Introduction Methods Procedure Conclusion and Future Work
... synthesized matched our predicted values. Therefore we continued the experiment We will be using a green fluorescent protein (GFP) containing a six-histidine tag as the protein of interest. It has a molecular weight about 27kD, which should work well with our molecule containing eight prolines. Curr ...
... synthesized matched our predicted values. Therefore we continued the experiment We will be using a green fluorescent protein (GFP) containing a six-histidine tag as the protein of interest. It has a molecular weight about 27kD, which should work well with our molecule containing eight prolines. Curr ...
word
... Human diseases so far: 8 of them by students Basic facts – protein/ mRNA defect – basic characteristics of disease Other human diseases discussed in book How are lipids synthesized – from cytosolic aqueous-soluble precursors and inserted into membranes Topology of compartments – from lumen of ER to ...
... Human diseases so far: 8 of them by students Basic facts – protein/ mRNA defect – basic characteristics of disease Other human diseases discussed in book How are lipids synthesized – from cytosolic aqueous-soluble precursors and inserted into membranes Topology of compartments – from lumen of ER to ...
FST 123 - Enzymology Homework IS `13
... c. What predictions can you make about the results of a native PAGE at pH 7.6 (State any assumptions you might need to make about the % acrylamide in the gel.) d. Sketch the elution profile of these proteins from a carboxymethyl cellulose ion exchange chromatography column, run at pH 6.25 (with a sa ...
... c. What predictions can you make about the results of a native PAGE at pH 7.6 (State any assumptions you might need to make about the % acrylamide in the gel.) d. Sketch the elution profile of these proteins from a carboxymethyl cellulose ion exchange chromatography column, run at pH 6.25 (with a sa ...
Rough ER
... of misfolded proteins contributes to a number of neurodegenerative, immune, and endocrine pathologies, as well as other age-related illnesses. Research focuses on the possibility that the buildup of misfolded proteins can also contribute to vascular and cardiac diseases. However, evidence that s ...
... of misfolded proteins contributes to a number of neurodegenerative, immune, and endocrine pathologies, as well as other age-related illnesses. Research focuses on the possibility that the buildup of misfolded proteins can also contribute to vascular and cardiac diseases. However, evidence that s ...
Document
... chemistry, analytical chemistry, molecular biology & the potency of the product • Different methods have different levels of detection ie, values can go from grams to ...
... chemistry, analytical chemistry, molecular biology & the potency of the product • Different methods have different levels of detection ie, values can go from grams to ...
Genetically Modified Organism
... To obtain optimal resolution of proteins, a “stacking” gel is poured over the top of the “resolving” gel. The stacking gel lower concentration of acrylamide (larger pore size), lower pH different ionic content This allows the proteins in a lane to be concentrated into a tight band before entering th ...
... To obtain optimal resolution of proteins, a “stacking” gel is poured over the top of the “resolving” gel. The stacking gel lower concentration of acrylamide (larger pore size), lower pH different ionic content This allows the proteins in a lane to be concentrated into a tight band before entering th ...
Detection Systems in Immunohistochemistry
... in a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and DiaminoBenzidine (DAB) results in the reduction of DAB to an insoluble brown precipitate, visible under the light microscope. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) is also used in an analogous method, in which case a phosphorylated naphthol is used as the substrate ...
... in a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and DiaminoBenzidine (DAB) results in the reduction of DAB to an insoluble brown precipitate, visible under the light microscope. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) is also used in an analogous method, in which case a phosphorylated naphthol is used as the substrate ...
Plasma membrane
... membranes. Along with typical saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, The relative proportions of these fatty acids can be modulated by the bacterium to maintain the optimum fluidity of the membrane (e.g. following temperature change). As a phospholipid bilayer, the lipid portion of the outer membran ...
... membranes. Along with typical saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, The relative proportions of these fatty acids can be modulated by the bacterium to maintain the optimum fluidity of the membrane (e.g. following temperature change). As a phospholipid bilayer, the lipid portion of the outer membran ...
TWO-DAY COURSE, Saturday and Sunday 12 Peptides and
... of proteins. This course is designed as an introduction for researchers needing to expand their knowledge of the use of mass spectrometry-based methods for the identification, characterization, and quantification of peptides and proteins. Background material in basic protein chemistry will be provid ...
... of proteins. This course is designed as an introduction for researchers needing to expand their knowledge of the use of mass spectrometry-based methods for the identification, characterization, and quantification of peptides and proteins. Background material in basic protein chemistry will be provid ...
