review question for mid exam 2
... 21. If you push on a heavy box that is at rest, you must exert some force to start its motion. However, once the box is sliding, you can apply a smaller force to maintain its motion. Why? 22. State any one of Newton’s laws of motion, one that you like the most, and describe what it means in your own ...
... 21. If you push on a heavy box that is at rest, you must exert some force to start its motion. However, once the box is sliding, you can apply a smaller force to maintain its motion. Why? 22. State any one of Newton’s laws of motion, one that you like the most, and describe what it means in your own ...
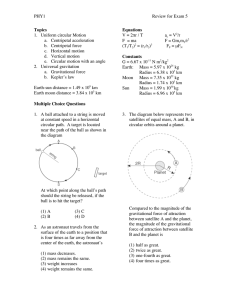
Printed 1996 B1 Two identical objects A and B of mass M move on a
... initially moves to the right with speed vo. Object A initially moves to the right with speed 3vo, so that it collides with object B. Friction is negligible. Express your answers to the following in terms of M and v o. a. ...
... initially moves to the right with speed vo. Object A initially moves to the right with speed 3vo, so that it collides with object B. Friction is negligible. Express your answers to the following in terms of M and v o. a. ...
Physics 111 Problem Set 8, Chapter 9
... Problem 9 – 40P: An 8.0 kg body is traveling at 2.0 m/s with no external force acting on it. At a certain instant an internal explosion occurs, splitting the body into two chunks of 4.0 kg mass each. The explosion gives the chunks an additional 16 J of kinetic energy. Neither chunk leaves the line ...
... Problem 9 – 40P: An 8.0 kg body is traveling at 2.0 m/s with no external force acting on it. At a certain instant an internal explosion occurs, splitting the body into two chunks of 4.0 kg mass each. The explosion gives the chunks an additional 16 J of kinetic energy. Neither chunk leaves the line ...
Questions - HCC Learning Web
... Show the equations and calculations, and box your answer. Be sure to include the units. ...
... Show the equations and calculations, and box your answer. Be sure to include the units. ...
CCA Review - Net Start Class
... 37. If I drive 50 miles per hour and the nearest Starbucks is 5 miles away, how long will it take before I can get a latte? 38. If it took 10 seconds at a speed of 20 m/s to reach an object, how far away was the object? 39. An object in freefall is moving at a speed of 60 m/s, how long has it been f ...
... 37. If I drive 50 miles per hour and the nearest Starbucks is 5 miles away, how long will it take before I can get a latte? 38. If it took 10 seconds at a speed of 20 m/s to reach an object, how far away was the object? 39. An object in freefall is moving at a speed of 60 m/s, how long has it been f ...
Symbols a = acceleration t = time d = distance s = speed Ѵ = velocity
... Context: Acceleration in freefall or rate of speed (gravity) is constant. g=9.8m/sec2 friction Definition: The force of one surface rubbing against another, with the total effect being to decrease motion Context: If you want ski quickly down a slope, adjust your weight so little friction exists betw ...
... Context: Acceleration in freefall or rate of speed (gravity) is constant. g=9.8m/sec2 friction Definition: The force of one surface rubbing against another, with the total effect being to decrease motion Context: If you want ski quickly down a slope, adjust your weight so little friction exists betw ...
Bellringer
... between the sounds you heard when the nuts were spaced at different distances? If so, what was the difference? The unequally spaced nuts should have had the same amount of time between each sound while the equally spaced nuts should have had unequal time intervals between the sounds. What do you t ...
... between the sounds you heard when the nuts were spaced at different distances? If so, what was the difference? The unequally spaced nuts should have had the same amount of time between each sound while the equally spaced nuts should have had unequal time intervals between the sounds. What do you t ...
Freezing Point of Water
... 7. If the fundamental frequency is 20Hz, what is the frequency of the 5th harmonic? 100Hz (harmonic x natural frequency) 8. What is the harmonic of the diagram to the right? 3 9. What would be an example of harmonic motion? Anything that repeats Sound and Light 1. Sound is a compressional wave, whic ...
... 7. If the fundamental frequency is 20Hz, what is the frequency of the 5th harmonic? 100Hz (harmonic x natural frequency) 8. What is the harmonic of the diagram to the right? 3 9. What would be an example of harmonic motion? Anything that repeats Sound and Light 1. Sound is a compressional wave, whic ...
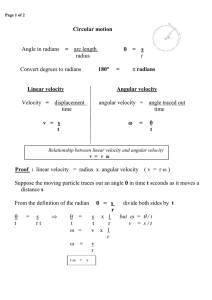
Circular motion: Extra problems
... 11. A 55.0-kg ice-skater is moving at 4.00 m/s when she grabs the loose end of a rope, the opposite end of which is tied to a pole. She then moves in a circle of radius 0.800 m around the pole. (a) Determine the force exerted by the horizontal rope on her arms. (b) Compare this force with her ...
