
Physics 1010: The Physics of Everyday Life
... – Change in velocity divided by elapsed time – Slope on velocity versus time graph • Position is related to acceleration • Acceleration given by force (F = ma) • Position, Velocity, Acceleration are all ...
... – Change in velocity divided by elapsed time – Slope on velocity versus time graph • Position is related to acceleration • Acceleration given by force (F = ma) • Position, Velocity, Acceleration are all ...
VCE Physics
... (b) In which section is the cyclist travelling at her slowest (but not zero) speed ? (c) What is her speed in part (b) above ? (d) What distance did she cover in the first 40 seconds of her journey ? (e) In which section(s) of the graph is her speed the greatest ? (f) What is her displacement from h ...
... (b) In which section is the cyclist travelling at her slowest (but not zero) speed ? (c) What is her speed in part (b) above ? (d) What distance did she cover in the first 40 seconds of her journey ? (e) In which section(s) of the graph is her speed the greatest ? (f) What is her displacement from h ...
Lesson 1 - SchoolRack
... Do you agree or disagree? 4. Gravity is a force that depends on the masses of two objects and the distance between them. 5. All forces change the motion of objects. 6. The net force on an object is equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration of the object. ...
... Do you agree or disagree? 4. Gravity is a force that depends on the masses of two objects and the distance between them. 5. All forces change the motion of objects. 6. The net force on an object is equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration of the object. ...
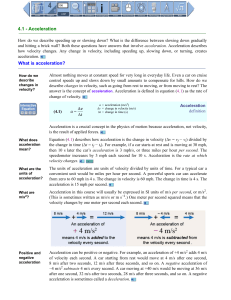
4.1 - Acceleration What is acceleration?
... Acceleration can be positive or negative. For example, an acceleration of +4 m/s2 adds 4 m/s of velocity each second. A car starting from rest would move at 4 m/s after one second, 8 m/s after two seconds, 12 m/s after three seconds, and so on. A negative acceleration of −4 m/s2 subtracts 4 m/s ever ...
... Acceleration can be positive or negative. For example, an acceleration of +4 m/s2 adds 4 m/s of velocity each second. A car starting from rest would move at 4 m/s after one second, 8 m/s after two seconds, 12 m/s after three seconds, and so on. A negative acceleration of −4 m/s2 subtracts 4 m/s ever ...
Sci-Fi Helper - Parallel Universes
... One thing though, every story about UFOs we hear these days, about their possible way of propulsion and all the side effects of their engine, appear to be related to high magnetic fields and antigravity devices. People report time slowing down, time going faster, space being distorted, ships moving ...
... One thing though, every story about UFOs we hear these days, about their possible way of propulsion and all the side effects of their engine, appear to be related to high magnetic fields and antigravity devices. People report time slowing down, time going faster, space being distorted, ships moving ...
Sci-Fi Helper - Parallel Universes
... One thing though, every story about UFOs we hear these days, about their possible way of propulsion and all the side effects of their engine, appear to be related to high magnetic fields and antigravity devices. People report time slowing down, time going faster, space being distorted, ships moving ...
... One thing though, every story about UFOs we hear these days, about their possible way of propulsion and all the side effects of their engine, appear to be related to high magnetic fields and antigravity devices. People report time slowing down, time going faster, space being distorted, ships moving ...
PHYSICS COURSE DESCRIPTION - McCall
... 5. Describe the relationship between ocean tides gravitational pull 6. Explain the effects of the sun and the moon on the Earth 7. How does gravitational force related to the distance between the objects 8. Define gravitational field 9. Explain the detection of gravitational fields 10. Cite Einstein ...
... 5. Describe the relationship between ocean tides gravitational pull 6. Explain the effects of the sun and the moon on the Earth 7. How does gravitational force related to the distance between the objects 8. Define gravitational field 9. Explain the detection of gravitational fields 10. Cite Einstein ...
Rolling downhill - Net Start Class
... Acceleration of falling objects. We all have a lot of experience with acceleration. A falling object is an interesting special case, because the acceleration is constant—it’s constantly increasing its speed. Figure 7.3 shows how a ball falls. The black circles represent the ball’s position every ten ...
... Acceleration of falling objects. We all have a lot of experience with acceleration. A falling object is an interesting special case, because the acceleration is constant—it’s constantly increasing its speed. Figure 7.3 shows how a ball falls. The black circles represent the ball’s position every ten ...
Response to Physics Draft by AIP
... the discovery that light was an electromagnetic wave; (Comment: very challenging without an understanding of electromagnetism which is in Unit 3. Suggest that this section is deleted) interactions between light and matter that involve the processes of reflection, refraction and absorption; (Comm ...
... the discovery that light was an electromagnetic wave; (Comment: very challenging without an understanding of electromagnetism which is in Unit 3. Suggest that this section is deleted) interactions between light and matter that involve the processes of reflection, refraction and absorption; (Comm ...
Momentum and Collision
... Because the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant, the total initial momentum of the boater and the boat will be equal to the total final momentum of the boater and the boat. m1v1,i + m2v2,i = m1v1,f + m2v2,f ...
... Because the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant, the total initial momentum of the boater and the boat will be equal to the total final momentum of the boater and the boat. m1v1,i + m2v2,i = m1v1,f + m2v2,f ...
[pdf]
... tion wave vector. The light-scattering cross sections, which originate from local director fluctuations, depend on the directions of the electric field and the propagation vectors with respect to the average molecular orientation. Furthermore, nematic liquid crystals strongly scatter visible light; ...
... tion wave vector. The light-scattering cross sections, which originate from local director fluctuations, depend on the directions of the electric field and the propagation vectors with respect to the average molecular orientation. Furthermore, nematic liquid crystals strongly scatter visible light; ...
Vectors [1
... 3) Bill is sitting on a tree limb that is 4 meters above the ground with a bucket of water. He wants to dump the water so that it falls on his friend Tim who is approaching on a bike at a constant speed of 8 meters per second. How far away should Tim be from a point directly under Bill when Bill dum ...
... 3) Bill is sitting on a tree limb that is 4 meters above the ground with a bucket of water. He wants to dump the water so that it falls on his friend Tim who is approaching on a bike at a constant speed of 8 meters per second. How far away should Tim be from a point directly under Bill when Bill dum ...
Double-slit experiment From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump
... "particles",[15] "waves", "location", "movement from one place to another", etc. In contrast to the way of conceptualizing the macroscopic world of everyday experience, attempting to describe the motion of a single photon is problematic. As Philipp Frank observes, investigating the motion of single ...
... "particles",[15] "waves", "location", "movement from one place to another", etc. In contrast to the way of conceptualizing the macroscopic world of everyday experience, attempting to describe the motion of a single photon is problematic. As Philipp Frank observes, investigating the motion of single ...















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852296_1-154a32bfa66424b5b516963269d16032-300x300.png)




