
The causes and molecular consequences of polyploidy
... replicated, and gap phase, without cell division), endomitosis (mitosis without the final cell division),22 or nuclear fusion; (2) impairments in meiosis, which can affect either the first or the second meiotic divisions; and (3) postmeiotic genome doubling.12 The unreduced gametes from diploids (2X ...
... replicated, and gap phase, without cell division), endomitosis (mitosis without the final cell division),22 or nuclear fusion; (2) impairments in meiosis, which can affect either the first or the second meiotic divisions; and (3) postmeiotic genome doubling.12 The unreduced gametes from diploids (2X ...
MOLECULAR CYTOGENETIC ANALYSES IN WHEAT AND
... decades many results have been achieved in this field. Basic breeding material with more favourable agronomic properties have been developed carrying genes or chromosome segments from the Aegilops, Secale, Agropyron and Triticum genera. Translocations, and addition and substitution lines developed u ...
... decades many results have been achieved in this field. Basic breeding material with more favourable agronomic properties have been developed carrying genes or chromosome segments from the Aegilops, Secale, Agropyron and Triticum genera. Translocations, and addition and substitution lines developed u ...
Bioinformatics 3 V7 * Function Annotation, Gene Regulation
... Left: Protein – DNA contacts involve many arginine (R) and lysine (K) residues ...
... Left: Protein – DNA contacts involve many arginine (R) and lysine (K) residues ...
Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
... Organization of genetic material in bacteria: plasmids Examples of naturally-occuring plasmids and relevant features ...
... Organization of genetic material in bacteria: plasmids Examples of naturally-occuring plasmids and relevant features ...
here
... The neuropilin-2 (NRP2) gene is localized to 2q34, an autism susceptibility locus. NRP2 has been demonstrated to both guide axons and to control neuronal migration in the central nervous system. It has been reported that NRP2 may be required in vivo for sorting migrating cortical and ...
... The neuropilin-2 (NRP2) gene is localized to 2q34, an autism susceptibility locus. NRP2 has been demonstrated to both guide axons and to control neuronal migration in the central nervous system. It has been reported that NRP2 may be required in vivo for sorting migrating cortical and ...
Temporal genomic evolution of bird sex chromosomes
... and Z chromosomes. We focus all our analyses throughout this study between these two sets of chromosomes of a similar size, because microchromosomes have very different genomic features (i.e., recombination rate, gene density, GC content, repeat content etc.) compared to others [50], which influence ...
... and Z chromosomes. We focus all our analyses throughout this study between these two sets of chromosomes of a similar size, because microchromosomes have very different genomic features (i.e., recombination rate, gene density, GC content, repeat content etc.) compared to others [50], which influence ...
1305077113_457396
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
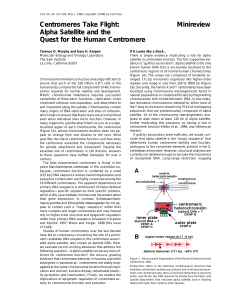
Minireview Alpha Satellite and the Quest for the Human Centromere
... question. Functional centromeric DNAs need to be identified and mapped precisely within populations, and within extensive phylogenies that contain both closely related and distant species that are accessible to experimental manipulation. Lessons learned from centromere studies may be relevant to und ...
... question. Functional centromeric DNAs need to be identified and mapped precisely within populations, and within extensive phylogenies that contain both closely related and distant species that are accessible to experimental manipulation. Lessons learned from centromere studies may be relevant to und ...
However, if
... ■ a combination of both genes and the environment. Both variation and variability are of evolutionary advantage only if they have a genetic basis. Genetic variation in individuals (and therefore variability in a population) arises as a result of sexual reproduction. This involves gamete formation (b ...
... ■ a combination of both genes and the environment. Both variation and variability are of evolutionary advantage only if they have a genetic basis. Genetic variation in individuals (and therefore variability in a population) arises as a result of sexual reproduction. This involves gamete formation (b ...
Ch 07 Overview - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
Molecular Biology and Genetics
... constructing an mRNA molecule from DNA is known as transcription (Figure 1.6 and Figure 1.7). The double helix of DNA unwinds and the nucleotides follow basically the same base pairing rules to form the correct sequence in the mRNA. This time, however, uracil (U) pairs with each adenine (A) in the D ...
... constructing an mRNA molecule from DNA is known as transcription (Figure 1.6 and Figure 1.7). The double helix of DNA unwinds and the nucleotides follow basically the same base pairing rules to form the correct sequence in the mRNA. This time, however, uracil (U) pairs with each adenine (A) in the D ...
Relative Rates of Nucleotide Substitution in Frogs
... mtDNA substitution rates to a greater extent than scnDNA substitution rates (Rand 1994). Alternatively, the ratio of substitution rates may be more or less constant across divergent taxa, implying that evolution has arrived at some fundamental constant determined by the balance between error minimiz ...
... mtDNA substitution rates to a greater extent than scnDNA substitution rates (Rand 1994). Alternatively, the ratio of substitution rates may be more or less constant across divergent taxa, implying that evolution has arrived at some fundamental constant determined by the balance between error minimiz ...
Ch. 7: Presentation Slides
... chromosome 21 is one of the acrocentrics in a Robertsonian translocation, the rearrangement leads to a familial type of Down syndrome • The heterozygous carrier is phenotypically normal, but a high risk of Down syndrome results from aberrant segregation in meiosis • Approximately 3 percent of childr ...
... chromosome 21 is one of the acrocentrics in a Robertsonian translocation, the rearrangement leads to a familial type of Down syndrome • The heterozygous carrier is phenotypically normal, but a high risk of Down syndrome results from aberrant segregation in meiosis • Approximately 3 percent of childr ...
