Lecture 4
... addition. • Vector components • Mathematical description of vector addition (addition of components) • Unit Vectors 95.141, F2010, Lecture 4 ...
... addition. • Vector components • Mathematical description of vector addition (addition of components) • Unit Vectors 95.141, F2010, Lecture 4 ...
here
... 7) This is possibly the worst question. You cannot assume that the speed at the first cone is zero. Notice how there is only a slight increase in speed over this distance. The v-t graph is shown below. The speed will be greater than the starting value that is around 35 m/s, but not doubled. We are g ...
... 7) This is possibly the worst question. You cannot assume that the speed at the first cone is zero. Notice how there is only a slight increase in speed over this distance. The v-t graph is shown below. The speed will be greater than the starting value that is around 35 m/s, but not doubled. We are g ...
horizontal velocity - Marble Falls High School
... Computer-generated trajectories of a baseball with and without drag. ...
... Computer-generated trajectories of a baseball with and without drag. ...
p14jmacProjectile Motion
... Computer-generated trajectories of a baseball with and without drag. ...
... Computer-generated trajectories of a baseball with and without drag. ...
chapter-6-with-changes-thursday-jan-9
... and return to your hand, but in parabolic path because the bus would be moving, your hand also would be moving. The bus, your hand, and the ball would all have the same horizontal velocity. ...
... and return to your hand, but in parabolic path because the bus would be moving, your hand also would be moving. The bus, your hand, and the ball would all have the same horizontal velocity. ...
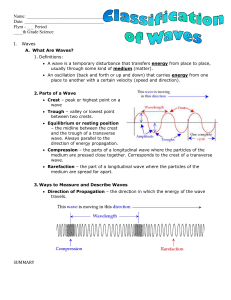
Waves What Are Waves? Definitions: A wave is a temporary
... λ = velocity (m/s) frequency (Hz) Amplitude – the maximum distance the particles of a medium move away from their resting position as a wave passes through the medium. Basically, amplitude is the height of a wave above the midline resting position. Frequency – the number of complete waves (osc ...
... λ = velocity (m/s) frequency (Hz) Amplitude – the maximum distance the particles of a medium move away from their resting position as a wave passes through the medium. Basically, amplitude is the height of a wave above the midline resting position. Frequency – the number of complete waves (osc ...
Contents - Perimeter Institute
... slows down time. The closer an object is to a large mass, the slower time passes. Together, these two effects mean that clocks inside GPS satellites run faster than clocks in GPS receivers on Earth. If not corrected, this would lead to timing errors that would result in GPS measurements rapidly accu ...
... slows down time. The closer an object is to a large mass, the slower time passes. Together, these two effects mean that clocks inside GPS satellites run faster than clocks in GPS receivers on Earth. If not corrected, this would lead to timing errors that would result in GPS measurements rapidly accu ...
The Lorentz transformation
... when the units of distance and time (and all other units that depend on them) are chosen appropriately. For example, one could work with seconds for time, and light-seconds for distance. (One light-second is equal to 299792458 metres). The only problem with this approach is that you must apply it co ...
... when the units of distance and time (and all other units that depend on them) are chosen appropriately. For example, one could work with seconds for time, and light-seconds for distance. (One light-second is equal to 299792458 metres). The only problem with this approach is that you must apply it co ...
THE VALIDITY OF VELOCITY MEASUREMENT DURING UPPER
... Retro reflective markers were attached to the acromion, greater tubercle of humerus, medial epicondyle of humerus, lateral epicondyle of humerus, styloid process of radius, styloid process of ulna, terminal points of the barbell and the medial point of the barbell. Moreover, four light-weight rigid ...
... Retro reflective markers were attached to the acromion, greater tubercle of humerus, medial epicondyle of humerus, lateral epicondyle of humerus, styloid process of radius, styloid process of ulna, terminal points of the barbell and the medial point of the barbell. Moreover, four light-weight rigid ...
Gravity and Inertia (Rec. 1.23.14) (* file)
... consequences of this model. If special relativistic effects are observational phenomena only, without an aether, then there is nothing that can be done, for example, about unwanted relative mass increase. Nothing can be done about purely observational phenomena, if there is no physical mechanism tha ...
... consequences of this model. If special relativistic effects are observational phenomena only, without an aether, then there is nothing that can be done, for example, about unwanted relative mass increase. Nothing can be done about purely observational phenomena, if there is no physical mechanism tha ...
Essential Physics Activities on a Budget Price
... 3. Use the distances traveled and average time s to make a “Distance vs. Time” graph (always named as “y vs. x”) using MS Excel. Label this and all graphs as directed in class. 4. Use the MS Excel “Add Trendline” function to draw the best straight lines through your data points and to compute the “b ...
... 3. Use the distances traveled and average time s to make a “Distance vs. Time” graph (always named as “y vs. x”) using MS Excel. Label this and all graphs as directed in class. 4. Use the MS Excel “Add Trendline” function to draw the best straight lines through your data points and to compute the “b ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF BLACK HOLES∗
... happens with such extremely heavy objects, one has to consider Einstein’s theory of relativity, both Special Relativity and General Relativity, the theory that describes the gravitational field when velocities are generated comparable to that of light. Soon after Albert Einstein formulated this beau ...
... happens with such extremely heavy objects, one has to consider Einstein’s theory of relativity, both Special Relativity and General Relativity, the theory that describes the gravitational field when velocities are generated comparable to that of light. Soon after Albert Einstein formulated this beau ...