What is the difference between RMSF? RMSD? B-Factor?
... difference between two structures by a score between (0,1], where 1 indicates a perfect match between two structures[1]. Generally scores below 0.20 corresponds to randomly chosen unrelated proteins whereas structures with a score higher than 0.5 assume roughly the same fold ...
... difference between two structures by a score between (0,1], where 1 indicates a perfect match between two structures[1]. Generally scores below 0.20 corresponds to randomly chosen unrelated proteins whereas structures with a score higher than 0.5 assume roughly the same fold ...
Enzyme
... •Quaternary protein structure: The way in which two or more polypeptide sub-units associate to form a single three-dimensional protein unit. Non-covalent forces are responsible for quaternary structure essential to the function of proteins. ...
... •Quaternary protein structure: The way in which two or more polypeptide sub-units associate to form a single three-dimensional protein unit. Non-covalent forces are responsible for quaternary structure essential to the function of proteins. ...
Proteins
... • C. A protein with two or more peptide chains • D. The shape of a globular protein • E. Disulfide bonds between R groups ...
... • C. A protein with two or more peptide chains • D. The shape of a globular protein • E. Disulfide bonds between R groups ...
Document
... • Integrate databases and applications • Integrate public domain and commercial systems that visualize DNA sequences, proteins, etc. ...
... • Integrate databases and applications • Integrate public domain and commercial systems that visualize DNA sequences, proteins, etc. ...
Expression of KCNA10, a Voltage-Gated K Channel, in Glomerular
... KCNA10 is the only Kv channel gene that is more abundantly expressed in kidney than in brain (18). Figure 1c confirms that KCNA10 protein is highly expressed in kidney and readily detectable in both crude and purified membrane vesicles preparations. Brush border membranes, largely composed of apical ...
... KCNA10 is the only Kv channel gene that is more abundantly expressed in kidney than in brain (18). Figure 1c confirms that KCNA10 protein is highly expressed in kidney and readily detectable in both crude and purified membrane vesicles preparations. Brush border membranes, largely composed of apical ...
slides
... used codon-based models to predict positive selection in protein evolution within 175 of these sequence clusters. results show that codons that display positive selection appear to be less frequent in helical and strand regions are overrepresented in amino acid residues that are associated with a ch ...
... used codon-based models to predict positive selection in protein evolution within 175 of these sequence clusters. results show that codons that display positive selection appear to be less frequent in helical and strand regions are overrepresented in amino acid residues that are associated with a ch ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;12)(q25;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2000 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2000 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
SystemsBiologyPaper
... Mass spectrometry can provide other types of data besides peptide identification. Post-translational modifications can be identified through analysis of the spectra. Proteins that are modified have different spectral features. For example, phosphorylated proteins have a prominent peak added due to t ...
... Mass spectrometry can provide other types of data besides peptide identification. Post-translational modifications can be identified through analysis of the spectra. Proteins that are modified have different spectral features. For example, phosphorylated proteins have a prominent peak added due to t ...
Ming Li Talk about Bioinformatics - the David R. Cheriton School of
... Being homologous means that they have ...
... Being homologous means that they have ...
Back to Table of Contents
... The sequence of amino acids in a protein defines its primary structure. The blueprint for each amino acid is laid down by sets of three letters known as base triplets that are found in the coding regions of genes. These base triplets are recognized by ribosomes, the protein building sites of the ce ...
... The sequence of amino acids in a protein defines its primary structure. The blueprint for each amino acid is laid down by sets of three letters known as base triplets that are found in the coding regions of genes. These base triplets are recognized by ribosomes, the protein building sites of the ce ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... “Community effect” in early development In tumor biology---cancer cells stimulate their own proliferation ...
... “Community effect” in early development In tumor biology---cancer cells stimulate their own proliferation ...
PDF File
... transporter (37), which extrude anticancer drugs, bile acids, and others. Expression of the efflux proteins in bacteria renders the organisms resistant to many antibiotics, organic solvents, hydrophobic dyes, and surfactants. Structure of the efflux pump in Gram-negative bacteria is particularly com ...
