Red-Electrostatics Protons have what type of charge? Electrons
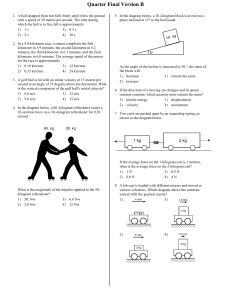
... 28. In circuit 1, two identical light bulbs are connected in parallel to each other and in series with a 12 V battery. In circuit 2, the same two light bulbs are connected in series with the 12 V battery. Which circuit produces more light? 29. In a parallel circuit, what happens to the current in th ...
... 28. In circuit 1, two identical light bulbs are connected in parallel to each other and in series with a 12 V battery. In circuit 2, the same two light bulbs are connected in series with the 12 V battery. Which circuit produces more light? 29. In a parallel circuit, what happens to the current in th ...
studyguide_forces-1
... B. There cannot be a force without motion. C. If there is motion, then a force is acting. D. Forces act on objects at rest. E. Moving objects stop when the force is used up. F. The stronger the force, the faster an object moves. G. Forces make things go, losing energy makes them stop. H. A force is ...
... B. There cannot be a force without motion. C. If there is motion, then a force is acting. D. Forces act on objects at rest. E. Moving objects stop when the force is used up. F. The stronger the force, the faster an object moves. G. Forces make things go, losing energy makes them stop. H. A force is ...
Standard Physics Mid
... (c) horizontal line (d) parabolic curve 4. A train is traveling northward with a velocity of 100 km/hr. A child on this train walks southward with a velocity of 5 km/hr. The child’s velocity with respect to he ground is (a) 95 km/hr N (b) 95 km/hr S (c) 105 km/hr N (d) 105 km/hr S 5. A ball is throw ...
... (c) horizontal line (d) parabolic curve 4. A train is traveling northward with a velocity of 100 km/hr. A child on this train walks southward with a velocity of 5 km/hr. The child’s velocity with respect to he ground is (a) 95 km/hr N (b) 95 km/hr S (c) 105 km/hr N (d) 105 km/hr S 5. A ball is throw ...
Study Guide for Physics Final Exam—1st semester
... 50. Give examples of action/reaction pairs. How do the magnitude of the two forces compare? ...
... 50. Give examples of action/reaction pairs. How do the magnitude of the two forces compare? ...
Maxwell distribution of speeds
... any frequency, Maxwell concluded that visible light forms only a small part of the entire spectrum of possible electromagnetic radiation. Maxwell used the later-abandoned concept of the ether to explain that electromagnetic radiation did not involve action at a distance. He proposed that electromagn ...
... any frequency, Maxwell concluded that visible light forms only a small part of the entire spectrum of possible electromagnetic radiation. Maxwell used the later-abandoned concept of the ether to explain that electromagnetic radiation did not involve action at a distance. He proposed that electromagn ...
1 - alcdsb
... Draw a free-body diagram to show the forces that are acting on a skydiver at each point in the skydiver's fall. a) immediately after jumping out of the airplane b) at terminal velocity (falling at a constant maximum speed) c) immediately after opening the parachute ...
... Draw a free-body diagram to show the forces that are acting on a skydiver at each point in the skydiver's fall. a) immediately after jumping out of the airplane b) at terminal velocity (falling at a constant maximum speed) c) immediately after opening the parachute ...
2014-15 1st Semester Physics Review
... a. doubling the large mass c. reducing the small mass by half b. doubling the distance between the masses d. reducing the distance between the masses by half ____ 20. Objects on the surface of Earth experience a large downward force although the universal gravitational constant is very small. Which ...
... a. doubling the large mass c. reducing the small mass by half b. doubling the distance between the masses d. reducing the distance between the masses by half ____ 20. Objects on the surface of Earth experience a large downward force although the universal gravitational constant is very small. Which ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... A proton is placed in an electric field between two parallel plates. If the plates are 6.0 cm apart and have a potential difference between them of 750 V, a) how much work is done against the electric field when the proton is moved 3.0 cm parallel to the plates? (0) b) how much work is done against ...
... A proton is placed in an electric field between two parallel plates. If the plates are 6.0 cm apart and have a potential difference between them of 750 V, a) how much work is done against the electric field when the proton is moved 3.0 cm parallel to the plates? (0) b) how much work is done against ...
mDv
... What happens to gravitational force if the distance is cut in half? ex. A 20 N gravitational force exists between two objects 100 m apart. What would the force be if they were 50 m apart? What if the mass is ...
... What happens to gravitational force if the distance is cut in half? ex. A 20 N gravitational force exists between two objects 100 m apart. What would the force be if they were 50 m apart? What if the mass is ...
Chapter5Class3 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Banking the curve can help keep cars from skidding. In fact, for every banked curve, there is one speed at which the entire centripetal force is supplied by the ...
... Banking the curve can help keep cars from skidding. In fact, for every banked curve, there is one speed at which the entire centripetal force is supplied by the ...
Physics - Teachers
... • When the distance an object covers increases or decreases over a given unit of time. • The distance an object can travel in an amount of time either increases or decreases. ...
... • When the distance an object covers increases or decreases over a given unit of time. • The distance an object can travel in an amount of time either increases or decreases. ...
Contents and Introduction
... The fields due to a moving point charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143 ...
... The fields due to a moving point charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143 ...
Chasing your tail for science.
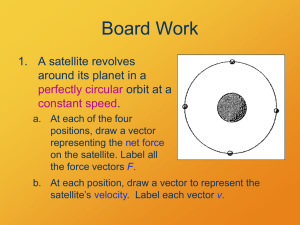
... You have just studied circular motion. It has 2 dimensions. Speed can be constant but velocity will always change. Moving in a circle causes velocity to constantly change. But which way? Lets study!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
... You have just studied circular motion. It has 2 dimensions. Speed can be constant but velocity will always change. Moving in a circle causes velocity to constantly change. But which way? Lets study!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...