DHaganTalk1
... function. -The protein folding “problem” and why it has become one of the most basic intellectual challenges in Molecular Biology. ...
... function. -The protein folding “problem” and why it has become one of the most basic intellectual challenges in Molecular Biology. ...
Slide 1 - Genomecluster at Oakland University
... • Swiss-Prot is an annotated protein sequence database that was established in 1986. Currently, maintained collaboratively at – The Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB) – The European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) ...
... • Swiss-Prot is an annotated protein sequence database that was established in 1986. Currently, maintained collaboratively at – The Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB) – The European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) ...
Document
... Surrounded by double membrane and contain own DNA, but codes for very few proteins! (a few dozen) Instead, most genes from prokaryotic ancestor have been transferred to the nucleus, so proteins must be imported ...
... Surrounded by double membrane and contain own DNA, but codes for very few proteins! (a few dozen) Instead, most genes from prokaryotic ancestor have been transferred to the nucleus, so proteins must be imported ...
Protein Threading Optimization Using
... Protein structure prediction - Prediction of the threedimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence. Homology Modeling - Comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three ...
... Protein structure prediction - Prediction of the threedimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence. Homology Modeling - Comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three ...
Slide 1
... Ionic Bonds – btw acidic n basic side chains (salt bridges) Hydrophobic interactions – non-polar side chains on the interior and vice-versa ...
... Ionic Bonds – btw acidic n basic side chains (salt bridges) Hydrophobic interactions – non-polar side chains on the interior and vice-versa ...
classification of intra- and intermolecular forces
... energy)/individually weak, forces are cumulative → stable in parallel. ...
... energy)/individually weak, forces are cumulative → stable in parallel. ...
UNIT 2: BIOCHEMISTRY/ENZYMES
... of molecule (you may not be able to find one for nucleic acids, which is fine). • 2. For each molecule, include a description, as well as a drawing of what the actual carbon molecule looks like. • 3. Your placemats will be laminated and ready for you to use! ...
... of molecule (you may not be able to find one for nucleic acids, which is fine). • 2. For each molecule, include a description, as well as a drawing of what the actual carbon molecule looks like. • 3. Your placemats will be laminated and ready for you to use! ...
Health Science 1110-2007 Module 3 Organic Chemistry Lab 3
... is DNA, which we will study further in the next unit. Carbs Question 3. Admittedly, the wording on this question is a little “off”, but, what is the least "intrusive" change you can do to a sugar and still make another, different sugar? (Hint, in the “Disaccharides” exercise take a look at the 3rd c ...
... is DNA, which we will study further in the next unit. Carbs Question 3. Admittedly, the wording on this question is a little “off”, but, what is the least "intrusive" change you can do to a sugar and still make another, different sugar? (Hint, in the “Disaccharides” exercise take a look at the 3rd c ...
Chapter5 The Structure and Functionof Macromolecules Discussion
... 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain what determines protein conformation and why it is impo ...
... 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain what determines protein conformation and why it is impo ...
GRIM-19 interacts with HtrA2: To identify the cellular proteins that
... Greenebaum Cancer Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD $Laboratory of Immune Cell Biology, National Cancer Institute, ...
... Greenebaum Cancer Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD $Laboratory of Immune Cell Biology, National Cancer Institute, ...
Name: Pd: _____ Date: Modeling Protein Structure Background
... 2. This primary structure will fold to form the secondary structure, which includes the formation of hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another. a. Represent these interactions by folding your pipe cleaner into an alpha helix or a betapleated sheet. b. ...
... 2. This primary structure will fold to form the secondary structure, which includes the formation of hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another. a. Represent these interactions by folding your pipe cleaner into an alpha helix or a betapleated sheet. b. ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... • Clusters of conserved residues are called “motifs” -- motifs carry out a particular function or form a particular structure that is important for the conserved protein. motif ...
... • Clusters of conserved residues are called “motifs” -- motifs carry out a particular function or form a particular structure that is important for the conserved protein. motif ...
Protein folding
... isomerase) is by far the most common tertiary fold. It is estimated that 10% of all known enzymes have this supersecondary structure. The members of this large family of proteins catalyze very different reactions. Currently, there are 85 enzymes in the TIM database including oxido/reductases, hydrol ...
... isomerase) is by far the most common tertiary fold. It is estimated that 10% of all known enzymes have this supersecondary structure. The members of this large family of proteins catalyze very different reactions. Currently, there are 85 enzymes in the TIM database including oxido/reductases, hydrol ...
introduction
... Validate motifs against 3D model No Secondary structure prediction No: use single sequence methods No: single sequence methods Motif search Secondary structure prediction Use other data ...
... Validate motifs against 3D model No Secondary structure prediction No: use single sequence methods No: single sequence methods Motif search Secondary structure prediction Use other data ...
Classification of Amino Acids
... ESI-TOF Electrospary ionization mass spectrometry Passing of analyte solution through a charged needle with a high electrical potential Dispersion of charged microdroplets (fine mist) ...
... ESI-TOF Electrospary ionization mass spectrometry Passing of analyte solution through a charged needle with a high electrical potential Dispersion of charged microdroplets (fine mist) ...
ppt part 1 - Embrace Challenge
... • Compare protein profiles • Construct cladograms • Stain polyacrylamide gels • Laboratory Extensions ...
... • Compare protein profiles • Construct cladograms • Stain polyacrylamide gels • Laboratory Extensions ...
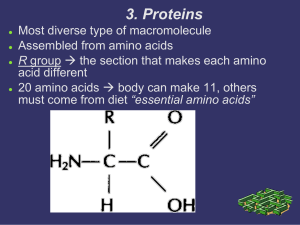
3. Proteins
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
An insight into the (un)stable protein formulation
... direct indication for changes of the protein structure. By comparing the shape of the amide I band of an unknown protein with those of proteins with structures already analyzed by x-ray diffraction or NMR, its secondary structure can be derived by using multivariate statistical methods. As an illust ...
... direct indication for changes of the protein structure. By comparing the shape of the amide I band of an unknown protein with those of proteins with structures already analyzed by x-ray diffraction or NMR, its secondary structure can be derived by using multivariate statistical methods. As an illust ...
Protein Structure Prediction The Protein Folding Problem
... What Determines Fold? • in general, the amino-acid sequence of a protein determines the 3D shape of a protein [Anfinsen et al., 1950s] • but some exceptions – all proteins can be denatured – some molecules have multiple conformations – some proteins get folding help from chaperones – prions can chan ...
... What Determines Fold? • in general, the amino-acid sequence of a protein determines the 3D shape of a protein [Anfinsen et al., 1950s] • but some exceptions – all proteins can be denatured – some molecules have multiple conformations – some proteins get folding help from chaperones – prions can chan ...
Interactome

In molecular biology, an interactome is the whole set of molecular interactions in a particular cell. The term specifically refers to physical interactions among molecules (such as those among proteins, also known as protein-protein interactions) but can also describe sets of indirect interactions among genes (genetic interactions). Mathematically, interactomes are generally displayed as graphs.The word ""interactome"" was originally coined in 1999 by a group of French scientists headed by Bernard Jacq. Though interactomes may be described as biological networks, they should not be confused with other networks such as neural networks or food webs.