... 11. A 55.0-kg ice-skater is moving at 4.00 m/s when she grabs the loose end of a rope, the opposite end of which is tied to a pole. She then moves in a circle of radius 0.800 m around the pole. (a) Determine the force exerted by the horizontal rope on her arms. (b) Compare this force with her ...
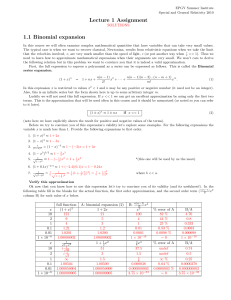
Lecture 1 Assignment 1.1 Binomial expansion
... Also, this is an infinite series but the form shown here is up to some arbitrary integer m. Luckily we will not need this full expression. If x << 1 we can get an excellent approximation by using only the first two terms. This is the approximation that will be used often in this course and it should ...
... Also, this is an infinite series but the form shown here is up to some arbitrary integer m. Luckily we will not need this full expression. If x << 1 we can get an excellent approximation by using only the first two terms. This is the approximation that will be used often in this course and it should ...
File
... Acceleration is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity. An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity. Sports announcers will occasionally say that a person is accelerating if he/she is moving fast. Yet acceleration has nothing to do with going fast. A person can be ...
... Acceleration is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity. An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity. Sports announcers will occasionally say that a person is accelerating if he/she is moving fast. Yet acceleration has nothing to do with going fast. A person can be ...
Physical Science Semester Exam Study Guide 1st Semester 1
... 2. The medium seismic waves travel through is a. a vacuum. c. air. b. rocks and other materials inside earth d. energy. 3. Sound waves are a. transverse waves. c. circular waves. b. longitudinal waves. d. polarized waves. 4. The frequency of a sound wave determines a. the pitch of the sound. c. how ...
... 2. The medium seismic waves travel through is a. a vacuum. c. air. b. rocks and other materials inside earth d. energy. 3. Sound waves are a. transverse waves. c. circular waves. b. longitudinal waves. d. polarized waves. 4. The frequency of a sound wave determines a. the pitch of the sound. c. how ...
Physics Questions
... The car driver hears 440 Hz, but the van driver hears a lower frequency. The car driver hears 440 Hz, but the van driver hears a higher frequency. Both drivers hear the same frequency and it is lower than 440 Hz. ...
... The car driver hears 440 Hz, but the van driver hears a lower frequency. The car driver hears 440 Hz, but the van driver hears a higher frequency. Both drivers hear the same frequency and it is lower than 440 Hz. ...
Motion
... a book is being slid across the table there are 4 forces acting upon the book. The table and gravity are equal so the book does not move up or down. The push of the book acts in one direction and friction acts in the opposite direction The push is a bigger force, so it causes the book to move ...
... a book is being slid across the table there are 4 forces acting upon the book. The table and gravity are equal so the book does not move up or down. The push of the book acts in one direction and friction acts in the opposite direction The push is a bigger force, so it causes the book to move ...
Eight Grade TAKS review
... • To describe a force, you must know two things-the size of the force and the direction of the force. – For example, think about two teams in a tug of war. – Each team pulls with equal force in opposite directions. – Neither team can make the other move. ...
... • To describe a force, you must know two things-the size of the force and the direction of the force. – For example, think about two teams in a tug of war. – Each team pulls with equal force in opposite directions. – Neither team can make the other move. ...
Aalborg Universitet CERN Experiment and Violation of Newton’s Second Law
... energy and move at linear speed c. If the released energy, even when it is a portion of matter and before converting to energy, move at constant speed, logically the constancy the speed of light would be possible. Consider that the light speed is constant in special relativity. ...
... energy and move at linear speed c. If the released energy, even when it is a portion of matter and before converting to energy, move at constant speed, logically the constancy the speed of light would be possible. Consider that the light speed is constant in special relativity. ...
Final exam
... Q2) A 5-kg block is released from rest at the top of the track shown in Figure 7.17. The track is 6-m high and smooth except for the portion AB whose length is 4 m, where µk = 0.4. At the end of the track the block hits a spring of force constant 600 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the sprin ...
... Q2) A 5-kg block is released from rest at the top of the track shown in Figure 7.17. The track is 6-m high and smooth except for the portion AB whose length is 4 m, where µk = 0.4. At the end of the track the block hits a spring of force constant 600 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the sprin ...