SS Review for Final
... angle of 60° with the horizontal, and the other is fired at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. Compared to the arrow fired at 60°, the arrow fired at 45° has a (A) longer flight time and longer horizontal range (B) longer flight time and shorter horizontal range (C) shorter flight time and longer ...
... angle of 60° with the horizontal, and the other is fired at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. Compared to the arrow fired at 60°, the arrow fired at 45° has a (A) longer flight time and longer horizontal range (B) longer flight time and shorter horizontal range (C) shorter flight time and longer ...
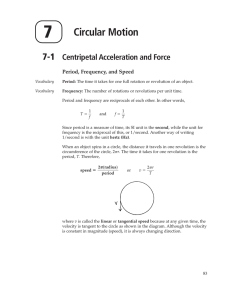
Ch 7 Notes
... of time. The rotation angle is the amount of rotation and is analogous to linear distance. We define the rotation angle Δθ to be the ratio of the arc length to the radius of ...
... of time. The rotation angle is the amount of rotation and is analogous to linear distance. We define the rotation angle Δθ to be the ratio of the arc length to the radius of ...
The shortest path between two points, Geodesics and Mechanics
... we modify our definition of distance. We measure the distances differently depending on the position. For example, if the lifeguard runs twice as fast as he swims, one meter in the water will count for 2 meters on the beach. By using this way of measuring distance (in mathematics, we say that we use ...
... we modify our definition of distance. We measure the distances differently depending on the position. For example, if the lifeguard runs twice as fast as he swims, one meter in the water will count for 2 meters on the beach. By using this way of measuring distance (in mathematics, we say that we use ...
Centripetal Force
... outer edge of a rotating object than it is closer to the axis. • Tangential speed: speed of something moving along a circular path, since the direction of motion is always tangent to the circle. It depends on rotational speed and the distance from the axis of rotation. • Rotational speed: the number ...
... outer edge of a rotating object than it is closer to the axis. • Tangential speed: speed of something moving along a circular path, since the direction of motion is always tangent to the circle. It depends on rotational speed and the distance from the axis of rotation. • Rotational speed: the number ...
end of section a
... 11. A young child of mass 20 kg stands at the centre of a uniform horizontal platform which rotates at a constant angular speed of 3.0 rad s–1. The child begins to walk radially outwards towards the edge of the platform. The maximum frictional force between the child and the platform is 200 N. What ...
... 11. A young child of mass 20 kg stands at the centre of a uniform horizontal platform which rotates at a constant angular speed of 3.0 rad s–1. The child begins to walk radially outwards towards the edge of the platform. The maximum frictional force between the child and the platform is 200 N. What ...
Problem 1 - University of Rochester
... Imagine two electrically charged particles are separated by a distance of 0.5 meters. Particle A has a mass of 2 kg and carries a positive electrical charge of +1 Coulombs. Particle B has a mass of 4 kg and carries a charge -1.5 Coulombs. a) On the sketch below, indicate with a little arrow the dire ...
... Imagine two electrically charged particles are separated by a distance of 0.5 meters. Particle A has a mass of 2 kg and carries a positive electrical charge of +1 Coulombs. Particle B has a mass of 4 kg and carries a charge -1.5 Coulombs. a) On the sketch below, indicate with a little arrow the dire ...
CMock exam IV paper 2
... questions in this question book, while Section B contains conventional questions printed separately in Question-Answer Book B. You are advised to finish Section A in ...
... questions in this question book, while Section B contains conventional questions printed separately in Question-Answer Book B. You are advised to finish Section A in ...
motion - Clinton Public Schools
... • Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
... • Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
Light waves, radio waves and photons
... which affected both cells simultaneously would not affect the balance, and no current should flow in the high resistance R, but uncorrelated fluctuations in the two beams would cause a fluctuating voltage to develop across R and so would affect the electrometer. Campbell’s experiment failed -- as he ...
... which affected both cells simultaneously would not affect the balance, and no current should flow in the high resistance R, but uncorrelated fluctuations in the two beams would cause a fluctuating voltage to develop across R and so would affect the electrometer. Campbell’s experiment failed -- as he ...
semester_one_practice_problems_10
... will the driver be exceeding the 20 m/s speed limit? What was his speed? . d. If the driver of the car lives at the top of the second hill, which is 10 m high, will the car be able to coast to his driveway? If so, how fast will he be going? If not, how high will the car travel before it comes to a s ...
... will the driver be exceeding the 20 m/s speed limit? What was his speed? . d. If the driver of the car lives at the top of the second hill, which is 10 m high, will the car be able to coast to his driveway? If so, how fast will he be going? If not, how high will the car travel before it comes to a s ...
circular motion
... • In 1673, Christian Huygens was able to determine the following relationship between ac, v and R. • Changing velocity is acceleration. The acceleration of the object is directed toward the center of the circle, and is of constant magnitude a=v2/r, where r is the radius of the circle and v is the sp ...
... • In 1673, Christian Huygens was able to determine the following relationship between ac, v and R. • Changing velocity is acceleration. The acceleration of the object is directed toward the center of the circle, and is of constant magnitude a=v2/r, where r is the radius of the circle and v is the sp ...