Detecting hydrophobic proteins by western blot
... Use protease inhibitors to avoid degradation of your sample during processing. Note that the reducing agent in the Laemmli buffer should either be added fresh, or once added the Laemmli buffer should be stored frozen. You can substitute LDS for SDS in the Laemmli buffer (this is available commercial ...
... Use protease inhibitors to avoid degradation of your sample during processing. Note that the reducing agent in the Laemmli buffer should either be added fresh, or once added the Laemmli buffer should be stored frozen. You can substitute LDS for SDS in the Laemmli buffer (this is available commercial ...
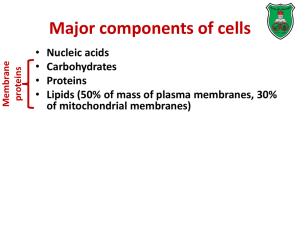
Major components of cells
... – FTIs did not block prenylation of other Ras isoforms (N-Ras and K-Ras) and their tumorigenic activity. – There are other farnesylated proteins with important roles in the cell ...
... – FTIs did not block prenylation of other Ras isoforms (N-Ras and K-Ras) and their tumorigenic activity. – There are other farnesylated proteins with important roles in the cell ...
(L0668) - Datasheet - Sigma
... acids in human. The antibody is affinity-purified using the immunizing peptide immobilized on agarose. ...
... acids in human. The antibody is affinity-purified using the immunizing peptide immobilized on agarose. ...
L2_Principle of protein folding in the cellular environment
... • Proteins that help the folding of other proteins, usually through cycles of binding and release, without forming part of their final native structure. • Increase in the efficiency, not the specificity, of protein folding • Change in emphasis from post-translational modification to co-translational ...
... • Proteins that help the folding of other proteins, usually through cycles of binding and release, without forming part of their final native structure. • Increase in the efficiency, not the specificity, of protein folding • Change in emphasis from post-translational modification to co-translational ...
simulating protein analysis using gel electrophoresis
... ‘well’) at one end of a jello-like material (called an agarose gel). The gel is placed into a liquid (called a buffer) that conducts electricity well. There is a positive electrode at one end of the gel and a negative electrode at the other. The negative electrode is nearest to the end where the pro ...
... ‘well’) at one end of a jello-like material (called an agarose gel). The gel is placed into a liquid (called a buffer) that conducts electricity well. There is a positive electrode at one end of the gel and a negative electrode at the other. The negative electrode is nearest to the end where the pro ...
Cellular compartmentalization
... Here is an illustration of how proteins targeted to the mitochondria are delivered. First the protein must carry the appropriate signal sequence. Then, it attaches to a receptor protein on the outer membrane. This complex diffuses until it reaches a contact site, where it is treaded through both ch ...
... Here is an illustration of how proteins targeted to the mitochondria are delivered. First the protein must carry the appropriate signal sequence. Then, it attaches to a receptor protein on the outer membrane. This complex diffuses until it reaches a contact site, where it is treaded through both ch ...
gelbank
... proteome, separation of complex protein mixtures into discrete protein components measurement of relative abundance and identification of each protein Component. The most widely used separation method is: 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis ...
... proteome, separation of complex protein mixtures into discrete protein components measurement of relative abundance and identification of each protein Component. The most widely used separation method is: 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis ...
Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... NH3+ groups of two amino acids can react with the resulting loss of a water molecule to form a ...
... NH3+ groups of two amino acids can react with the resulting loss of a water molecule to form a ...
Crystallizing a clearer understanding of the protein
... the cellular level. Given the array of intelligent functions that proteins conduct in organisms, however, that moniker may not do them justice. Numbering in the millions, proteins—which are chains of amino acids—grow and repair cells, trigger chemical processes or transport molecules; they can be st ...
... the cellular level. Given the array of intelligent functions that proteins conduct in organisms, however, that moniker may not do them justice. Numbering in the millions, proteins—which are chains of amino acids—grow and repair cells, trigger chemical processes or transport molecules; they can be st ...
Lecture 5
... Getting the Label in: Histology Very often, the molecular biology required to transform eukaryotic cells is prohibitive. An alternative option is ‘fix’ the cell at a certain time and then label it. This is cellular level histology. 1. Grow cells under desired conditions 2. ‘Fix’ cells in a tissue s ...
... Getting the Label in: Histology Very often, the molecular biology required to transform eukaryotic cells is prohibitive. An alternative option is ‘fix’ the cell at a certain time and then label it. This is cellular level histology. 1. Grow cells under desired conditions 2. ‘Fix’ cells in a tissue s ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.