5. Universal Laws of Motion
... spontaneously turn into particles (for example, in particle accelerators) ...
... spontaneously turn into particles (for example, in particle accelerators) ...
Speed measures how fast position changes
... What was its speed? 3. A car is going 60 miles/hour. How far will it go in half an hour? 4. A boat is going 25 miles/hour. How long will it take for it to travel 100 miles? 5. 1 mile/minute = ___ miles/hour ...
... What was its speed? 3. A car is going 60 miles/hour. How far will it go in half an hour? 4. A boat is going 25 miles/hour. How long will it take for it to travel 100 miles? 5. 1 mile/minute = ___ miles/hour ...
Revision Semester 2 Physics test File
... proportional and in the same direction as the applied force, and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the rocket takes off to the sky, it is burning fuel. That means its mass is decreasing by the second, and naturally, its acceleration will increase since it is inversely proportional to ...
... proportional and in the same direction as the applied force, and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the rocket takes off to the sky, it is burning fuel. That means its mass is decreasing by the second, and naturally, its acceleration will increase since it is inversely proportional to ...
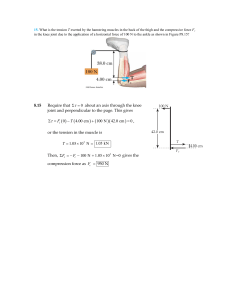
Ch 08-151
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
Higher ODU Printed Notes
... In practical situations the force is not constant, but comes to a peak and then decreases. Impulse = Area under a Force-time graph In any collision involving impulse, the unbalanced force calculated is always the average force and the maximum force experienced would be greater than the calculated a ...
... In practical situations the force is not constant, but comes to a peak and then decreases. Impulse = Area under a Force-time graph In any collision involving impulse, the unbalanced force calculated is always the average force and the maximum force experienced would be greater than the calculated a ...
Modeling with Integrals as Net Change
... (a) How fast is the car going when the 8 seconds are up? (b) How far did the car travel during these 8 seconds? ...
... (a) How fast is the car going when the 8 seconds are up? (b) How far did the car travel during these 8 seconds? ...
Let`s Pause for Two Questions from the Audience
... instantaneous speed during the race? Tortoise ...
... instantaneous speed during the race? Tortoise ...
Impulse and Momentum
... Before he can move, a tackler, running at a velocity of +4.8 m/s, grabs him. The tackler holds onto the receiver, and the two move off together with a velocity of +2.6 m/s. The mass of the tackler is 116 kg. Assuming that momentum is conserved, find the mass of the receiver. ...
... Before he can move, a tackler, running at a velocity of +4.8 m/s, grabs him. The tackler holds onto the receiver, and the two move off together with a velocity of +2.6 m/s. The mass of the tackler is 116 kg. Assuming that momentum is conserved, find the mass of the receiver. ...
THE ATOM
... electrons from a metal surface, causing the photoelectric effect. C. Einstein's equation for the photoelectric effect is hf = KE + w where hf = energy of a photon whose frequency is f, KE = kinetic energy of the emitted electron, and w = energy needed to pull the electron from the metal. ...
... electrons from a metal surface, causing the photoelectric effect. C. Einstein's equation for the photoelectric effect is hf = KE + w where hf = energy of a photon whose frequency is f, KE = kinetic energy of the emitted electron, and w = energy needed to pull the electron from the metal. ...
Force - sciencewitheinstein
... •Longest Wavelength is Red •Shortest Wavelength is Violet •You see color because of the way light interacts with an object. ...
... •Longest Wavelength is Red •Shortest Wavelength is Violet •You see color because of the way light interacts with an object. ...
Force
... •Longest Wavelength is Red •Shortest Wavelength is Violet •You see color because of the way light interacts with an object. ...
... •Longest Wavelength is Red •Shortest Wavelength is Violet •You see color because of the way light interacts with an object. ...
NAME________ DATE
... An older incorrect theory of motion stated that an object's motion would continue only as long as there was a force applied to the object. Some science fiction movies would even show rockets traveling through space with their engines roaring to keep the rocket moving at a constant speed. How does th ...
... An older incorrect theory of motion stated that an object's motion would continue only as long as there was a force applied to the object. Some science fiction movies would even show rockets traveling through space with their engines roaring to keep the rocket moving at a constant speed. How does th ...