Form B
... B) This collision does not conserve the energy of the box. C) This collision conserves only momentum of the box D) This collision conserves neither momentum nor energy E) In the collision there is only a force on the box F) In the collision there is only a force on the spring. G) In the collision th ...
... B) This collision does not conserve the energy of the box. C) This collision conserves only momentum of the box D) This collision conserves neither momentum nor energy E) In the collision there is only a force on the box F) In the collision there is only a force on the spring. G) In the collision th ...
advanced placement chemistry
... B. What term in the distance formula does the lower rectangular area of the graph represent? C. What term in the distance formula does the upper triangular area of the graph represent? D. Using the knowledge that the area under the velocity-time graph is the objects total displacement (Δx), use Geom ...
... B. What term in the distance formula does the lower rectangular area of the graph represent? C. What term in the distance formula does the upper triangular area of the graph represent? D. Using the knowledge that the area under the velocity-time graph is the objects total displacement (Δx), use Geom ...
Solutions to the 2017 Sample Exam Paper
... openings were very narrow and very close together. He described the pattern of light that he observed on the screen on the other side of the black slide. (1) He observed a pattern of bright and dark vertical lines, with a bright line in the centre of the pattern in line with the light source and a p ...
... openings were very narrow and very close together. He described the pattern of light that he observed on the screen on the other side of the black slide. (1) He observed a pattern of bright and dark vertical lines, with a bright line in the centre of the pattern in line with the light source and a p ...
- Science
... the distance traveled by the amount of time it takes to travel that distance – Constant speed - Speed that does not change – Instantaneous speed - Speed of an object at any given time ...
... the distance traveled by the amount of time it takes to travel that distance – Constant speed - Speed that does not change – Instantaneous speed - Speed of an object at any given time ...
Forces & Motion Review - Warren County Schools
... Describe Speed • A way to describe motion – Average speed - Rate of motion calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the amount of time it takes to travel that distance – Constant speed - Speed that does not change – Instantaneous speed - Speed of an object at any given time ...
... Describe Speed • A way to describe motion – Average speed - Rate of motion calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the amount of time it takes to travel that distance – Constant speed - Speed that does not change – Instantaneous speed - Speed of an object at any given time ...
velocity of propagation
... We know that the speed of light in free space is 299,792,458 meters per second, which works out to 299,792,458/0.3048 = 983,571,056.43 feet per second, or 983,571,056.43/5,280 = 186,282.4 miles per second. The reciprocal of the free space value of the speed of light in feet per second is the time it ...
... We know that the speed of light in free space is 299,792,458 meters per second, which works out to 299,792,458/0.3048 = 983,571,056.43 feet per second, or 983,571,056.43/5,280 = 186,282.4 miles per second. The reciprocal of the free space value of the speed of light in feet per second is the time it ...
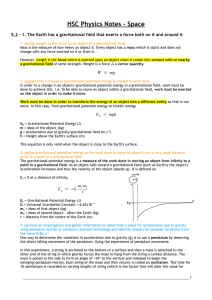
HSC Physics Notes - Space
... 2. explain that a change in gravitational potential energy is related to work done In order to a change in an object's gravitational potential energy in a gravitational field, work must be done to achieve this. I.e. To be able to move an object within a gravitational field, work must be exerted on t ...
... 2. explain that a change in gravitational potential energy is related to work done In order to a change in an object's gravitational potential energy in a gravitational field, work must be done to achieve this. I.e. To be able to move an object within a gravitational field, work must be exerted on t ...
presentation source
... “Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it.” What does this really mean? ...
... “Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it.” What does this really mean? ...
Motion Notes
... 1. As the distance between two objects increases the gravitational force decreases, and vice-versa. 2. The force of gravity is proportional to their mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
... 1. As the distance between two objects increases the gravitational force decreases, and vice-versa. 2. The force of gravity is proportional to their mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
Physics Pre-Assessment
... 14) An airplane flying into a headwind loses ground speed, and an air plane flying with the wind gains ground speed. If an airplane flies at right angles to the wind, then ground speed is______. a) less b) unchanged c) more 15) Which of the following would NOT be considered a projectile? a) A canno ...
... 14) An airplane flying into a headwind loses ground speed, and an air plane flying with the wind gains ground speed. If an airplane flies at right angles to the wind, then ground speed is______. a) less b) unchanged c) more 15) Which of the following would NOT be considered a projectile? a) A canno ...
p250t2f03
... an inclined plane (as in the lecture demonstration). The object which has the greatest total kinetic energy at the bottom of the plane (after rolling down from the same height h) is the (A) hoop. (B) disk. (C) both have the same final KE. (D) more information would be required to answer this questio ...
... an inclined plane (as in the lecture demonstration). The object which has the greatest total kinetic energy at the bottom of the plane (after rolling down from the same height h) is the (A) hoop. (B) disk. (C) both have the same final KE. (D) more information would be required to answer this questio ...
Change in Momentum and Impulse Homework 1. A 0.17 kg hockey
... the impulse exerted on the ball? What is the impulse exerted on the racket? 4. *A 0.25 kg beach ball rolling at a speed of 7 m/s collides with a heavy exercise ball at rest. The beach ball bounces straight back with a speed of 4 m/s. That is the change in momentum of the beach ball? What is the impu ...
... the impulse exerted on the ball? What is the impulse exerted on the racket? 4. *A 0.25 kg beach ball rolling at a speed of 7 m/s collides with a heavy exercise ball at rest. The beach ball bounces straight back with a speed of 4 m/s. That is the change in momentum of the beach ball? What is the impu ...
These problems - Tasker Milward Physics Website
... 1. A track star with a mass of 50kg is running with a velocity of 9m/s. Find the momentum of the runner. 2. How fast must a 58Kg football player run in order to have the same momentum as a 53kg player with a velocity of 6.2m/s? 3. An 85kg diver jumps from a diving board 3.0 m above the water and com ...
... 1. A track star with a mass of 50kg is running with a velocity of 9m/s. Find the momentum of the runner. 2. How fast must a 58Kg football player run in order to have the same momentum as a 53kg player with a velocity of 6.2m/s? 3. An 85kg diver jumps from a diving board 3.0 m above the water and com ...
Physics Semester 1 Review
... 10. An engine is used to lift a 5000 kg truck to a height of 2 m at constant speed. In the lifting process, the engine received 5×105 J of heat from the fuel burned in its interior. What is the efficiency of the engine? 11. A Carnot heat engine is to be designed with an efficiency of 60%. If the low ...
... 10. An engine is used to lift a 5000 kg truck to a height of 2 m at constant speed. In the lifting process, the engine received 5×105 J of heat from the fuel burned in its interior. What is the efficiency of the engine? 11. A Carnot heat engine is to be designed with an efficiency of 60%. If the low ...
Momentum
... applied to a 5kg object vs. the time the force is applied. Find the final velocity of the object if the original velocity was 12m/s. ...
... applied to a 5kg object vs. the time the force is applied. Find the final velocity of the object if the original velocity was 12m/s. ...