The Pleiotropy Problem for Evolution
... pituitary gland, which increases not only height and size of hand and foot, but also controls the entire body size. Many genes have well-known pleiotropic effects, including one important gene called p53 and all heat-shock genes that are part of the genetic systems responding to temperature fluctuati ...
... pituitary gland, which increases not only height and size of hand and foot, but also controls the entire body size. Many genes have well-known pleiotropic effects, including one important gene called p53 and all heat-shock genes that are part of the genetic systems responding to temperature fluctuati ...
t - nslc.wustl.edu
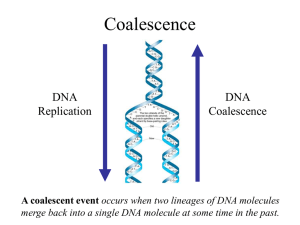
... between events is shorter. Moreover, a population tree need not exist at all. ...
... between events is shorter. Moreover, a population tree need not exist at all. ...
Gene Technology
... Issues associated with genetic engineering There is a protein know as the lac repressor ...
... Issues associated with genetic engineering There is a protein know as the lac repressor ...
genetic disorder of haemoglobin
... Major abnormalities & problems in SCA Sickling of the red cell during deoxygenation, as the HbS has low solubility at low O2 partial pressure and precipitates. Chronic haemolytic anaemia due to repeated sickling in tissues and unsickling in the lungs. Plugging of microcapillaries by rigid sick ...
... Major abnormalities & problems in SCA Sickling of the red cell during deoxygenation, as the HbS has low solubility at low O2 partial pressure and precipitates. Chronic haemolytic anaemia due to repeated sickling in tissues and unsickling in the lungs. Plugging of microcapillaries by rigid sick ...
Slide 1
... – score - A score between 0 and 1000. – strand - Defines the strand - either '+' or '-'. – thickStart - The starting position at which the feature is drawn thickly – thickEnd - The ending position at which the feature is drawn thickly – itemRgb - An RGB value of the form R,G,B (e.g. 255,0,0). – bloc ...
... – score - A score between 0 and 1000. – strand - Defines the strand - either '+' or '-'. – thickStart - The starting position at which the feature is drawn thickly – thickEnd - The ending position at which the feature is drawn thickly – itemRgb - An RGB value of the form R,G,B (e.g. 255,0,0). – bloc ...
Diseases of genetic background. Malformations
... The risk of disease is related the number of affected genes The risk is higher in children whose both parents are affected Rate of recurrance is 2-7% Next child =% Identical twins: less than 100% (20-40%) Disorderes:Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, Gout, schisophrenia Cleft palate ...
... The risk of disease is related the number of affected genes The risk is higher in children whose both parents are affected Rate of recurrance is 2-7% Next child =% Identical twins: less than 100% (20-40%) Disorderes:Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, Gout, schisophrenia Cleft palate ...
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 2
... d.75% 57. Both Mr. Nock and Mrs. Nock have Cc genotypes. All of Mr. and Mrs. Nock’s seven children have the Cc genotype. Their NEXT child will be… a.Cc b. cc c. CC or cc d. CC, or Cc, or cc 58. In lemurs, a red crest is dominant over a brown crest. (Ian and Desiree are lemurs). Ian’s father had a br ...
... d.75% 57. Both Mr. Nock and Mrs. Nock have Cc genotypes. All of Mr. and Mrs. Nock’s seven children have the Cc genotype. Their NEXT child will be… a.Cc b. cc c. CC or cc d. CC, or Cc, or cc 58. In lemurs, a red crest is dominant over a brown crest. (Ian and Desiree are lemurs). Ian’s father had a br ...
Genetic Engineering / Recombinant DNA technology Genetic
... Introduction of genes from organism to another, thus creating a transgenic organism Creation of organism with desirable or altered characteristics The sum total of all genes in an organism makes up its genome. Genes are the segment of nucleic acids that code for a specific polypeptide. Genes are mad ...
... Introduction of genes from organism to another, thus creating a transgenic organism Creation of organism with desirable or altered characteristics The sum total of all genes in an organism makes up its genome. Genes are the segment of nucleic acids that code for a specific polypeptide. Genes are mad ...
Mutations in the gene encoding methyl-CpG-binding
... vitro and revealed that the first three reduced binding by over 100-fold, while the T158M mutation only resulted in a 2-fold reduction [37]. Moreover, because of XCI, each cell has either the wild-type or the mutant MECP2active. This excludes a possible dominant-negative mechanism in which the prote ...
... vitro and revealed that the first three reduced binding by over 100-fold, while the T158M mutation only resulted in a 2-fold reduction [37]. Moreover, because of XCI, each cell has either the wild-type or the mutant MECP2active. This excludes a possible dominant-negative mechanism in which the prote ...
SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to
... • A very small percentage of all mutations actually have a positive effect these are called beneficial mutations. • These mutations lead to new versions of proteins that help an organism and its future generations better adapt to changes in their environment. • Example: – Deletion of CCR5 gene leads ...
... • A very small percentage of all mutations actually have a positive effect these are called beneficial mutations. • These mutations lead to new versions of proteins that help an organism and its future generations better adapt to changes in their environment. • Example: – Deletion of CCR5 gene leads ...
HONORS BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2010
... 52. Why is “all of the organisms in a forest” NOT considered a population? 53. What is an ecosystem? Provide a DEFINITION and an EXAMPLE. 54. DESCRIBE some biotic factors that might impact an ecosystem. Provide a DEFINITION and EXAMPLES. 55. DESCRIBE some abiotic factors that might impact an ecosyst ...
