Forces and Motion-part 1 2015
... • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Which would have more mass, a cotton ball or a lead ball the same size? The lead ball • An object that is small may have more mass than an object that is bigger. It just depends on what it is made of. • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a ch ...
... • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Which would have more mass, a cotton ball or a lead ball the same size? The lead ball • An object that is small may have more mass than an object that is bigger. It just depends on what it is made of. • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a ch ...
39 Questionable Assumptions in Modern Physics
... • It depends on the definition of matter. • To exert its influence elsewhere, matter must possess ‘fields’. • If an element’s field is inseparable from it (permanently attached), then it is actually present throughout all space. • Then all forces are ‘local contact forces’. • Energy density: the inf ...
... • It depends on the definition of matter. • To exert its influence elsewhere, matter must possess ‘fields’. • If an element’s field is inseparable from it (permanently attached), then it is actually present throughout all space. • Then all forces are ‘local contact forces’. • Energy density: the inf ...
Serway_ISM_V1 1 Chapter 5
... The kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the speed of the particle. Thus, doubling the speed will increase the kinetic energy by a factor of 4. This is seen from ...
... The kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the speed of the particle. Thus, doubling the speed will increase the kinetic energy by a factor of 4. This is seen from ...
Free Fall - Cobb Learning
... • Consider an apple falling from a tree. We know that it starts at rest and gains speed as it falls, or accelerates. • Gravity causes the apple to accelerate downward and is said to be in free fall. Free fall: when an object is only affected by gravity – SI unit: m/s2 ( for acceleration due to gravi ...
... • Consider an apple falling from a tree. We know that it starts at rest and gains speed as it falls, or accelerates. • Gravity causes the apple to accelerate downward and is said to be in free fall. Free fall: when an object is only affected by gravity – SI unit: m/s2 ( for acceleration due to gravi ...
Gravitation Force
... • The laws by which the states of physical systems undergo change are not affected, whether these changes of state be referred to the one or the other of two systems in uniform translatory motion relative to each other. The Principle of Invariant Light Speed • Light in vacuum propagates with the spe ...
... • The laws by which the states of physical systems undergo change are not affected, whether these changes of state be referred to the one or the other of two systems in uniform translatory motion relative to each other. The Principle of Invariant Light Speed • Light in vacuum propagates with the spe ...
5. Universal Laws of Motion
... Universal Law of Gravitation Between every two objects there is an attractive force, the magnitude of which is directly proportional to the mass of each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of the objects. ...
... Universal Law of Gravitation Between every two objects there is an attractive force, the magnitude of which is directly proportional to the mass of each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of the objects. ...
Chapter 5 Solutions
... Since the rollers on the ramp used by David were frictionless, he did not do any work overcoming nonconservative forces as he slid the block up the ramp. Neglecting any change in kinetic energy of the block (either because the speed was constant or was essentially zero during the lifting process), t ...
... Since the rollers on the ramp used by David were frictionless, he did not do any work overcoming nonconservative forces as he slid the block up the ramp. Neglecting any change in kinetic energy of the block (either because the speed was constant or was essentially zero during the lifting process), t ...
Particles and Waves
... particles were fired towards a gold leaf within a vacuum. His results showed that: A. Most alphas passed straight through without much deflection. B. Every so often an alpha was deflected through a large angle. For each result, state what conclusion(s) were made about the structure of the atom. ...
... particles were fired towards a gold leaf within a vacuum. His results showed that: A. Most alphas passed straight through without much deflection. B. Every so often an alpha was deflected through a large angle. For each result, state what conclusion(s) were made about the structure of the atom. ...
Section 19-4: Mass Spectrometer: An Application of Force on a Charge
... a positive charge, but the accelerator can also work for negatively charged particles if we reverse the battery attached to the capacitor. Let’s apply what we learned in Chapter 17. If we define the particle’s electric potential energy to be zero at the negative plate ...
... a positive charge, but the accelerator can also work for negatively charged particles if we reverse the battery attached to the capacitor. Let’s apply what we learned in Chapter 17. If we define the particle’s electric potential energy to be zero at the negative plate ...
Matching - Hauserphysics
... 5. Find the speed of a car that travels 500 miles in 10 hours. A) 729 mph B) 9 m/s C) 50 mph D) 0.11 mph 6. Find the time it takes to walk a distance of 15 meters at a speed of 3 m/s. A) 450 seconds B) 50 seconds C) 50 m/s ...
... 5. Find the speed of a car that travels 500 miles in 10 hours. A) 729 mph B) 9 m/s C) 50 mph D) 0.11 mph 6. Find the time it takes to walk a distance of 15 meters at a speed of 3 m/s. A) 450 seconds B) 50 seconds C) 50 m/s ...
3.1 TQ Centrifugal Force Apparatus
... A centripetal force acts towards the centre of a circular path and keeps the body moving in this path; otherwise the body would observe a straight line motion. In line with Newton's second law of motion, the centripetal force also produces an acceleration having the same direction it has. By definit ...
... A centripetal force acts towards the centre of a circular path and keeps the body moving in this path; otherwise the body would observe a straight line motion. In line with Newton's second law of motion, the centripetal force also produces an acceleration having the same direction it has. By definit ...
Physics
... no teacher input own choosing Reach conclusions based Discover Coulomb’s Law for strictly on repeatable, themselves explainable observations Read and draw circuit diagrams Know and apply the differences between series and parallel circuits Know how magnets are used to make electricity Know how ele ...
... no teacher input own choosing Reach conclusions based Discover Coulomb’s Law for strictly on repeatable, themselves explainable observations Read and draw circuit diagrams Know and apply the differences between series and parallel circuits Know how magnets are used to make electricity Know how ele ...
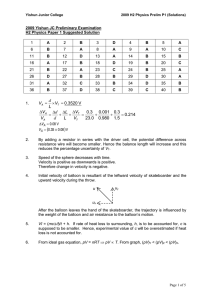
2009-YJC-PH-H2-P1-Prelim-soln
... would have reduced by half on the c.r.o. Since the same trace is obtained, the new intensity corresponds to twice of the original wave amplitude. As intensity (amplitude)2, the new intensity should be four times greater. ...
... would have reduced by half on the c.r.o. Since the same trace is obtained, the new intensity corresponds to twice of the original wave amplitude. As intensity (amplitude)2, the new intensity should be four times greater. ...
Crust
... An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force An object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Consider the Following Inertia: tendency to resist a change in motion ...
... An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force An object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Consider the Following Inertia: tendency to resist a change in motion ...
R - Life Learning Cloud
... You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled. You must show sufficient working to make your methods clear to the Examiner. Answers without working may not gain full credit. ...
... You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled. You must show sufficient working to make your methods clear to the Examiner. Answers without working may not gain full credit. ...
Heat, Force, Motion, Electricity, Magnetism, sound, light
... A truck manufacturer reduces the mass of a car by 350 kg. If the new design is otherwise identical to the old design, how will the new truck compare to the old truck? ...
... A truck manufacturer reduces the mass of a car by 350 kg. If the new design is otherwise identical to the old design, how will the new truck compare to the old truck? ...