee ...
... allelic variation is present in genes encoding for biosynthetic enzymes, analyzing enzyme activity as a quantitative trait in a segregating population is expected to point towards the genes encoding the enzyme under investigation. Here, the advantage of using Arabidopsis is clear: the genome has bee ...
Document
... $ tophat –p 4 –o ctrl chr22 thrombin_control.txt # Run TopHAT using chr22 as reference and sequences in the control. # -p indicates the number of cpus (4). # -o indicates the output directory (ctrl). ...
... $ tophat –p 4 –o ctrl chr22 thrombin_control.txt # Run TopHAT using chr22 as reference and sequences in the control. # -p indicates the number of cpus (4). # -o indicates the output directory (ctrl). ...