... transporter (37), which extrude anticancer drugs, bile acids, and others. Expression of the efflux proteins in bacteria renders the organisms resistant to many antibiotics, organic solvents, hydrophobic dyes, and surfactants. Structure of the efflux pump in Gram-negative bacteria is particularly com ...
AP Bio A final exam study guide
... Explain the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules relating this property to interactions with water molecules (hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic). Give examples. ...
... Explain the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules relating this property to interactions with water molecules (hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic). Give examples. ...
Protein Ubiquitination
... important role in protein folding. Chaperons safeguard the folding of nascent chains. ...
... important role in protein folding. Chaperons safeguard the folding of nascent chains. ...
23_ FL23SitesofProteinProcessing
... proteins. Its main job is to separate & process proteins that are staying from those that are needed by other cells. ...
... proteins. Its main job is to separate & process proteins that are staying from those that are needed by other cells. ...
viral networks
... http://www.dnatube.com/video/993/Plasmid• Only need the sequenced genome (or sequence of Cloning interest) • Scalable, its possible to screen for interactions among many proteins creating a more high-throughput screen (ex. viral genome) • Protein/polypeptides can be from various sources; eukaryotes, ...
... http://www.dnatube.com/video/993/Plasmid• Only need the sequenced genome (or sequence of Cloning interest) • Scalable, its possible to screen for interactions among many proteins creating a more high-throughput screen (ex. viral genome) • Protein/polypeptides can be from various sources; eukaryotes, ...
Slide 1
... The silver-stained SDS gel (Fig. 5A) demonstrated that osmotic shock and heat treatment markedly increased the purity of ALP. The vast majority of proteins become insoluble when exposed to high temperature, but ALP remains soluble while maintaining its enzymatic activity, making this simple method a ...
... The silver-stained SDS gel (Fig. 5A) demonstrated that osmotic shock and heat treatment markedly increased the purity of ALP. The vast majority of proteins become insoluble when exposed to high temperature, but ALP remains soluble while maintaining its enzymatic activity, making this simple method a ...
Organic Compounds
... Provide structure for: cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones…most everything in the body! Special Function: Proteins are responsible for cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
... Provide structure for: cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones…most everything in the body! Special Function: Proteins are responsible for cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
Molecules of life 2.4 - Madison County Schools
... A. These macromolecules are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. B. Unlike the other macromolecules (proteins, carbs, and nucleic acids), lipids do not have a single monomer. They are all classified as lipids because they are hydrophobic molecules. “Hydro” means “water”; “phobic” means “fear of”. C. Lip ...
... A. These macromolecules are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. B. Unlike the other macromolecules (proteins, carbs, and nucleic acids), lipids do not have a single monomer. They are all classified as lipids because they are hydrophobic molecules. “Hydro” means “water”; “phobic” means “fear of”. C. Lip ...
Poster
... changes into a beta sheets rich protein. This conformational change can cause a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Mad Cow Disease in cattle, Scrapie in sheep and Creutzfeldt-Jacobs Disease in humans. Prions are found not only in mammals, but in other organisms as well, and have been ext ...
... changes into a beta sheets rich protein. This conformational change can cause a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Mad Cow Disease in cattle, Scrapie in sheep and Creutzfeldt-Jacobs Disease in humans. Prions are found not only in mammals, but in other organisms as well, and have been ext ...
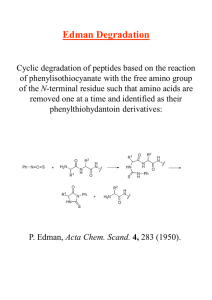
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Over Expression of IPTG inducible GST protein in E.coli BL21
... nitrocellulose membrane was carefully taken and subjected for immunodetection. The non specific sites in membrane are blocked with blocking buffer for two hours, which blocks all the proteins except GST. Later incubation with anti-GST HRP conjugate antibody bind only to the GST in the membrane. On w ...
... nitrocellulose membrane was carefully taken and subjected for immunodetection. The non specific sites in membrane are blocked with blocking buffer for two hours, which blocks all the proteins except GST. Later incubation with anti-GST HRP conjugate antibody bind only to the GST in the membrane. On w ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.