Assignment 2
... 3. Circle coding codons; cross-out non-coding areas 4. Draw a diagram showing the sequence of mRNA before and after splicing as well as complementary tRNA in a proper order carrying proper aminoacids. 5. Suggest 3 different point mutations in the DNA sequence that could happen inside the coding area ...
... 3. Circle coding codons; cross-out non-coding areas 4. Draw a diagram showing the sequence of mRNA before and after splicing as well as complementary tRNA in a proper order carrying proper aminoacids. 5. Suggest 3 different point mutations in the DNA sequence that could happen inside the coding area ...
PhD position opened in Switzerland for a developmental / cell
... creative experimental wet-lab biologist with strong skills in developmental biology and cell biology. The successful candidate will preferably start in March 2016, but not later than September 2016. ...
... creative experimental wet-lab biologist with strong skills in developmental biology and cell biology. The successful candidate will preferably start in March 2016, but not later than September 2016. ...
Chapter 4 • Lesson 20
... contain two types of nucleic acids—DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Each nucleic acid is named for the sugar it contains: deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. You will learn more about RNA in the next lesson. DNA and RNA both contain fivecarbon sugar molecules. Although the s ...
... contain two types of nucleic acids—DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Each nucleic acid is named for the sugar it contains: deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. You will learn more about RNA in the next lesson. DNA and RNA both contain fivecarbon sugar molecules. Although the s ...
Bio Unit 7b DNA packet
... are separated by an enzyme ______________________________ when DNA copies itself. protein 16. Changes in the order of amino acids will change the ___________________________ produced. Messenger RNA or mRNA 17. ______________________________ carries the code for amino acids. Genes 18. _______________ ...
... are separated by an enzyme ______________________________ when DNA copies itself. protein 16. Changes in the order of amino acids will change the ___________________________ produced. Messenger RNA or mRNA 17. ______________________________ carries the code for amino acids. Genes 18. _______________ ...
forensics_by_students
... examination of DNA sequences. To identify individuals, 13 DNA regions are scanned. Each region varies from person to person. The unique data provided by an individual is used to create a DNA profile which is also known as their fingerprint. There is an extremely small chance that another person has ...
... examination of DNA sequences. To identify individuals, 13 DNA regions are scanned. Each region varies from person to person. The unique data provided by an individual is used to create a DNA profile which is also known as their fingerprint. There is an extremely small chance that another person has ...
Genes And Chromosomes
... heterogametic producing two types of ova (A + Z) and (A + W) in the ratio 1:1. 4. ZO-ZZ Method : It occurs in moths and butterflies. The females have one chromosome less than the males, and thus are heterogametic, producing two types of ova (A + Z) and (A + O) in the ratio 1:1. 5. Haplodiploidy : I ...
... heterogametic producing two types of ova (A + Z) and (A + W) in the ratio 1:1. 4. ZO-ZZ Method : It occurs in moths and butterflies. The females have one chromosome less than the males, and thus are heterogametic, producing two types of ova (A + Z) and (A + O) in the ratio 1:1. 5. Haplodiploidy : I ...
DNA Technology - 2 What are plasmids?
... What happens when the bacterial cell replicates its chromosome? It also replicates the plasmid DNA (including any foreign DNA as well) ...
... What happens when the bacterial cell replicates its chromosome? It also replicates the plasmid DNA (including any foreign DNA as well) ...
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists
... possible to identify which genes are near each other on a chromosome. This information is called a linkage map. In animals, we can also create inbred strains which have entirely homozygous alleles. These strains are useful for understanding patterns of dominance and polygenic traits (among many othe ...
... possible to identify which genes are near each other on a chromosome. This information is called a linkage map. In animals, we can also create inbred strains which have entirely homozygous alleles. These strains are useful for understanding patterns of dominance and polygenic traits (among many othe ...
DOC - National Council on Skin Cancer Prevention
... few typical mistakes. There may be no signs or symptoms while the overexposure is occurring and it usually takes a few hours following the exposure before the skin becomes red or tender. If you stay in the sun until your skin turns red, it may already be very severely damaged by that time. The skin ...
... few typical mistakes. There may be no signs or symptoms while the overexposure is occurring and it usually takes a few hours following the exposure before the skin becomes red or tender. If you stay in the sun until your skin turns red, it may already be very severely damaged by that time. The skin ...
Ch. 15: Presentation Slides
... • Genotype frequency = proportion of individuals in a population with a specific genotype • Genotype frequencies may differ from one population to another • Allele frequency = proportion of any specific allele in a population • Allele frequencies are estimated from genotype ...
... • Genotype frequency = proportion of individuals in a population with a specific genotype • Genotype frequencies may differ from one population to another • Allele frequency = proportion of any specific allele in a population • Allele frequencies are estimated from genotype ...
chapter 20: dna technology and genomics
... This is simply the tool that will carry the gene of interest. b) It is usually DNA that will carry the new or foreign gene into whatever cell we want the gene to be expressed. ...
... This is simply the tool that will carry the gene of interest. b) It is usually DNA that will carry the new or foreign gene into whatever cell we want the gene to be expressed. ...
DNA Replication
... can separate the 2 strands & create a new strand using 1 strand as a template. • Our end product is 2 identical double stranded DNA molecules. – The 2 strands are called complementary. ...
... can separate the 2 strands & create a new strand using 1 strand as a template. • Our end product is 2 identical double stranded DNA molecules. – The 2 strands are called complementary. ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Mutation and Disease Part 1
... o Imbalances of Globin Chain Production Accumulation of Free Globin Chains in the RBC Precursors Hemolysis of RBC Hemolytic Anemia with Hyperplasia of Bone Marrow What type of mutation occurs in a-thalassemia? o Deletion What type of mutation occurs in B-thalassemia? o Null Mutation What is th ...