Corchorus yellow vein virus, a New World geminivirus from the Old
... more recently than Old World viruses and suggested that they may have evolved after the continental separation of the Americas from Gondwana approximately 130 million years ago. Rybicki (1994) speculated that whiteflies moving from Asia to the Americas may have transmitted viruses that were the ance ...
... more recently than Old World viruses and suggested that they may have evolved after the continental separation of the Americas from Gondwana approximately 130 million years ago. Rybicki (1994) speculated that whiteflies moving from Asia to the Americas may have transmitted viruses that were the ance ...
Gentile, Margaret: Computational Methods for the Design of PCR Primers for the Amplification of functional Markers from Environmental Samples
... Computational methods have been reported for designing PCR primers for divergent sequences from multiple sequence alignments from both amino acid sequences (Kariko, 1995) and from protein sequences (Rose et al.,1998). In the study using amino acid sequences, primers were designed that could amplify ...
... Computational methods have been reported for designing PCR primers for divergent sequences from multiple sequence alignments from both amino acid sequences (Kariko, 1995) and from protein sequences (Rose et al.,1998). In the study using amino acid sequences, primers were designed that could amplify ...
PTC Receptor Project Lab Protocol
... Investigators will then use NCBI’s BLAST search engine to compare each of their sequences with those in NCBI’s gene database to make sure they have in fact amplified the correct region of the human genome. More detailed sequence analyses to identify the SNPs and the corresponding PTC amino acid hapl ...
... Investigators will then use NCBI’s BLAST search engine to compare each of their sequences with those in NCBI’s gene database to make sure they have in fact amplified the correct region of the human genome. More detailed sequence analyses to identify the SNPs and the corresponding PTC amino acid hapl ...
Investigation of the premelanosome protein
... including 4 out of 11 exons were re-sequenced in rabbits with different putative alleles at the dilute locus (Figure 1). These fragments encompassed exon 1 and upstream flanking and downstream intronic regions (360 bp), exon 2 with part of preceding intron 1 and downstream intron 2 regions (357 bp), ...
... including 4 out of 11 exons were re-sequenced in rabbits with different putative alleles at the dilute locus (Figure 1). These fragments encompassed exon 1 and upstream flanking and downstream intronic regions (360 bp), exon 2 with part of preceding intron 1 and downstream intron 2 regions (357 bp), ...
Summary 121 Summary The Hox genes form a subset of the
... number of genes present in a cluster varies between animal species; the number of clusters in each species also varies. The Hox clusters are thought to have arisen by tandem duplication of a single gene, followed, in vertebrates, by duplication of the cluster itself. As a consequence, Hox genes occu ...
... number of genes present in a cluster varies between animal species; the number of clusters in each species also varies. The Hox clusters are thought to have arisen by tandem duplication of a single gene, followed, in vertebrates, by duplication of the cluster itself. As a consequence, Hox genes occu ...
Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in human
... Correlation with predicted secondary structure Secondary structure predictions of the exon sequences containing the SNPs show that SNPs are found in all the secondary structural elements: helical, beta-sheet and coil regions. While the absolute number of SNPs in coils is generally more than the numb ...
... Correlation with predicted secondary structure Secondary structure predictions of the exon sequences containing the SNPs show that SNPs are found in all the secondary structural elements: helical, beta-sheet and coil regions. While the absolute number of SNPs in coils is generally more than the numb ...
Exploring HLA Diversity in Brazil
... EC: We’re conducting two different research studies. The first study is an evaluation of HLA genetics from a population point of view. For this study, we are using normal, healthy individuals. No one has performed deep sequencing of the HLA region on such a mixed population, and the available databa ...
... EC: We’re conducting two different research studies. The first study is an evaluation of HLA genetics from a population point of view. For this study, we are using normal, healthy individuals. No one has performed deep sequencing of the HLA region on such a mixed population, and the available databa ...
Where Is DNA Found?
... People in the News Sir Alec Jeffreys is credited with DNA profiling using RFLP. In September of 1984 after years of work, he saw his first series of blots on an X-ray. The technique was first used in forensics, when in 1985 he was asked by police to confirm the rape confession of 17 year old Richar ...
... People in the News Sir Alec Jeffreys is credited with DNA profiling using RFLP. In September of 1984 after years of work, he saw his first series of blots on an X-ray. The technique was first used in forensics, when in 1985 he was asked by police to confirm the rape confession of 17 year old Richar ...
BLAST seminar
... between a query sequence and all database sequences. • Very fast algorithm • Can be used to search extremely large databases • Sufficiently sensitive and selective for most purposes • Robust – the default parameters can usually be used ...
... between a query sequence and all database sequences. • Very fast algorithm • Can be used to search extremely large databases • Sufficiently sensitive and selective for most purposes • Robust – the default parameters can usually be used ...
Evolution of genes, evolution of species: the case of aminoacyl
... Doolittle and Brown (1994) called ‘‘the Woesian revolution,’’ was probably the delineation of the three kingdoms of life (Eukaryotes, Eubacteria, and Archaebacteria) based on the analysis of ribosomal RNA sequences (Fox et al. 1977; Woese and Fox 1977). Later, Iwabe et al. (1989) and Gogarten et al. ...
... Doolittle and Brown (1994) called ‘‘the Woesian revolution,’’ was probably the delineation of the three kingdoms of life (Eukaryotes, Eubacteria, and Archaebacteria) based on the analysis of ribosomal RNA sequences (Fox et al. 1977; Woese and Fox 1977). Later, Iwabe et al. (1989) and Gogarten et al. ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.



















![PA ALKF-[FY]-[STA]-[STAD]-[VM]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002279064_1-5287fab8d5ca72543328286b23cc5a55-300x300.png)


