Kinematics Problems
... stone must have a constant downward acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 (this acceleration does not change during the stone’s flight). Since the question has defined upwards as the positive direction, we know that the acceleration experienced by the stone must be – 9.8 m/s2. Therefore we can eliminate options ...
... stone must have a constant downward acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 (this acceleration does not change during the stone’s flight). Since the question has defined upwards as the positive direction, we know that the acceleration experienced by the stone must be – 9.8 m/s2. Therefore we can eliminate options ...
Previous solved assignments physics PHY101
... No, not unless the book tends to slide or does slide across the table. For example, if it is pushed toward the left by another force, then friction between the book and table will act toward the right. Friction forces occur only when an object tends to slide or is sliding. ...
... No, not unless the book tends to slide or does slide across the table. For example, if it is pushed toward the left by another force, then friction between the book and table will act toward the right. Friction forces occur only when an object tends to slide or is sliding. ...
The Fundamental Physics of Electromagnetic Waves
... wrote that when “the speeds have become the same… [the kinetic energy] becom[es] zero”. Coriolis’ caveats were soon forgotten, however. By the time James Clerk Maxwell (18311879) later wrote his basic physics textbook, he errantly summarized, “The kinetic energy of a body is the energy it has in vir ...
... wrote that when “the speeds have become the same… [the kinetic energy] becom[es] zero”. Coriolis’ caveats were soon forgotten, however. By the time James Clerk Maxwell (18311879) later wrote his basic physics textbook, he errantly summarized, “The kinetic energy of a body is the energy it has in vir ...
Ch#7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q#3: A car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 1.5 s. Assuming the same average power is delivered by the car, how long does it take to accelerate it from zero to 60 m/s. (Ignore friction). (Ans: 6.0 s) ...
... Q#3: A car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 1.5 s. Assuming the same average power is delivered by the car, how long does it take to accelerate it from zero to 60 m/s. (Ignore friction). (Ans: 6.0 s) ...
further questions
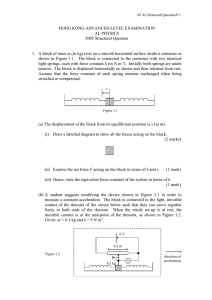
... (a) an expression for the velocity of the trolley (b) the acceleration of the trolley (c) the time it takes the trolley to reach the bottom of the runway (d) the velocity of the trolley at the bottom of the runway. 7. A box slides down a smooth slope with an acceleration of 4 m s-2. The velocity of ...
... (a) an expression for the velocity of the trolley (b) the acceleration of the trolley (c) the time it takes the trolley to reach the bottom of the runway (d) the velocity of the trolley at the bottom of the runway. 7. A box slides down a smooth slope with an acceleration of 4 m s-2. The velocity of ...
ReviewWavesO
... We now want to expand the picture in the following way: EM waves propagate in 3D not just 1D as we have considered. - Diffraction - waves coming from a finite source spread out. EM waves propagate through material and are modified. - Dispersion - waves are slowed down by media, different frequency ...
... We now want to expand the picture in the following way: EM waves propagate in 3D not just 1D as we have considered. - Diffraction - waves coming from a finite source spread out. EM waves propagate through material and are modified. - Dispersion - waves are slowed down by media, different frequency ...
Chapter 3: Motion and Forces Goals of Period 3
... Example 3.1 involved motion at a constant speed. In reality, few objects travel at a constant speed for long. In most real life examples, we use the average speed of an object as it travels between two points, as shown in example 3.2. (Example 3.2) If you drive for 3 hours at an average speed of 55 ...
... Example 3.1 involved motion at a constant speed. In reality, few objects travel at a constant speed for long. In most real life examples, we use the average speed of an object as it travels between two points, as shown in example 3.2. (Example 3.2) If you drive for 3 hours at an average speed of 55 ...
Chapter 7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q#3: A car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 1.5 s. Assuming the same average power is delivered by the car, how long does it take to accelerate it from zero to 60 m/s. (Ignore friction). (Ans: 6.0 s) ...
... Q#3: A car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 1.5 s. Assuming the same average power is delivered by the car, how long does it take to accelerate it from zero to 60 m/s. (Ignore friction). (Ans: 6.0 s) ...
The Photon consists of a Positive and a Negative Charge
... photon’s characteristics. The method used is to expose a flow of extremely low energy, coherent and polarized photons to a static magnetic field. The magnetic field splits each photon into its two elementary particles; a negative and a positive charge. The negative or the positive charge is then exp ...
... photon’s characteristics. The method used is to expose a flow of extremely low energy, coherent and polarized photons to a static magnetic field. The magnetic field splits each photon into its two elementary particles; a negative and a positive charge. The negative or the positive charge is then exp ...
AH Physics staff guide N Fancey G Millar J Woolsey
... molecules to more stable, smaller molecules. This is a chemical reaction and the binding energies involved are much smaller of course. The difference in rest mass of the TNT molecule and the gaseous final products is too small to measure directly, but is equal to the kinetic energy release divided b ...
... molecules to more stable, smaller molecules. This is a chemical reaction and the binding energies involved are much smaller of course. The difference in rest mass of the TNT molecule and the gaseous final products is too small to measure directly, but is equal to the kinetic energy release divided b ...
Introduction - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
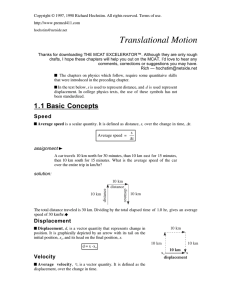
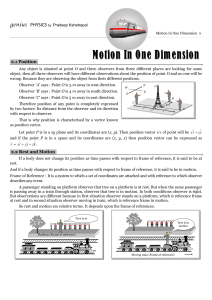
... (ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be. (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacement is single valued while dista ...
... (ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be. (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacement is single valued while dista ...
Notes on Relativistic Dynamics
... Then I present “why we need relativistic dynamics” (section 2.1), followed by one of the two “momentum motivations”, either the collision motivation (sections 2.2, 2.3, and 2.4) or the four-vector motivation (sections 3.1, 3.2 and 3.3). I leave the other motivation for reading. I’ve tried it both wa ...
... Then I present “why we need relativistic dynamics” (section 2.1), followed by one of the two “momentum motivations”, either the collision motivation (sections 2.2, 2.3, and 2.4) or the four-vector motivation (sections 3.1, 3.2 and 3.3). I leave the other motivation for reading. I’ve tried it both wa ...
Variable forces
... In this topic we consider the motion of an object of constant mass m moving in a straight line and subjected to a system of forces. In previous topics, the forces have been constant, and since F = ma, the acceleration was also constant, so the constant acceleration formulas could be used. However, i ...
... In this topic we consider the motion of an object of constant mass m moving in a straight line and subjected to a system of forces. In previous topics, the forces have been constant, and since F = ma, the acceleration was also constant, so the constant acceleration formulas could be used. However, i ...
ISNS4371_011107_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - opposes gravity and prevents us falling to the center of the Earth - what is measured by a weighing scale. For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surf ...
... - opposes gravity and prevents us falling to the center of the Earth - what is measured by a weighing scale. For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surf ...