... 52. Why is “all of the organisms in a forest” NOT considered a population? 53. What is an ecosystem? Provide a DEFINITION and an EXAMPLE. 54. DESCRIBE some biotic factors that might impact an ecosystem. Provide a DEFINITION and EXAMPLES. 55. DESCRIBE some abiotic factors that might impact an ecosyst ...
8.2 All Genetic Information Is Encoded in the Structure of DNA
... • The double helix • Hydrogen bond and base pairing • Antiparallel complementary DNA strands ...
... • The double helix • Hydrogen bond and base pairing • Antiparallel complementary DNA strands ...
Mutations in the Anopheles gambiae Pink
... the mutant alleles, F, progeny were inbred, and F2 mutant-eye males were backcrossed to wild-eye sib females. In the F3, mutant types were inbred to establish pure-breeding stocks. To determine complementation groups, males of all strains were crossed to the WE strain. To determine the rate of intra ...
... the mutant alleles, F, progeny were inbred, and F2 mutant-eye males were backcrossed to wild-eye sib females. In the F3, mutant types were inbred to establish pure-breeding stocks. To determine complementation groups, males of all strains were crossed to the WE strain. To determine the rate of intra ...
PowerPoint
... separate DNA fragments by size. A DNA sample is cut into fragments with restriction enzymes. Electrical current pulls DNA fragments through a gel. Smaller fragments move faster and travel farther than larger fragments. Fragments of different sizes appear as bands on the gel ...
... separate DNA fragments by size. A DNA sample is cut into fragments with restriction enzymes. Electrical current pulls DNA fragments through a gel. Smaller fragments move faster and travel farther than larger fragments. Fragments of different sizes appear as bands on the gel ...
here - PHGEN
... By definition, somatic mutations are mutations in cell lineages that do not lead to gametes. Thereby the mutations do not enter the germline and are not inherited. They arise at any time after postzygotic cell division throughout the whole lifetime of the individual due to the fact that any replicat ...
... By definition, somatic mutations are mutations in cell lineages that do not lead to gametes. Thereby the mutations do not enter the germline and are not inherited. They arise at any time after postzygotic cell division throughout the whole lifetime of the individual due to the fact that any replicat ...
A Long-Term Evolutionary Pressure on the Amount of Noncoding DNA
... competing organisms need to achieve not only a high fitness but also an appropriate level of nonneutral genetic variation, reflecting a trade-off between the exploration of new phenotypes and the reliable transmission of the current one. As nonfunctional sequences are not under immediate selection, ...
... competing organisms need to achieve not only a high fitness but also an appropriate level of nonneutral genetic variation, reflecting a trade-off between the exploration of new phenotypes and the reliable transmission of the current one. As nonfunctional sequences are not under immediate selection, ...
Course Intro and Expectations 2017
... • ~7000 coding sequence changes (non-synonymous variants). • ~500 amino acid substitutions predicted to be deleterious to gene function, the vast majority are in heterozygous state. • ~75 de novo SNPs acquired per generation ~7000 Mendelian inherited diseases (CF, DMD, etc) – these are defined as ra ...
... • ~7000 coding sequence changes (non-synonymous variants). • ~500 amino acid substitutions predicted to be deleterious to gene function, the vast majority are in heterozygous state. • ~75 de novo SNPs acquired per generation ~7000 Mendelian inherited diseases (CF, DMD, etc) – these are defined as ra ...
lecture 20 notes
... – also tends to cause a small duplication at the site • RNA transposons (retrotransposons) and some DNA transposons ...
... – also tends to cause a small duplication at the site • RNA transposons (retrotransposons) and some DNA transposons ...
Evolution vs. Creation Genesis 1:1 1. 3 How did life begin? A vitally
... evolution or creation? A. The best way to prove any theory is to observe the subjects of that theory in action. This is called empirical science. In empirical science a scientist formulates a hypothesis (i.e., what he thinks is true; e.g., diet A produces more milk in dairy cows than diet B). He the ...
... evolution or creation? A. The best way to prove any theory is to observe the subjects of that theory in action. This is called empirical science. In empirical science a scientist formulates a hypothesis (i.e., what he thinks is true; e.g., diet A produces more milk in dairy cows than diet B). He the ...
PCR: Basics & Miniturization
... rate leads to long lines for the machine and sign up sheets that force you to start your reactions at all hours. The RapidCycler™ can complete a 30 cycle reaction in less than 10 minutes. Finally, a machine that can keep up with the speed of the biochemistry. No more waiting in line. You can ...
... rate leads to long lines for the machine and sign up sheets that force you to start your reactions at all hours. The RapidCycler™ can complete a 30 cycle reaction in less than 10 minutes. Finally, a machine that can keep up with the speed of the biochemistry. No more waiting in line. You can ...
What does DNA look like?
... genes, and genes are passed from one generation to the next. Genes are parts of chromosomes, which are structures in the nucleus of most cells. Chromosomes are made of protein and DNA. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid (dee AHKS ee RIE boh noo KLEE ik AS id). DNA is the genetic material—the mater ...
... genes, and genes are passed from one generation to the next. Genes are parts of chromosomes, which are structures in the nucleus of most cells. Chromosomes are made of protein and DNA. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid (dee AHKS ee RIE boh noo KLEE ik AS id). DNA is the genetic material—the mater ...
Gen660_Lecture3B_GeneEvolution
... Most DNA substitutions are likely to be neutral = no effect on fitness. They arise through new mutations. Given a ~constant mutation rate, can convert the # of substitutions into time of divergence since speciation = molecular clock theory. ...
... Most DNA substitutions are likely to be neutral = no effect on fitness. They arise through new mutations. Given a ~constant mutation rate, can convert the # of substitutions into time of divergence since speciation = molecular clock theory. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.