... o Imbalances of Globin Chain Production Accumulation of Free Globin Chains in the RBC Precursors Hemolysis of RBC Hemolytic Anemia with Hyperplasia of Bone Marrow What type of mutation occurs in a-thalassemia? o Deletion What type of mutation occurs in B-thalassemia? o Null Mutation What is th ...
Chapter 14 When Allele Frequencies Stay Constant
... 2. For X-linked recessive traits, the frequency of the recessive allele in males is q and in females it is q 2. 3. For very rare inherited disorders, p approaches 1, so the carrier frequency is essentially 2q (approximately twice the frequency of the disease-causing allele). 14.4 DNA Profiling is B ...
... 2. For X-linked recessive traits, the frequency of the recessive allele in males is q and in females it is q 2. 3. For very rare inherited disorders, p approaches 1, so the carrier frequency is essentially 2q (approximately twice the frequency of the disease-causing allele). 14.4 DNA Profiling is B ...
DNA Replication
... (3) As you know, DNA is found within the vacuole of the cell. In order for each cell to function properly, it must have the correct amount of DNA. So, before cells divide, the DNA must replicate. DNA replication is kind of tricky, though, because the square shape of the molecule prevents contact wit ...
... (3) As you know, DNA is found within the vacuole of the cell. In order for each cell to function properly, it must have the correct amount of DNA. So, before cells divide, the DNA must replicate. DNA replication is kind of tricky, though, because the square shape of the molecule prevents contact wit ...
Primer extension technique for the detection of single nucleotide in
... Institute of Medical Genetics, Moskvorechie St 1, Moscow, 115478, USSR Submitted December 20, 1989 For diagnosis of many genetic disorders where the nature of the DNA alteration is known, it is quite enough to determine which nucleotide (normal or substituted) is present in certain site of the gene. ...
... Institute of Medical Genetics, Moskvorechie St 1, Moscow, 115478, USSR Submitted December 20, 1989 For diagnosis of many genetic disorders where the nature of the DNA alteration is known, it is quite enough to determine which nucleotide (normal or substituted) is present in certain site of the gene. ...
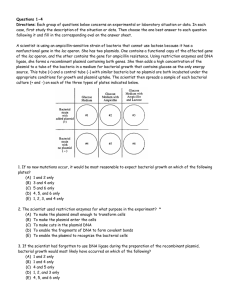
Questions 33-38
... of the lac operon, and the other contains the gene for ampicillin resistance. Using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase, she forms a recombinant plasmid containing both genes. She then adds a high concentration of the plasmid to a tube of the bacteria in a medium for bacterial growth that contains gl ...
... of the lac operon, and the other contains the gene for ampicillin resistance. Using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase, she forms a recombinant plasmid containing both genes. She then adds a high concentration of the plasmid to a tube of the bacteria in a medium for bacterial growth that contains gl ...
Final year project
... A population of genotype is evolved in exactly the same way as a normal genetic algorithm with evaluation, selection, crossover and mutation. When evaluating each genotype it must be first mapped to it’s phenotype. Then all permutations of the inputs are applied and then each cell output is tested a ...
... A population of genotype is evolved in exactly the same way as a normal genetic algorithm with evaluation, selection, crossover and mutation. When evaluating each genotype it must be first mapped to it’s phenotype. Then all permutations of the inputs are applied and then each cell output is tested a ...
Teacher`s Name: ___Julie
... I can recall and apply my knowledge of genetics terms to successfully complete my quiz. I can describe the experiments of major scientists in determining the structure of DNA and the central dogma. Procedure: 1. Bell Ringer 2. Vocabulary Quiz for absences and retakes 3. DNA Pioneers 4. Discussion: G ...
... I can recall and apply my knowledge of genetics terms to successfully complete my quiz. I can describe the experiments of major scientists in determining the structure of DNA and the central dogma. Procedure: 1. Bell Ringer 2. Vocabulary Quiz for absences and retakes 3. DNA Pioneers 4. Discussion: G ...
Lecture 4 and 5 notes
... (a) Protein electrophoresis to detect electrophoretic variants of proteins (in 1955 the wide application of this technique to Drosophila by Hubby and Lewontin, and to humans by Henry Harris, began the modern era of molecular investigations of genetic diversity) Adh gene in Drosophila melanogaster: m ...
... (a) Protein electrophoresis to detect electrophoretic variants of proteins (in 1955 the wide application of this technique to Drosophila by Hubby and Lewontin, and to humans by Henry Harris, began the modern era of molecular investigations of genetic diversity) Adh gene in Drosophila melanogaster: m ...
On the codon assignment of chain termination signals and the
... base [3]-[7]. Frameshifts are highly deleterious as they prevent translation in the correct reading frame of the codons downstream the mutation. They happen in directly repeated and palindromic sequences [10] (where the assumption of polymerase-error tolerance can be shown to be consistent) and in ...
... base [3]-[7]. Frameshifts are highly deleterious as they prevent translation in the correct reading frame of the codons downstream the mutation. They happen in directly repeated and palindromic sequences [10] (where the assumption of polymerase-error tolerance can be shown to be consistent) and in ...
Fact Sheet 56|FAMILIAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLAEMIA In summary
... Our body is made up of millions of cells, and in each cell there are instructions, called genes, that make all the necessary structural components and chemicals for the body to function. These genes are packaged onto little long strands known as chromosomes. We all have 46 chromosomes arranged into ...
... Our body is made up of millions of cells, and in each cell there are instructions, called genes, that make all the necessary structural components and chemicals for the body to function. These genes are packaged onto little long strands known as chromosomes. We all have 46 chromosomes arranged into ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.