Semester Exam Review
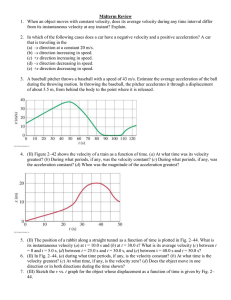
... 10. For the object whose motion is graphed in figure 1, which of the following is true. a. it is moving at a constant speed b. it is speeding up c. it is slowing down d. it is not moving e. it is accelerating 11. For the object whose motion is graphed in figure 2, which of the following is true. a. ...
... 10. For the object whose motion is graphed in figure 1, which of the following is true. a. it is moving at a constant speed b. it is speeding up c. it is slowing down d. it is not moving e. it is accelerating 11. For the object whose motion is graphed in figure 2, which of the following is true. a. ...
Circular Motion vr The Period T - FSU
... A particle of mass m moves with constant speed v on a circle of radius R. The following holds (pick one): 1. The centripetal force is v 2/R towards the center. 2. The centripetal force is m v 2/R towards the center. 3. The centripetal force is m v 2/R away from the center. 4. The centripetal force i ...
... A particle of mass m moves with constant speed v on a circle of radius R. The following holds (pick one): 1. The centripetal force is v 2/R towards the center. 2. The centripetal force is m v 2/R towards the center. 3. The centripetal force is m v 2/R away from the center. 4. The centripetal force i ...
Circular Motion - Effingham County Schools
... • Notice that the unit of measurement for torque contains a distance (meter) and a force (Newton). • To calculate the torque needed to turn something, multiply the force by the distance from the center of the object you are trying to turn. ...
... • Notice that the unit of measurement for torque contains a distance (meter) and a force (Newton). • To calculate the torque needed to turn something, multiply the force by the distance from the center of the object you are trying to turn. ...
Name - Deans Community High School
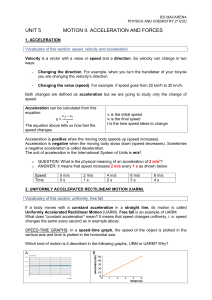
... From the speed-time graph below calculate: a) Acceleration over the first 5s. b) Total distance travelled over 8s. c) Average speed over the 8s. ...
... From the speed-time graph below calculate: a) Acceleration over the first 5s. b) Total distance travelled over 8s. c) Average speed over the 8s. ...
Notes-for-Force-and-Motion-Unit
... Universal Law of Gravitation: 1. Gravitational force exists between all objects simultaneously between all objects in the universe. (That’s why it’s called universal…) 2. The more mass an object has, the more gravitational force it exerts. 3. The farther away an object gets, the weaker the gravitat ...
... Universal Law of Gravitation: 1. Gravitational force exists between all objects simultaneously between all objects in the universe. (That’s why it’s called universal…) 2. The more mass an object has, the more gravitational force it exerts. 3. The farther away an object gets, the weaker the gravitat ...
phys1443-fall07
... It means that the force exerted on the particle 2 by particle 1 is an attractive force, pulling #2 toward #1. Gravitational force is a field force: Forces act on object without a physical contact between the objects at all times, independent of medium between them. The gravitational force exerted by ...
... It means that the force exerted on the particle 2 by particle 1 is an attractive force, pulling #2 toward #1. Gravitational force is a field force: Forces act on object without a physical contact between the objects at all times, independent of medium between them. The gravitational force exerted by ...
newton toybox
... object; Therefore, a greater unbalanced external force is needed to accelerate(speed up/slow down) an object of greater mass. Force = Mass X Acceleration Example: It takes more power to stop/move a heavier object than a lighter object ...
... object; Therefore, a greater unbalanced external force is needed to accelerate(speed up/slow down) an object of greater mass. Force = Mass X Acceleration Example: It takes more power to stop/move a heavier object than a lighter object ...
Circular
... A ball bearing is released from rest at a height h on a smooth track and completes the circular loop of the track. If R is the reaction acting on the ball bearing at the highest point A of the loop, which of A small object P of mass 0.3 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.5 m ...
... A ball bearing is released from rest at a height h on a smooth track and completes the circular loop of the track. If R is the reaction acting on the ball bearing at the highest point A of the loop, which of A small object P of mass 0.3 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.5 m ...
LECTURE 1: Email: “He who
... In his Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, Galileo (via his protagonist Salviati) poses the following thought experiment5: Shut yourself up below decks on some large ship... have the ship proceed with any speed you like, so long as the motion is uniform and not fluctuating this way and ...
... In his Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, Galileo (via his protagonist Salviati) poses the following thought experiment5: Shut yourself up below decks on some large ship... have the ship proceed with any speed you like, so long as the motion is uniform and not fluctuating this way and ...
Midterm Solutions
... 4. An unstretched spring is 12.00 cm long. When you hang a 0.876 kg weight from it, it stretches to a length of 14.40 cm. (a) What is the force constant (in N/m) of this spring? (b) What total mass must you hang from the spring to stretch it to a total length of 17.72 cm? (a) The force exerted on th ...
... 4. An unstretched spring is 12.00 cm long. When you hang a 0.876 kg weight from it, it stretches to a length of 14.40 cm. (a) What is the force constant (in N/m) of this spring? (b) What total mass must you hang from the spring to stretch it to a total length of 17.72 cm? (a) The force exerted on th ...
01. State of Physics - University of Central Florida
... and after the collision when planning your shots. No violation of the conservation of momentum law has yet to be found. It applies equally well to billiard balls, bumper cars and colliding subnuclear particles in multi-billion dollar accelerators. From the prohibition point of view we say that no ev ...
... and after the collision when planning your shots. No violation of the conservation of momentum law has yet to be found. It applies equally well to billiard balls, bumper cars and colliding subnuclear particles in multi-billion dollar accelerators. From the prohibition point of view we say that no ev ...
Document
... waves produced by the first tuning fork is 440 Hz, and the frequency of the sound waves produced by the second tuning fork is 880 Hz. If v1 denotes the speed of the sound waves produced by the first tuning fork and v2 denotes the speed of the sound waves produced by the second turning fork, then (A) ...
... waves produced by the first tuning fork is 440 Hz, and the frequency of the sound waves produced by the second tuning fork is 880 Hz. If v1 denotes the speed of the sound waves produced by the first tuning fork and v2 denotes the speed of the sound waves produced by the second turning fork, then (A) ...
Elastic Potential Energy
... transformed from one for to another, and transferred from one object to another, but the total amount remains constant. In a process, mechanical energy may be “lost” or “gained” due to the work that is done by nonconservative forces, but it simply is converted into or converted from another type of ...
... transformed from one for to another, and transferred from one object to another, but the total amount remains constant. In a process, mechanical energy may be “lost” or “gained” due to the work that is done by nonconservative forces, but it simply is converted into or converted from another type of ...