Physics 121C Mechanics
... 4. On the initial-position drawing of the particle, place a labeled vector for each force acting on it. 5. Calculate the total work done on the particle by the forces and equate this total to the change in the particle’s kinetic energy. Check: Make sure you pay attention to negative signs during you ...
... 4. On the initial-position drawing of the particle, place a labeled vector for each force acting on it. 5. Calculate the total work done on the particle by the forces and equate this total to the change in the particle’s kinetic energy. Check: Make sure you pay attention to negative signs during you ...
Document
... stationary turntable. If you suddenly flip the wheel over so that it is spinning in the opposite direction, the turntable will: ...
... stationary turntable. If you suddenly flip the wheel over so that it is spinning in the opposite direction, the turntable will: ...
Paradoxes about Light Phenomena: Photo
... space and time with lines of demarcation between matter, energy, time and space. As these quantities remain distinct and absolute, the speed of light changes. Einstein, however, perceived a Universe with no fixed lines between matter, energy, time, and space but with an absolute speed of light. He f ...
... space and time with lines of demarcation between matter, energy, time and space. As these quantities remain distinct and absolute, the speed of light changes. Einstein, however, perceived a Universe with no fixed lines between matter, energy, time, and space but with an absolute speed of light. He f ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion
... constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m guideline for a speed of 19 m/s. Tension is the centripe ...
... constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m guideline for a speed of 19 m/s. Tension is the centripe ...
CP7e: Ch. 8 Problems
... A student sits on a rotating stool holding two 3.0-kg objects. When his arms are extended horizontally, the objects are 1.0 m from the axis of rotation and he rotates with an angular speed of 0.75 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 3.0 kg ∙ m2 and is assumed to be constant. Th ...
... A student sits on a rotating stool holding two 3.0-kg objects. When his arms are extended horizontally, the objects are 1.0 m from the axis of rotation and he rotates with an angular speed of 0.75 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 3.0 kg ∙ m2 and is assumed to be constant. Th ...
Chapter 8 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q5. A projectile of mass m = 0.200 kg is fired at an angle of 60.0 degrees above the horizontal with a speed of 20.0 m/s. Find the work done on the projectile by the gravitational force during its flight from its firing point to the highest point on its trajectory. (A: –30.0 J) Q6. A 0.500-kg block ...
... Q5. A projectile of mass m = 0.200 kg is fired at an angle of 60.0 degrees above the horizontal with a speed of 20.0 m/s. Find the work done on the projectile by the gravitational force during its flight from its firing point to the highest point on its trajectory. (A: –30.0 J) Q6. A 0.500-kg block ...
Honors Review for Midterm
... 24. A wad of chewed bubble gum is moving with 1 unit of momentum when it collides with a heavy box that is initially at rest. The gum sticks to the box and both are set in motion with a combined momentum that is ___. ...
... 24. A wad of chewed bubble gum is moving with 1 unit of momentum when it collides with a heavy box that is initially at rest. The gum sticks to the box and both are set in motion with a combined momentum that is ___. ...
Development of three-dimensional integrated microchannel
... The manipulation technique with electrical method uses electrokinetic forces to drive particles such as cells and fluid to realize the particles’ movement. After voltage and electrical current are applied to electrodes, the particles are driven by the electrokinetic forces which are dielectrophoreti ...
... The manipulation technique with electrical method uses electrokinetic forces to drive particles such as cells and fluid to realize the particles’ movement. After voltage and electrical current are applied to electrodes, the particles are driven by the electrokinetic forces which are dielectrophoreti ...
Lab 7 Ballistic Pendulum! !
... Calculate the initial speed from this data. Include the uncertainty. Analysis Here is a case where two measurements of the same value are done two different ways without an expected value. How do we know if the two experiments agree? We now have two pdf’s, one for each experiment. One question we wa ...
... Calculate the initial speed from this data. Include the uncertainty. Analysis Here is a case where two measurements of the same value are done two different ways without an expected value. How do we know if the two experiments agree? We now have two pdf’s, one for each experiment. One question we wa ...
Relativity made relatively easy
... This book presents an extensive study of Special Relativity, aimed at an undergraduate level. It is not intended to be the first introduction to the subject for most students, although for a bright student it could function as that. Therefore basic ideas such as time dilation and space contraction a ...
... This book presents an extensive study of Special Relativity, aimed at an undergraduate level. It is not intended to be the first introduction to the subject for most students, although for a bright student it could function as that. Therefore basic ideas such as time dilation and space contraction a ...
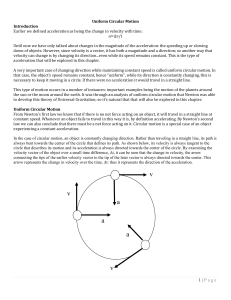
Circular Motion Chapter
... Often more than one force is acting on an object...including an object traveling in uniform circular motion. In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having t ...
... Often more than one force is acting on an object...including an object traveling in uniform circular motion. In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having t ...