Chapter 1 Units and Problem Solving
... • There is always centripetal acceleration no matter whether the circular motion is uniform or nonuniform. • It is the tangential acceleration that is zero in uniform circular motion. Example 7.4: A wheel is rotating wit a constant angular acceleration of 3.5 rad/s2. If the initial angular velocity ...
... • There is always centripetal acceleration no matter whether the circular motion is uniform or nonuniform. • It is the tangential acceleration that is zero in uniform circular motion. Example 7.4: A wheel is rotating wit a constant angular acceleration of 3.5 rad/s2. If the initial angular velocity ...
Student`s Alternative Conceptions of Free
... the presence of a continuing force in the same direction as the motion; the “motion implies force” misconception. Clement also noted that it is not likely that this misconception disappears simply because students are exposed to a physics course. The Newtonian ideas can be misperceived or distorted ...
... the presence of a continuing force in the same direction as the motion; the “motion implies force” misconception. Clement also noted that it is not likely that this misconception disappears simply because students are exposed to a physics course. The Newtonian ideas can be misperceived or distorted ...
Section 1: ON THE MOVE
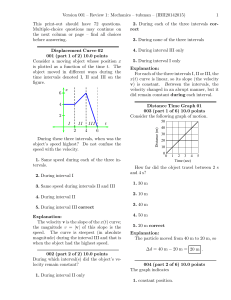
... The instantaneous speed of a moving object is estimated by measuring the distance the object travels in a very short time - Much less than 1 second. The smaller the measured time, the better will be the estimate for the object's instantaneous speed. For times longer than about 0.005 seconds, the spe ...
... The instantaneous speed of a moving object is estimated by measuring the distance the object travels in a very short time - Much less than 1 second. The smaller the measured time, the better will be the estimate for the object's instantaneous speed. For times longer than about 0.005 seconds, the spe ...
v(t) = v0 + at
... Where you started, and How fast and in what direction you started going, and How fast and in what direction you’re accelerating, and How long you have been going ...
... Where you started, and How fast and in what direction you started going, and How fast and in what direction you’re accelerating, and How long you have been going ...
Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... Only a small part of an iceberg protrudes above the water, while the bulk lies below the surface. The density of ice is 917 kg/m 3 and that of seawater is 1025 kg/m 3. Find the percentage of the iceberg's volume that lies below the surface. The latent heat of vaporization of H 2O at body temperature ...
... Only a small part of an iceberg protrudes above the water, while the bulk lies below the surface. The density of ice is 917 kg/m 3 and that of seawater is 1025 kg/m 3. Find the percentage of the iceberg's volume that lies below the surface. The latent heat of vaporization of H 2O at body temperature ...
VU2 Movement 2008
... applied to ideas of work, energy and power, including transfers between – kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy close to the Earth’s surface; – potential energy and kinetic energy in springs; ...
... applied to ideas of work, energy and power, including transfers between – kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy close to the Earth’s surface; – potential energy and kinetic energy in springs; ...
Ch7 notes
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular ac ...
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular ac ...
$doc.title
... experiences a force F, while box B experience a force 2F. What is true about their final speeds? A. The final speed of box A is equal to that of box B B. The final speed of box A is hal ...
... experiences a force F, while box B experience a force 2F. What is true about their final speeds? A. The final speed of box A is equal to that of box B B. The final speed of box A is hal ...
Notes for Mid
... 30m/s when it has an acceleration of 6m/s2. How long did this take? t = (30m/s)/(6m/s2) = 5s 1) A runner’s initial speed is 5m/s and he accelerates at 5m/s2 over a distance of 7.5 meters. What is his final speed? vf2 = (5m/s)2 + 2*(5m/s2)(7.5m) = 100m2/s2 or vf = 10m/s 2) Same problem except the fin ...
... 30m/s when it has an acceleration of 6m/s2. How long did this take? t = (30m/s)/(6m/s2) = 5s 1) A runner’s initial speed is 5m/s and he accelerates at 5m/s2 over a distance of 7.5 meters. What is his final speed? vf2 = (5m/s)2 + 2*(5m/s2)(7.5m) = 100m2/s2 or vf = 10m/s 2) Same problem except the fin ...
PER measurement
... states in optical fibres and components used in optical communication systems. While the concept of PER is relatively simple, the parameter can be ambiguous and confusing to interpret because the resulting polarisation state is a function of the phase difference between the components that are measu ...
... states in optical fibres and components used in optical communication systems. While the concept of PER is relatively simple, the parameter can be ambiguous and confusing to interpret because the resulting polarisation state is a function of the phase difference between the components that are measu ...
Ch 6 Solutions Glencoe 2013 - Aspen High School
... 16. Challenge A car racing on a flat track travels at 22 m/s around a curve with a 56-m radius. Find the car’s centripetal acceleration. What minimum coefficient of static friction between the tires and the road is necessary for the car to round the curve without slipping? SOLUTION: ...
... 16. Challenge A car racing on a flat track travels at 22 m/s around a curve with a 56-m radius. Find the car’s centripetal acceleration. What minimum coefficient of static friction between the tires and the road is necessary for the car to round the curve without slipping? SOLUTION: ...
free fall motion
... Free falling motion have two important characteristic that: a). Free falling bodies does not encounter air resistance. This characteristic is arise because the free falling bodies are only affected by gravitational force. This characteristic also showing us that the shape, mass, weight and any other ...
... Free falling motion have two important characteristic that: a). Free falling bodies does not encounter air resistance. This characteristic is arise because the free falling bodies are only affected by gravitational force. This characteristic also showing us that the shape, mass, weight and any other ...
In what ways do forces affect an object`s motion?
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
Externally fed accretion on to protostars
... infrared sources. Subsequent numerical simulations relaxed the assumption of self-similarity, but usually imposed a rigid boundary on the dense core, i.e. a fixed surface where the fluid velocity vanishes (e.g. Foster & Chevalier 1993; Ogino, Tomisaka & Nakamura 1999; Vorobyov & Basu 2005). In these ...
... infrared sources. Subsequent numerical simulations relaxed the assumption of self-similarity, but usually imposed a rigid boundary on the dense core, i.e. a fixed surface where the fluid velocity vanishes (e.g. Foster & Chevalier 1993; Ogino, Tomisaka & Nakamura 1999; Vorobyov & Basu 2005). In these ...